Dunaliella tertiolecta mutant strain with high growth rate and complex mutation breeding method thereof
A growth rate, Dunaliella technology, applied in the field of microbial engineering, can solve the problems of poor genetic stability of mutant algal strains, short screening time, and prone to reverse mutation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0063] Example 1 Screening of Dunaliella mutagenic strains with high growth rate
[0064] Using Dunaliella tertiolecta wild strain UTEX LB 999 (purchased from University of Texas) as the starting algae strain, subjected to UV mutagenesis, and then exposed to outdoor high temperature and high light (temperature 37°C to 45°C, light intensity 10000Lux-50000Lux), and it grew well. After separation and subculture, save it. After the above mutagenic algae strains were activated, they were screened in an artificial climate cabinet under normal culture conditions (25°C, 4000lux, 12h L / 12h D) through multiple steps, using the WFZ UV-2102PC UV-Vis spectrophotometer (purchased from You Nico Instruments Co., Ltd.) measured the OD value at 750nm of the algae solution, and screened out mutagenic algae strains with high growth rate step by step.
[0065] The composition and content of the culture broth are shown in Table 1. When preparing the culture broth, some ingredients are added in solid f...
Embodiment 2
[0081] Example 2 Identification characteristics of the screened mutant algae strain ENN0001-1
[0082] The algal cells of the mutant algae strain ENN0001-1 are pear-shaped or elliptical, about 6-10μM in length, with 2 equal-length flagella, no cellulosic cell wall, and only an outer membrane composed of glycoprotein and neuraminic acid. It can grow in EM, F / 2 and other media. The algae are evenly dispersed in the liquid medium and can swim. It grows well on EM solid medium, and obvious single algae colonies can be formed in 5-7 days. The algae form a regular round shape, and the algae body is yellow-green.
Embodiment 3
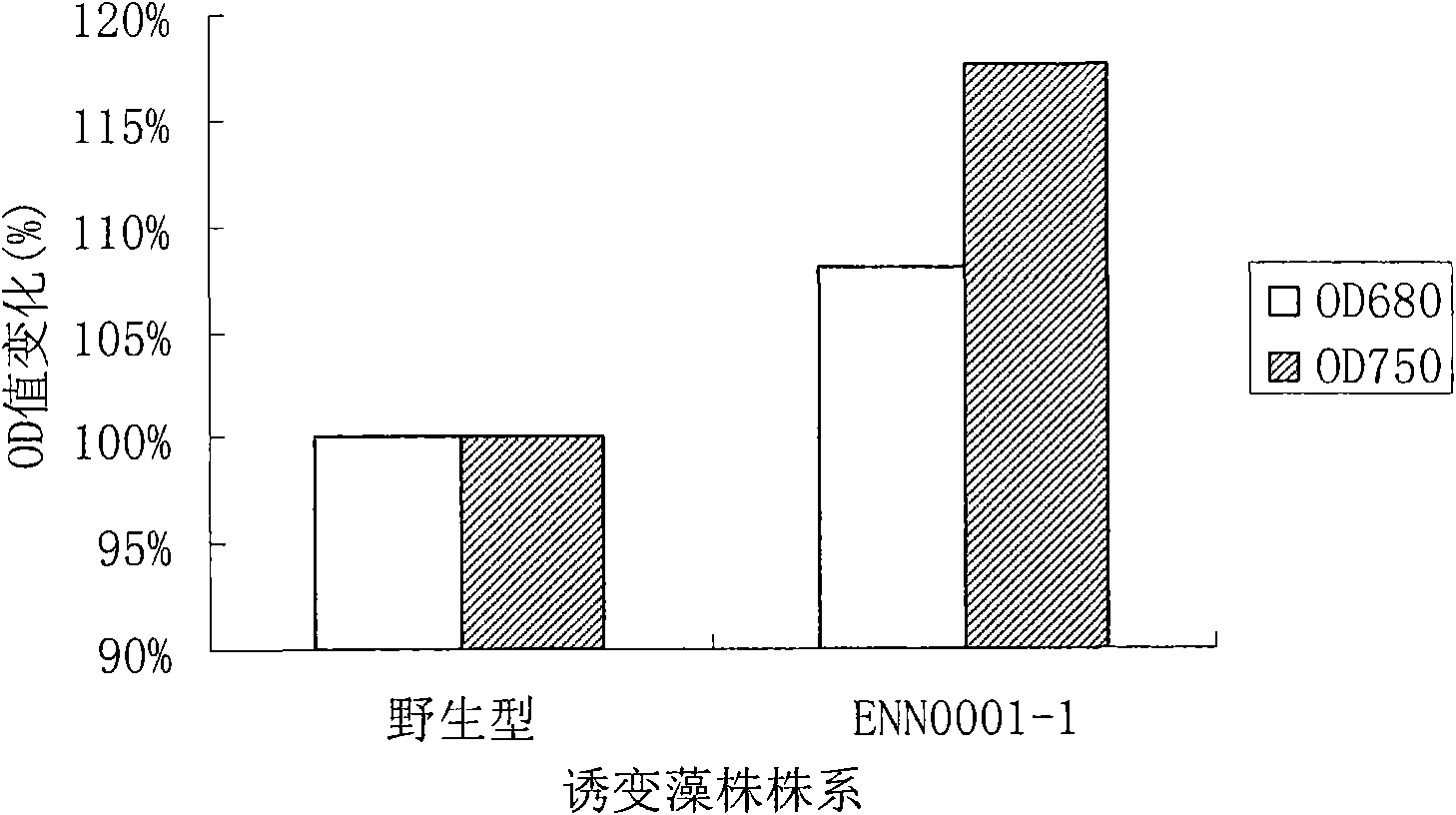
[0083] Example 3 Comparison of the production rate between the screened mutant algae strain ENN0001-1 and the wild-type algae strain
[0084] by figure 1 It can be seen that the biomass (OD) of mutant algae strain ENN0001-1 and wild-type algae strain UTEX LB 999 after the re-screening is completed 750 ) And chlorophyll content (OD 680 ). The normal culture conditions are: 25°C, 4000lux, 12h L / 12h D. The re-screening step is as follows: the mutagenic algae strains determined by the preliminary screening are activated by transferring to a solid medium plate once, and the single algae colonies are picked and inoculated into a 100 ml Erlenmeyer flask added with 20 ml EM medium. Cultivate for 10 days under normal culture conditions and measure OD 750 Value and adjust the same OD 750 The value of 0.1 was inoculated and passaged in a new 100ml Erlenmeyer flask supplemented with 20ml EM medium, with three parallel samples for each plant. After ten days of culture under normal culture con...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com