Method for purifying capsular polysaccharide
A technology of capsular polysaccharides and bacterial capsular polysaccharides, applied in the field of vaccines, can solve the problems of complex steps and low yield of extracted substances
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0106] A preferred embodiment of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0107] (1) Bacteria are fermented and cultivated in a bioreactor, and formaldehyde is added in the late stage of logarithmic growth to sterilize;
[0108] (2) Precipitation of soluble polysaccharides using cationic detergents, especially cetyltrimethylammonium salts (eg cetyltrimethylammonium bromide). Before the precipitation, the supernatant can be collected by centrifugation of the bacterial culture and the culture, or the collected supernatant can be concentrated;
[0109] (3) After precipitation, the precipitate was collected by centrifugation and redissolved. Preference is given to aqueous ethanol. The final ethanol concentration was between 20% and 30%. The optimum final ethanol concentration depends on the bacterial serogroup / type;
[0110] (4) Centrifuge the redissolved precipitate to collect the supernatant, and reprecipitate the polysaccharide. Preference is given to aqueous...
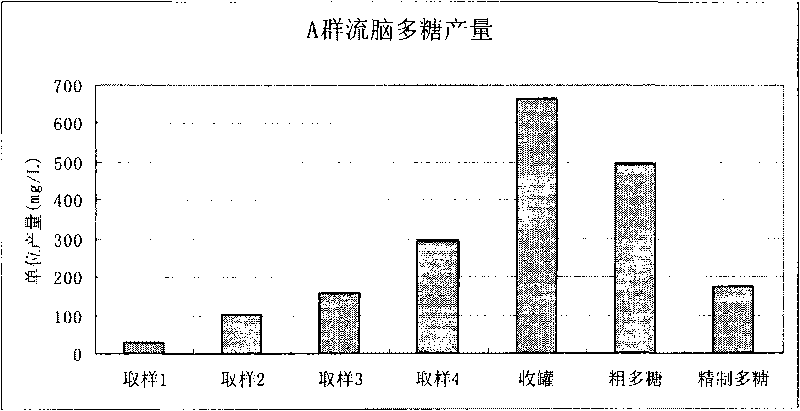
Embodiment 1
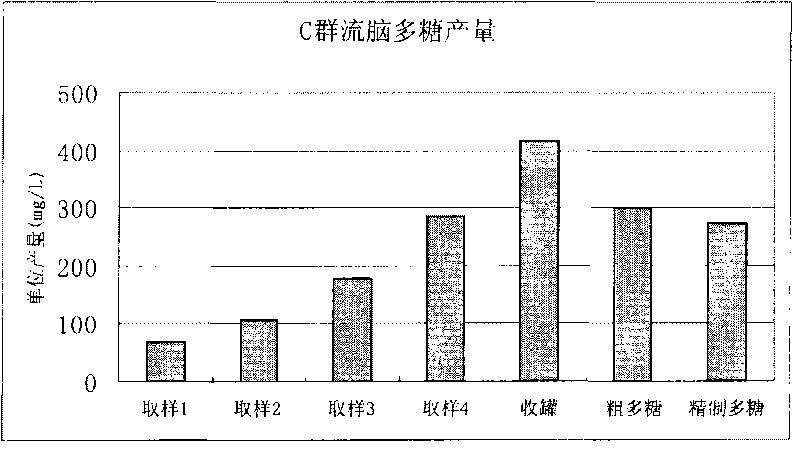
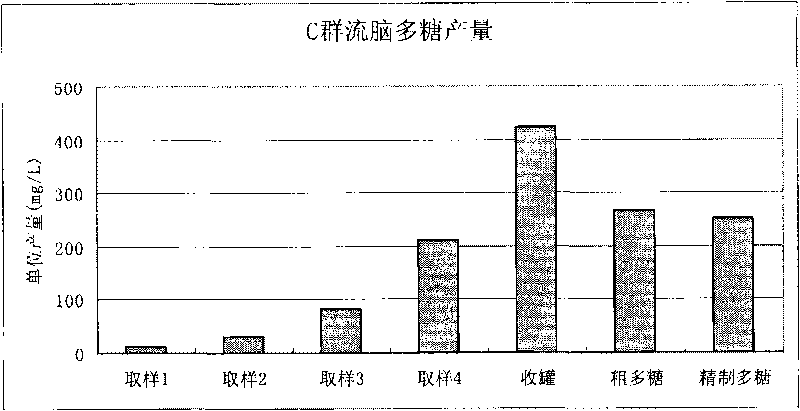
[0134] Example 1. Extraction of group C meningococcal meningitis polysaccharide
[0135] Open the freeze-dried group C ECM strains (bacteria number: CMCC 29025, purchased from the China Medical Bacteria Collection and Management Center), inoculate it into a common agar medium containing 10% sheep blood, and cultivate it under a carbon dioxide environment at 35-37°C for 16 Hour.
[0136] The cultured bacteria were inoculated into semi-comprehensive slant medium, and cultured for 16 hours at 35-37°C in a carbon dioxide environment. Scrape the bacterial lawn and inoculate until 50ml of improved semi-comprehensive medium is installed (prepared by yourself according to "Manufacture and Application of Microbial Culture Medium" , the medium mainly The ingredients are yogurt hydrolyzate, sodium glutamate, glycine, yeast dialyzate, ammonium chloride, magnesium sulfate, glucose, etc.) in a triangular flask, shake culture at 35-37°C for 3 hours, press 1% (v / v ) ratio to inoculate a 5L ...
Embodiment 2
[0139] Example 2. Extracting group C meningococcal meningitis polysaccharide from 5L tank culture
[0140] Freeze-dried Group C ECM strains (bacteria number: CMCC29205, purchased from the China Medical Bacteria Collection and Management Center) were opened, and the bacteria were cultured, sterilized and the culture supernatant was harvested as in Example 1. The incubation time in a 5 L fermenter was 10 hours. Add cetyltrimethylammonium bromide at 0.1% (w / v), and place at 2-8°C overnight to precipitate polysaccharides. The precipitated polysaccharide complexes were collected by centrifugation at 4000 rpm for 30 minutes. Precipitate the complex with 1M CaCl 2 Dissolve, add ethanol to 20% (v / v), most impurities such as nucleic acid and protein will not dissolve. The clarified supernatant was collected by centrifugation at 8000 rpm for 60 minutes. Add ethanol to 70% (v / v) to precipitate polysaccharides. The precipitated polysaccharide was collected by centrifugation, washed t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com