All-solid-state organic alloy electrolyte for dye-sensitized solar battery
A technology of solar cells and organic alloys, applied in capacitor electrolytes/absorbents, electrolytic capacitors, electric solid devices, etc., can solve the problems of low melting point, low photoelectric conversion efficiency, difficult dye-sensitized solar cells, etc., and achieve simple process, Conditions are easy to control and the effect of good long-term stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] Select two plastic crystals of neopentyl glycol (NPG) and succinonitrile (SCN), weigh NPG and SCN according to the molar ratio of 0%, 20%, 40%, 60%, 80%, and 100%, and put them in Heat together until completely melted, stir to make the mixture uniform, and cool to obtain an organic alloy. The melting point of these solid organic alloys increased with increasing NPG content, from 58°C to 122°C. Then add 1-5% iodine, 1-10% lithium iodide, 1-10% methyl ethyl imidazole iodine and other electrolytes that occupy the amount of the organic alloy substance, heat until completely melted, stir evenly, and cool to room temperature , that is, a solid organic alloy electrolyte is obtained. The melting point of the organic alloy electrolyte solution with NPG content of 80% reaches above 80°C.
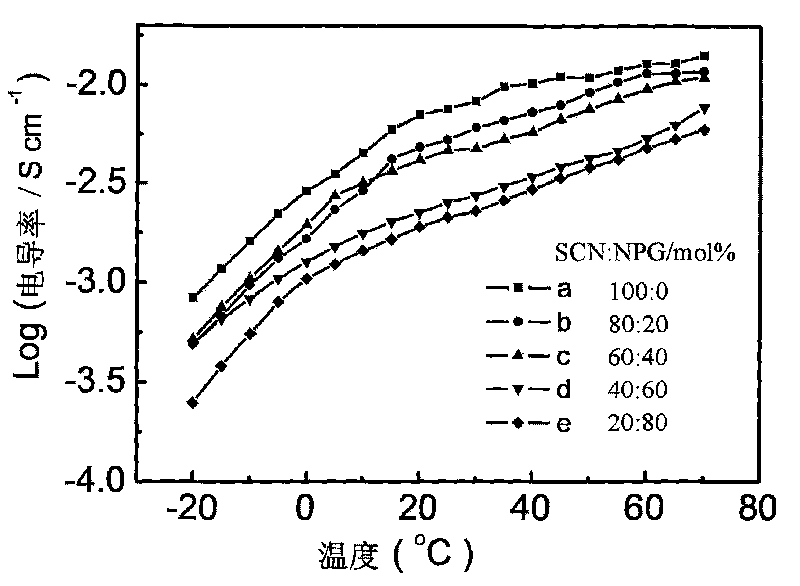
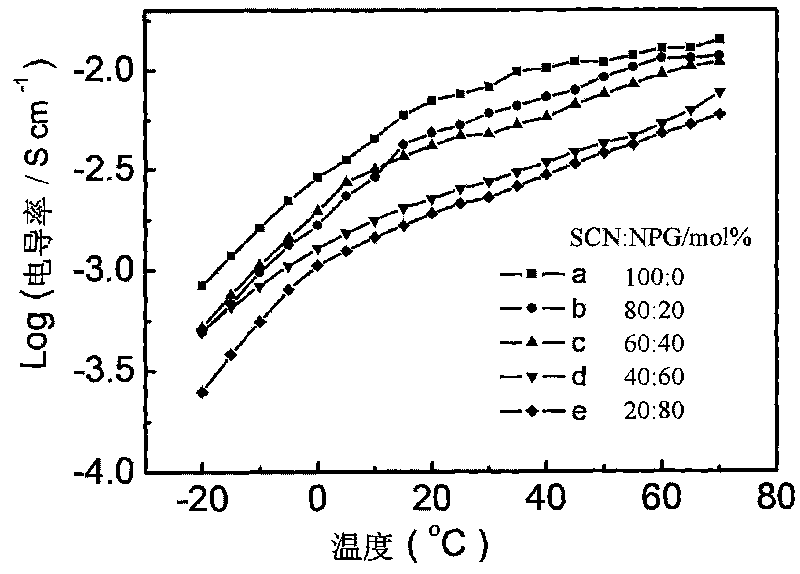
[0019] figure 1 It is a graph of the conductivity of the organic alloy electrolyte at different temperatures. It can be seen from the figure that the organic alloy electrolyte has a high ro...
Embodiment 2
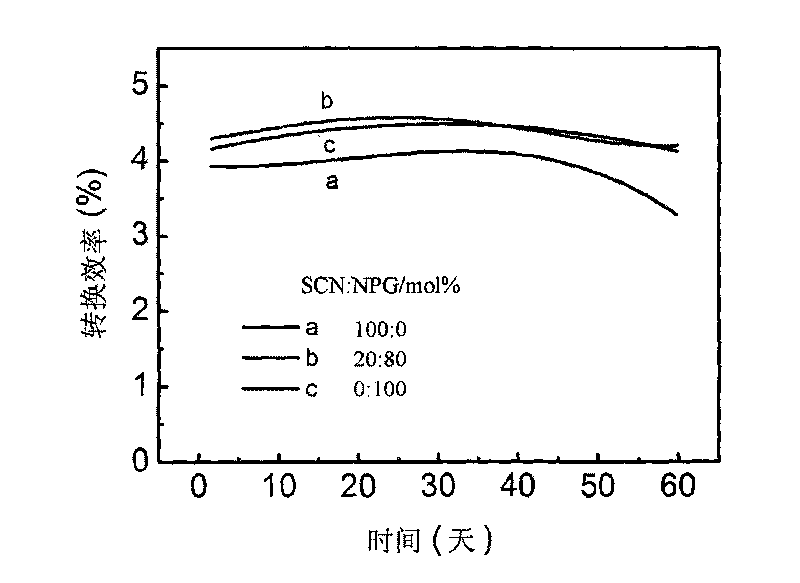
[0026] Two plastic crystals are selected, namely pentaerythritol (PER) and succinonitrile (SCN). Weigh PER and SCN according to the molar ratio of 20%, 40%, 60%, and 80%, and heat them together until they are completely melted, stir to make the mixture uniform, and cool to obtain an organic alloy material. Then add electrolytes such as 1-5% iodine, 1-10% lithium iodide, 1-10% methyl ethyl imidazole iodine, 1-10% tert-butylpyridine and other electrolytes of the amount of the organic alloy substance, and heat until completely melted, stirred evenly, and cooled to room temperature to obtain a solid organic alloy electrolyte. The room temperature conductivity of the solid organic alloy electrolyte reaches 0.05 ms cm -1 ~3ms cm -1 . The melting point of the organic alloy electrolyte with PER content of 80% reaches above 80°C. The photoelectric efficiency of DSSCs prepared from these solid organic alloy electrolytes reaches 2%-5%.
Embodiment 3
[0028] Choose neopentyl glycol (NPG), succinonitrile (SCN) and picoline iodine (MPI) three plastic crystals. Weigh NPG, SCN and MPI according to the molar ratio of 1:1:0, 1:1:1, 2:2:1, 3:3:1, 1:2:1, 2:1:1, and put Heat together until completely melted, stir to make the mixture uniform, and cool to obtain an organic alloy material. Then add 1-5% iodine, 1-10% lithium iodide, 1-10% methyl ethyl imidazole iodine and other electrolytes that occupy the amount of the organic alloy substance, heat until completely melted, stir evenly, and cool to room temperature , that is, a solid organic alloy electrolyte is obtained. The room temperature conductivity of the solid organic alloy electrolyte reaches 0.1 ms cm -1 ~5ms cm -1. The melting point of some organic alloy electrolytes has reached above 80°C. The photoelectric efficiency of DSSCs prepared from these solid organic alloy electrolytes reaches 2%-5%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| electrical conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com