Preparation method of isotope 13C-marked aldehyde
An isotope and acetaldehyde technology, which is applied in the field of preparation of isotope 13C-labeled acetaldehyde, can solve the problems of high temperature requirements, low acetylene yield and low purity, and achieves the effects of optimizing the process, optimizing the synthesis route, and being easy to prepare.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] an isotope 13 The preparation method of C mark acetaldehyde, the method comprises the following steps:
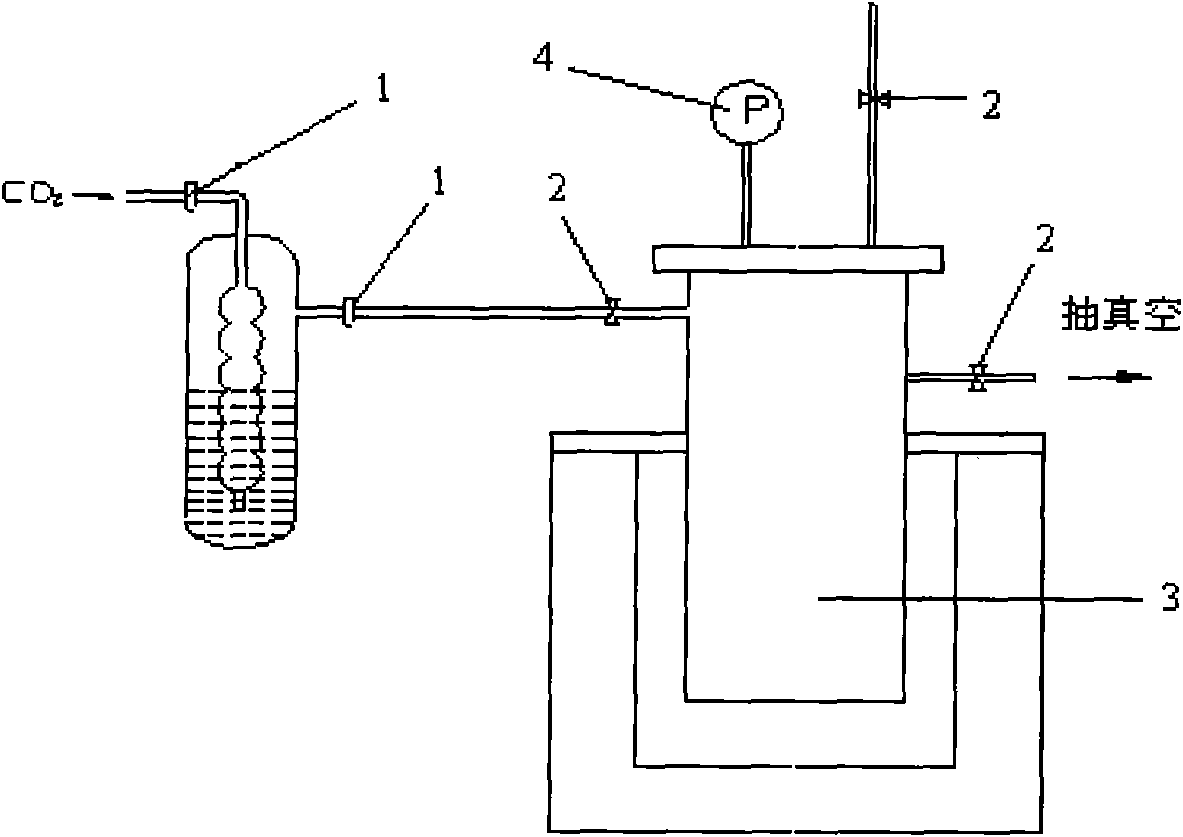
[0031] (1) Active metal and carbon dioxide generate metal carbide: adopt such as figure 1 The shown reactor includes a screw clamp 1, a stop valve 2, a heating reactor 3, and a vacuum gauge 4. Accurately weigh 15.6g (2.25mol) of lithium metal (purity higher than 99.9%), and release it quickly under the protection of argon. into the heating reactor 1, vacuumize after airtight and raise the temperature to 1200°C, open the screw clamp and start to feed 0.30mol 13 CO 2 , 13 CO 2 by Ba 13 CO 3 Quantitatively converted to get, 13 C abundance 99atom%. Observe the vacuum gauge 4, and control the vacuum degree in the heating reactor 1 through the stop valve 3 to keep it at -0.05~-0.1MPa, and pass it in about 4 hours 13 CO 2 , naturally cooled to room temperature after the reaction to obtain carbide of metal lithium.
[0032] (2) Hydrolysis of metal carbides to gene...
Embodiment 2
[0035](1) Active metals and carbon dioxide form metal carbides: Weigh 5.47g (0.225mol) of magnesium metal, quickly put it into the heating reactor under the protection of argon, vacuumize after sealing, and slowly raise the temperature. When the temperature reaches 500-700 ℃ stop vacuuming, continue to heat up to 600 ℃, open the screw clamp and feed 0.225molCO 2 , observe the vacuum gauge, control the vacuum degree in the heating reactor at -0.05~-0.1MPa through the stop valve, and pass the CO in about 10 hours 2 , After the reaction is completed, it is naturally cooled to 20°C to obtain carbides of metallic magnesium.
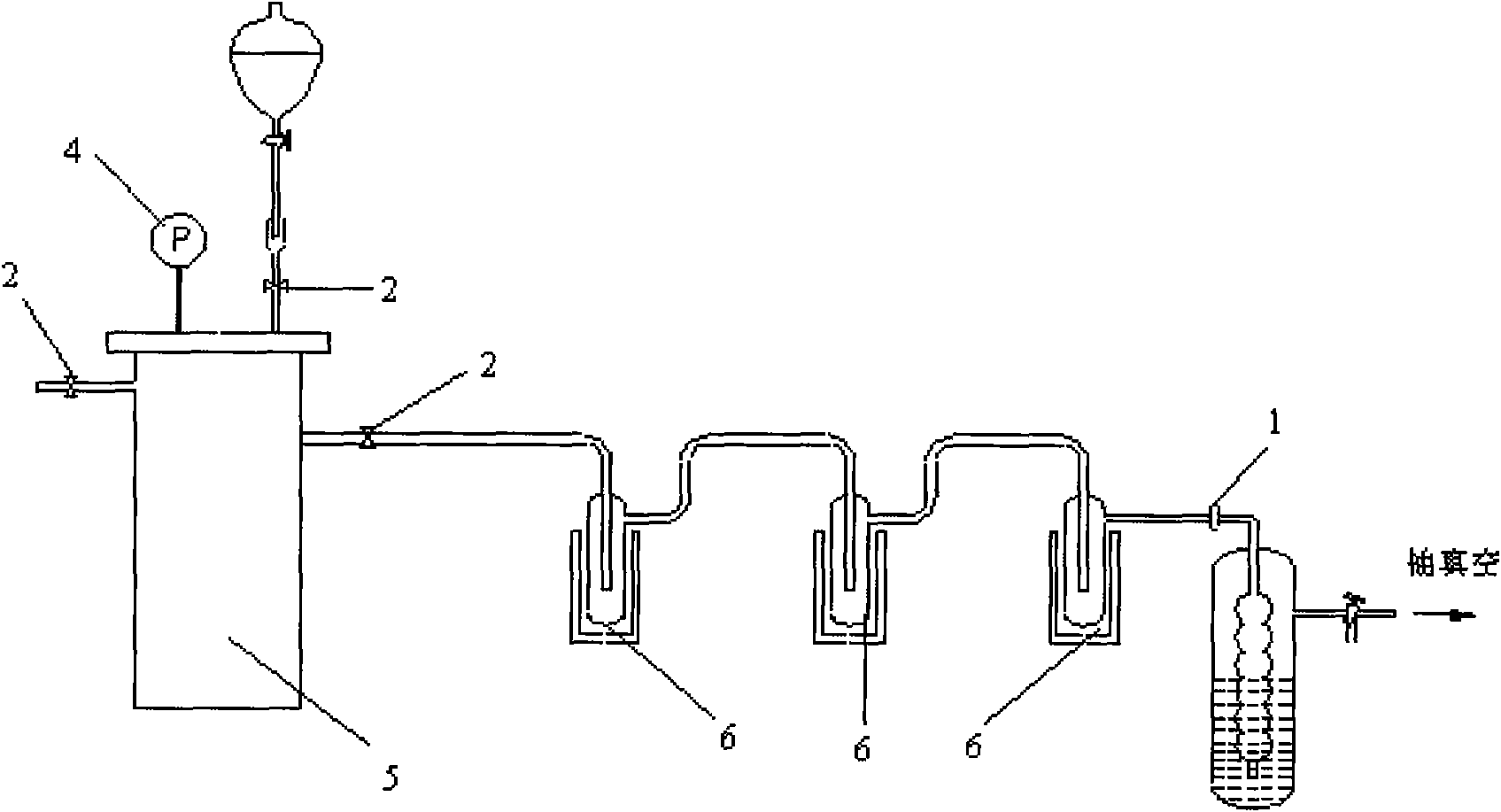
[0036] (2) Hydrolysis of metal carbides to generate acetylene: connect the reactor in step (1) to the hydrolysis reactor, turn on the vacuum pump and use the stop valve to control the vacuum degree of the system at 0.05Mpa, slowly add about 2L of deionized water dropwise, the The generated acetylene was absorbed by a cold trap with a temperature of -30°C, and...
Embodiment 3
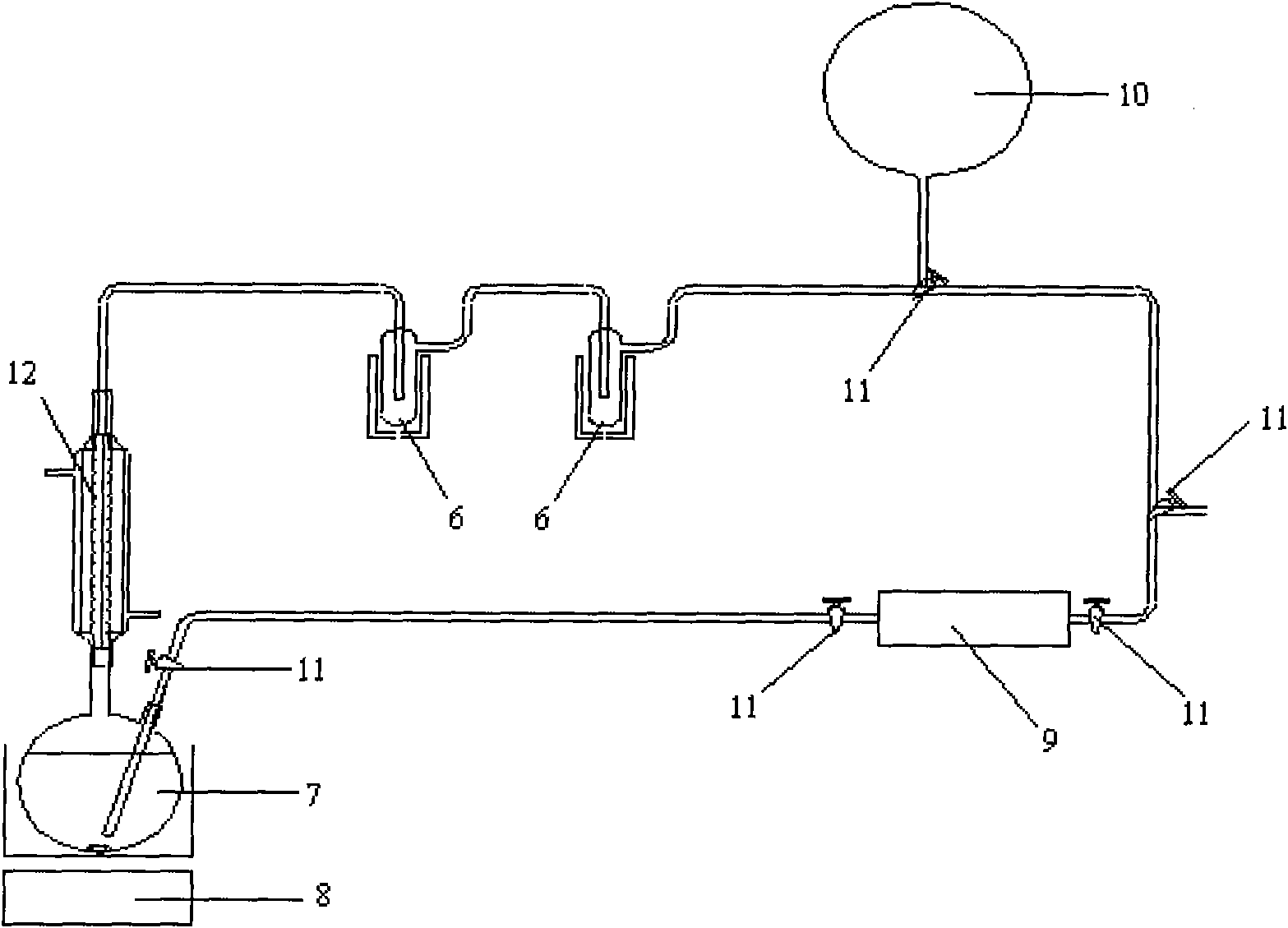
[0039] Step (1) is the same as step (2) and embodiment 1, prepare catalyst mother liquor according to following ratio in step (3): HgSO 4 (6.0g, 0.02mol), concentrated H 2 SO 4 (12.2g, 0.124mol) and deionized water (100ml, 5.55mol), while adding ferric sulfate (4.0g, 0.01mol) as a cocatalyst.
[0040] Vacuumize the reaction system, replace it with argon three times, feed 0.223mol acetylene, and keep the reaction temperature at 85°C. Under the action of a constant flow pump, acetylene gas bubbles into the reaction vessel first, and acetaldehyde is generated in the reaction vessel, and the product acetylene The aldehyde enters the reflux condenser and the alcohol-liquid nitrogen cold trap along with the unreacted acetylene, and the acetaldehyde is collected in the cold trap, and the unreacted acetylene enters the reactor again to continue the reaction until the amount of acetaldehyde produced no longer increases. After the reaction is complete, get 13 C labeled anhydrous acet...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com