High-growth-rate Dunaliella tertiolecta obtained through ultraviolet mutation breeding
A technology of growth rate and Dunaliella, which is applied in the field of microbial engineering, can solve the problem that the screening research of growth rate is blank and so on
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] Example 1 Mutagenesis Breeding of High Production Rate Dunaliella Mutants
[0055] The wild strain of Dunaliella tertiolecta UTEX LB 999 (purchased from the University of Texas) was used as the starting algal strain for ultraviolet mutagenesis, and then isolated and subcultured for preservation. After activation of the above-mentioned mutagenized algae strains, they were screened in an artificial climate box under normal culture conditions (25°C, 4000lux, 12hL / 12hD), and the OD 750 The value is to measure the mutagenized algae strains with high growth rate step by step.
[0056] The composition and content of the culture solution are shown in Table 1. When preparing the culture solution, some components are added to distilled water in solid form, and some components will be made into a mother solution of 50-1000 times in advance, and then diluted as needed when using Prepared as a culture medium.
[0057] Table 1 Composition and content of EM medium
[0058] ...
Embodiment 2
[0072] Identification characteristics of mutant algal strain ENN0001-6 obtained by screening in Example 2
[0073]The algal cells of the mutant algal strain ENN0001-6 were pear-shaped or oval, about 6-10 μM in length, with 2 equal-length flagella, no cellulosic cell wall, and only an outer membrane composed of glycoprotein and neuraminic acid. It can grow in EM, F / 2 and other media. The algae are evenly dispersed in the liquid medium and can swim. It grows well on EM solid medium, and obvious single algae colonies can be formed in 5-7 days. The algae fall into a regular circle, and the algae are green.
Embodiment 3
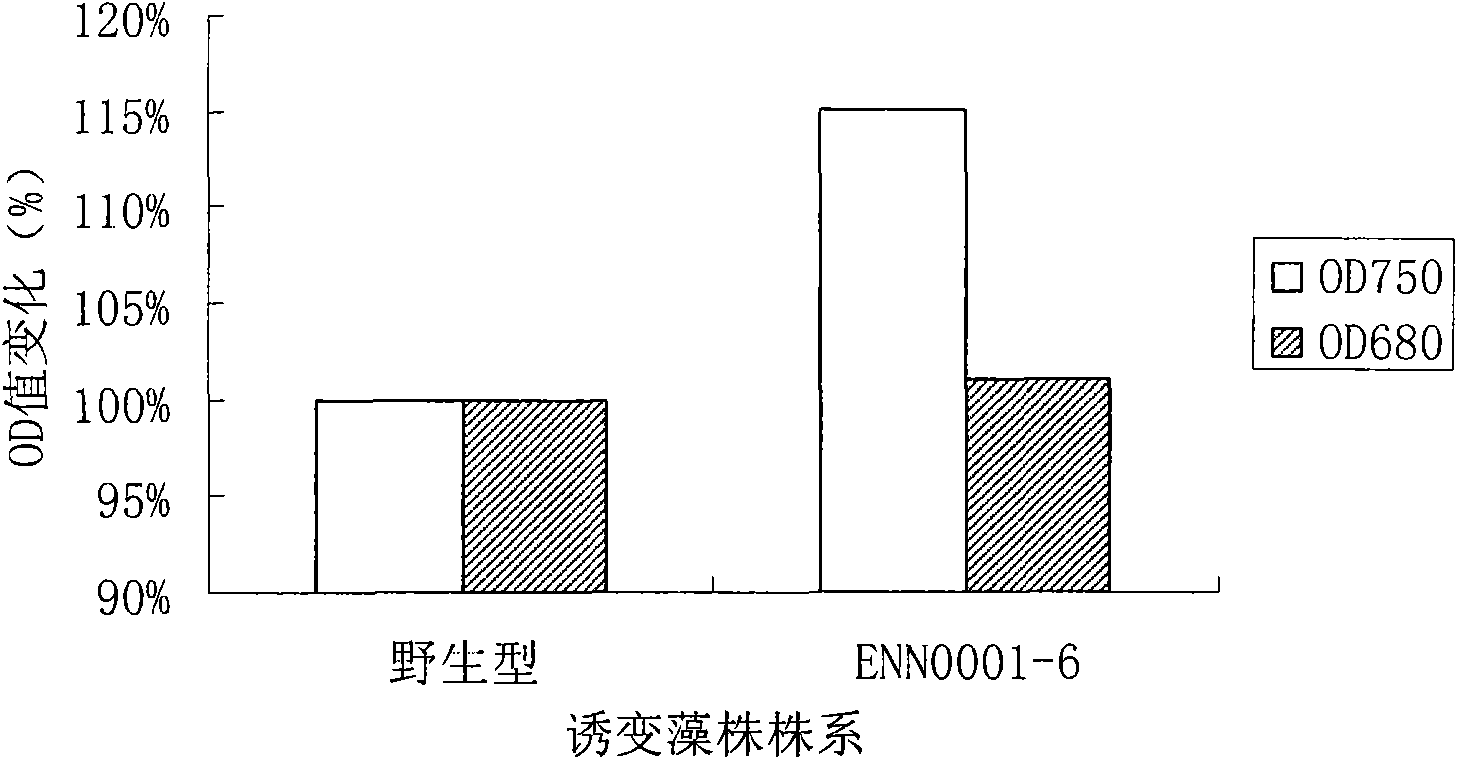
[0074] Example 3 Comparison of production rate of mutant algal strain ENN0001-6 obtained by screening and wild-type algal strain
[0075] Depend on figure 1 It can be seen that the biomass (OD 750 ) and chlorophyll content (OD 680 ). The normal culture conditions are: 25°C, 4000lux, 12h L / 12h D. The re-screening steps are as follows: the mutagenized algae strains determined by the primary screening are activated by transferring to a solid medium plate once, and a single algal colony is picked and inoculated into a 100ml Erlenmeyer flask added with 20ml EM medium. Cultured for 10 days under normal culture conditions, measured OD 750 value, and adjust the same OD 750 The value is 0.1, inoculated and subcultured in a new 100ml Erlenmeyer flask added with 20ml EM medium, and three parallel samples were set up for each plant. After ten days of culture under normal culture conditions, measure the OD 750 Value, and take 10ml of algae liquid and add 90ml of EM medium (1:10 i...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com