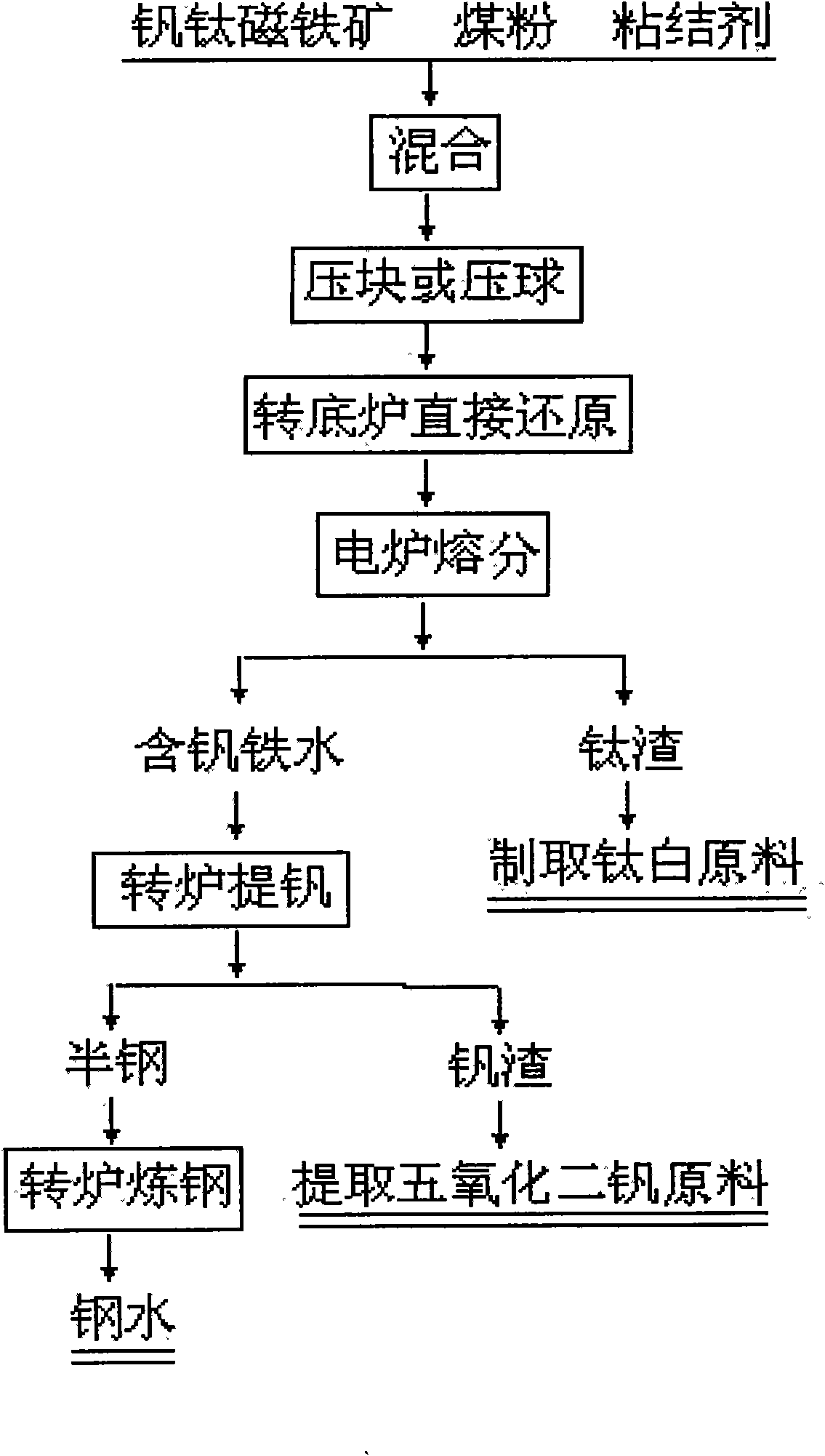
Method for recovering vanadium, titanium and iron from vanadium titanium magnetite
A technology for vanadium-titanium-magnetite and vanadium-titanium-iron, which is applied in the field of recovering vanadium-titanium-iron, can solve the problems of technical difficulty, large processing capacity, and difficulty in industrialization, and achieves simplified processing technology, reduced environmental pollution, and low realization difficulty. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Vanadium-titanium magnetite composition: TFe56%, TiO 2 12.5%, V 2 o 5 0.64%. Particle size-100 mesh, 100%, use <1mm anthracite coal powder, fixed carbon 80.29%, volatile matter 6.96%, ash content 11.62%, sulfur content 0.54%. Raw material ratio is: iron ore: coal powder: syrup=100:24:7. After mixing, use a powder tablet press to press into a block shape of 35×30×25mm without drying, and put the block material on the rotary hearth furnace pan through a distributor, with a thickness of 5-6cm.
[0027] The rotary hearth furnace is heated with gas, the maximum temperature is 1350°C, after 20 minutes, a metallized block with a metallization rate > 90% is obtained. The blocks are continuously melted into the electric furnace, and the temperature of the electric furnace is controlled at 1500-1600 ° C. After heating, they are quickly melted to obtain vanadium-containing molten iron and titanium slag. Titanium slag and vanadium-containing molten iron are regularly discharge...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Vanadium-titanium magnetite composition: Tfe57.5%, TiO 2 13.5%, V 2 o 5 0.59%. Particle size-below 100 orders, with <1mm anthracite coal powder, raw material ratio is: iron ore: coal powder: polyvinyl alcohol aqueous solution (concentration 3%)=100:24:6. After mixing, use a powder tablet press to press into Ф25mm balls, dry at 80°C for 1 hour, and the water content of the pellets is less than 1%. The dried balls are loaded into the rotary hearth furnace through a distributor, with a thickness of 4-5cm.
[0030] The rotary hearth furnace is heated with gas, the maximum temperature is 1350°C, and after 15 minutes, a metallized block with a metallization rate > 90% is obtained. The block enters the electric furnace at about 1200°C. The temperature of the electric furnace is controlled at 1550-1650°C, and it is quickly melted to obtain Vanadium-containing molten iron and titanium slag with black titanite as the main titanium-containing phase, titanium slag and vanadium-c...
Embodiment 3
[0032] Vanadium-titanium magnetite composition: Tfe54.5%, TiO 2 11.8%, V 2 o 5 0.55%. Below particle size-100 order, use<1mm anthracite coal powder, raw material ratio is: iron ore: coal powder: carboxymethyl cellulose aqueous solution (concentration 2%)=100:24:7. After mixing, use a powder tablet press to press into a block of 35×25×25mm, and dry it naturally in the air for 12 hours. The water content of the pellet is less than 1%. Thickness 4~5cm,.
[0033] The rotary hearth furnace is heated with gas, the maximum temperature is 1370°C, and the metallized block with a metallization rate > 90% is obtained after 15 minutes. The block enters the electric furnace at about 1200°C. The temperature of the electric furnace is controlled at 1550-1600°C, and it is quickly melted to obtain Vanadium-containing molten iron and titanium slag with black titanite as the main titanium-containing phase, titanium slag and vanadium-containing molten iron are regularly discharged into ladles...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com