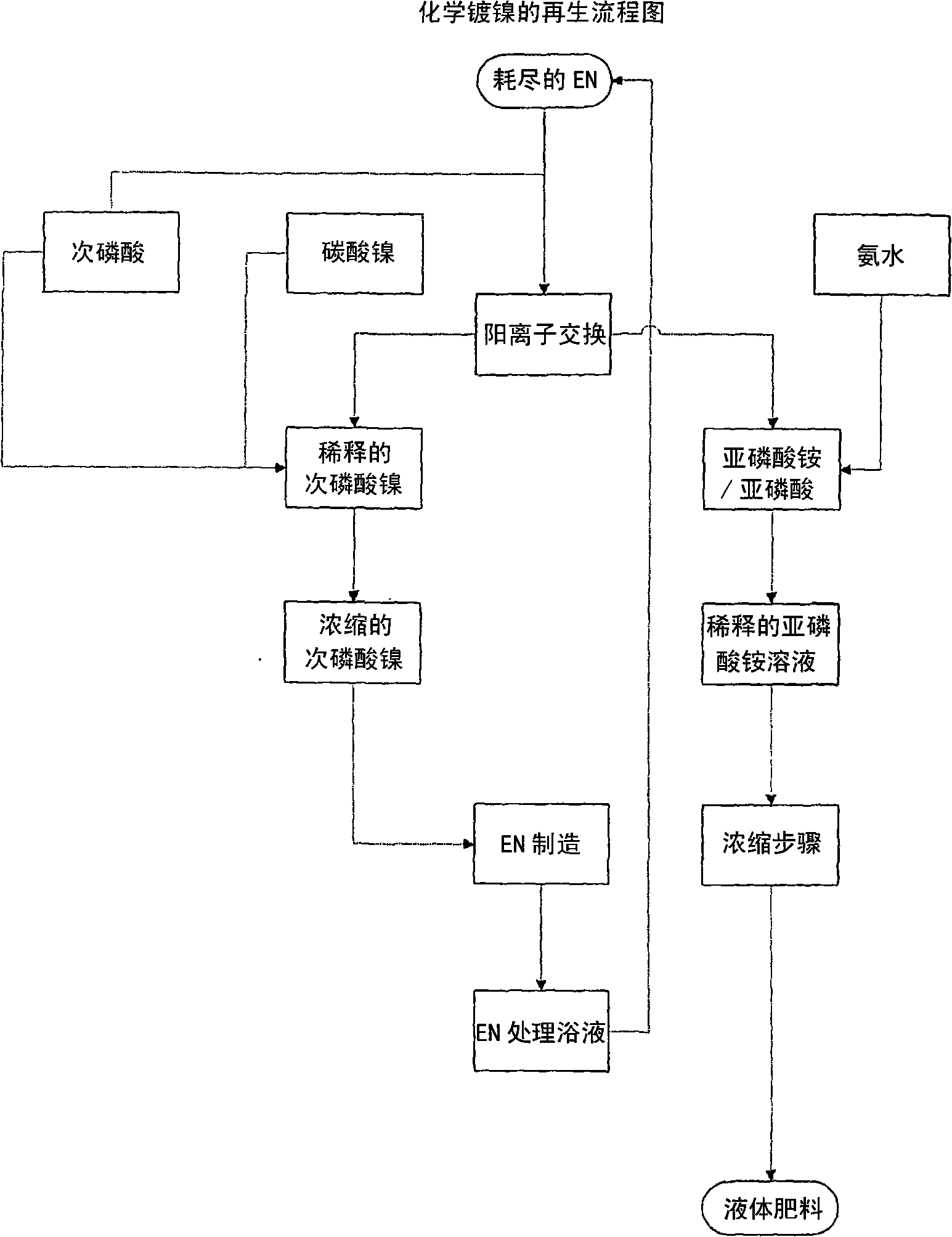
Method of recycling electroless nickel waste
一种化学镀镍、镍离子的技术,应用在化学仪器和方法、液态化学镀覆、卤化镍等方向,能够解决阻止大规模应用等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] The electroless nickel plating solution was composed according to the following formula:
[0037] Nickel metal 6g / l (added as nickel carbonate)
[0038] Hypophosphorous acid 27g / l
[0039] Acetic acid 18g / l
[0040] Lactic acid 26g / l
[0041] Lead 2ppm
[0043] Ammonia solution Sufficient to adjust pH to 4.8
[0044]Run the plating bath at 88-90°C. Nickel is plated from the bath, and the concentrations of hypophosphite and nickel are maintained by adding ammonium hypophosphite and nickel hypophosphite to the bath. The pH of the plating bath was maintained by adding an aqueous ammonia solution. The lead and iodate concentrations were maintained by adding lead in the form of lead acetate and ammonium iodate.
[0045] Run the plating bath in this manner until 4 metal "renewals" have been completed. At this point, analysis of the bath demonstrated that the bath contained the following composition:
[0046] Nickel metal 6g / l
[0047...
Embodiment 2
[0063] The plating bath described in Example 1 was run at 88-90°C. Nickel is plated from the plating bath, and the concentrations of hypophosphite and nickel are maintained by adding ammonium hypophosphite and nickel hypophosphite. The pH of the plating bath was maintained by adding potassium carbonate solution. The lead and iodate concentrations were maintained by adding lead in the form of lead acetate and ammonium iodate.
[0064] Run the plating bath in this manner until 4 metal "renewals" have been completed. At this point, analysis of the plating bath gave the following composition:
[0065] Nickel metal 6g / l
[0066] Hypophosphite ion 25g / l
[0067] Acetic acid 20g / l
[0068] Lactic acid 28g / l
[0069] Phosphite ion 125g / l
[0070] Potassium ions 120g / l
[0071] Ammonium ion 25g / l
[0072] The nickel ions were then removed from the plating bath using the method described in Example 1, but instead of using the acid form of the resin, treatment of the acid form o...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| surface pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| surface pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| surface pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com