Zero emission method of wastewater in lead-zinc metallurgical refinery
A zero-discharge, wastewater technology, applied in metallurgical wastewater treatment, chemical instruments and methods, water/sewage treatment, etc. Conducive to treatment and reuse, avoid water volume expansion, and improve the effect of nanofiltration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
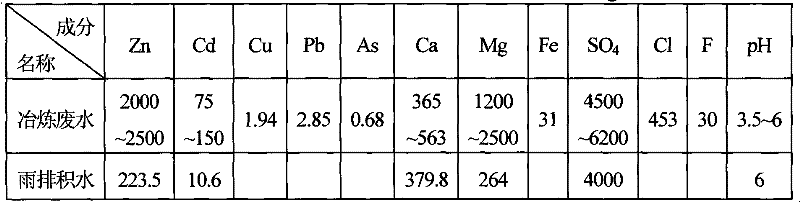
[0021] Embodiment 1: certain lead-zinc smelting plant waste water and rainwater accumulation water composition are as follows: (mg / L)
[0022]
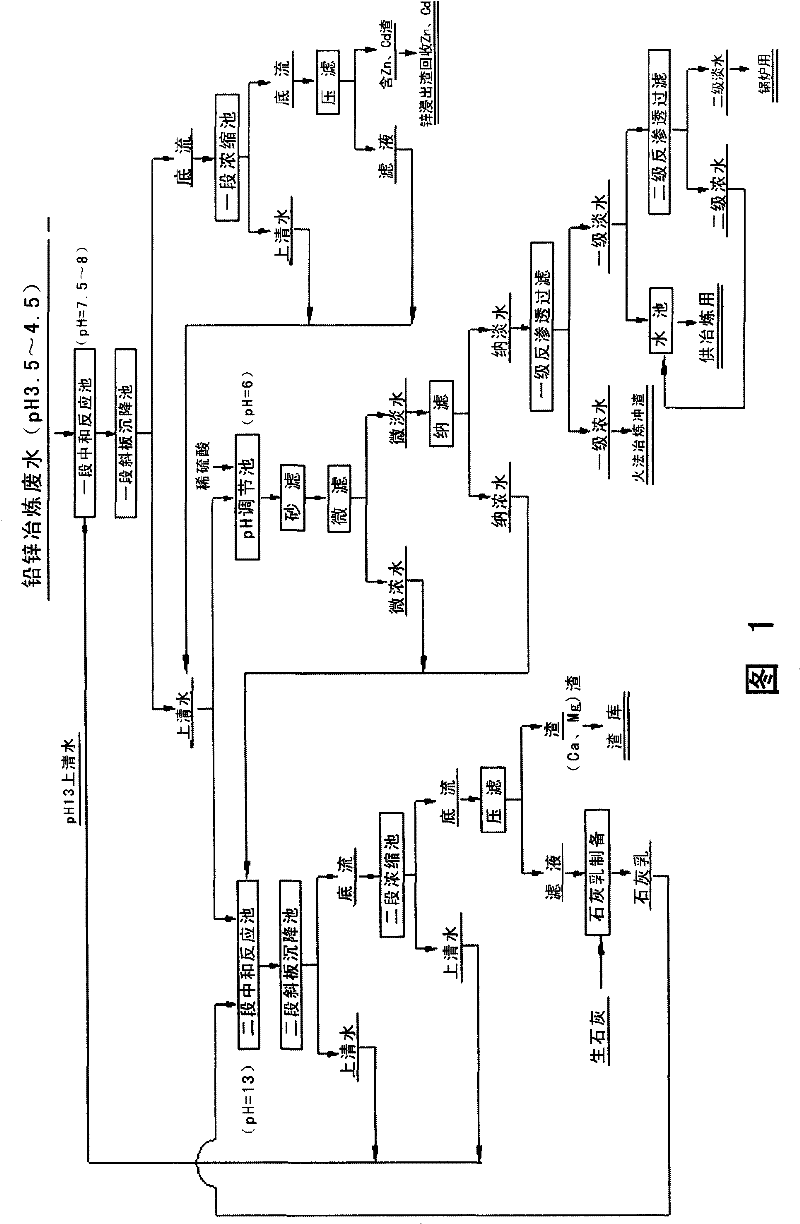
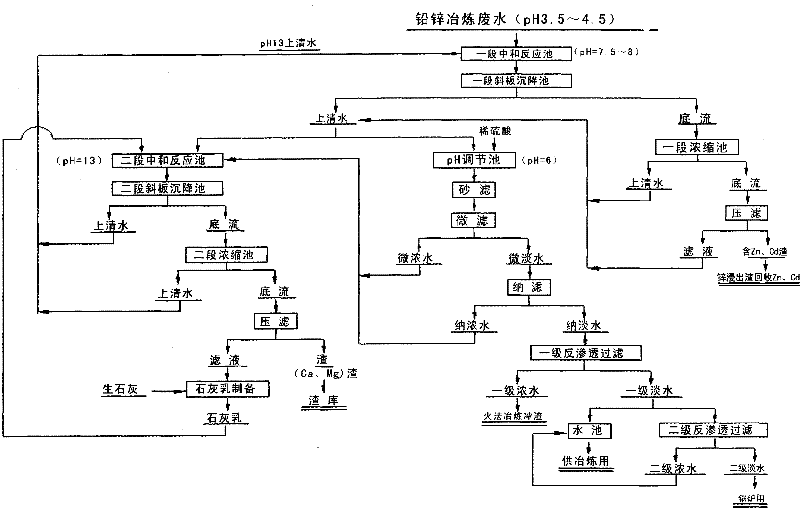
[0023] The supernatant water (pH=13) produced by the second stage of neutralization (milk of lime neutralization) for smelting wastewater was stirred in the first stage neutralization reaction tank for 20 minutes, and the pH at the end point was controlled to be 7.5-8, and the mixed solution was passed through a stage of ramp The liquid-solid separation is carried out in the plate settling tank and the concentration tank to obtain the bottom flow and supernatant water (pH=7.5~8). The bottom flow is sent to a filter press for filtration, and the filter residue contains 25-35% Zn and 1-1.5% Cd. The filter residue is sent to zinc leaching to recover Zn and Cd, and the recovery rates of Zn and Cd in the wastewater are up to 95% and 55% respectively. Most of the supernatant water (pH=7.5~8) neutralized in the first stage is sent to the ...
Embodiment 2
[0027] Embodiment 2: The composition of certain lead-zinc smelting wastewater is: (mg / L)
[0028] Zn
Cd
Cu
Pb
As
mn
Fe
Ca
Mg
SO 4
Cl
F
pH
1300
54.3
1.63
1.66
0.33
628
4.4
310
1130
5400
310
140
4.0
[0029] The waste water is neutralized with the supernatant water (PH=12) produced in the second stage of neutralization in the first stage of the neutralization reaction tank, and the end point is PH=8, and the mixed solution is subjected to liquid-solid separation through the inclined plate settling tank and the concentration tank. The bottom flow is sent to pressure filtration, and the filter residue contains 28% Zn and 0.8% Cd. Most of the supernatant water (PH=8) is sent to the second neutralization reaction tank for neutralization with milk of lime, and the pH is controlled to be 12. The mixed solution is separated from liquid and solid by inc...
Embodiment 3
[0031] Embodiment 3: The composition of certain lead-zinc smelting wastewater is: (mg / L)
[0032] Zn
Cd
Cu
Pb
As
mn
Fe
Ca
Mg
SO 4
Cl
pH
2687
120
0.82
0.93
0.19
870
25
406
2200
5860
332
5
[0033] The waste water is neutralized with the Mg-removed supernatant water (PH=13) produced in the second stage and in the first stage neutralization reaction tank, and the control end point is PH=7.5~8, and the mixed solution is concentrated through the inclined plate settling tank The pool is separated, the bottom flow is filtered through pressure, and the output filter residue contains Zn33% and Cd1%. Most of the supernatant water is sent to the second-stage neutralization reaction tank for neutralization with milk of lime, and the pH is controlled to be 13. The mixed solution is separated from the liquid and solid by the inclined plate settling tank and the concent...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com