Method for brewing beer
A technology of beer and dry matter, which is applied in the brewing of beer and the preparation of alcoholic beverages, etc. It can solve the problems of bad viscosity increase, turbidity increase, and low fermentation yield of wort and beer
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
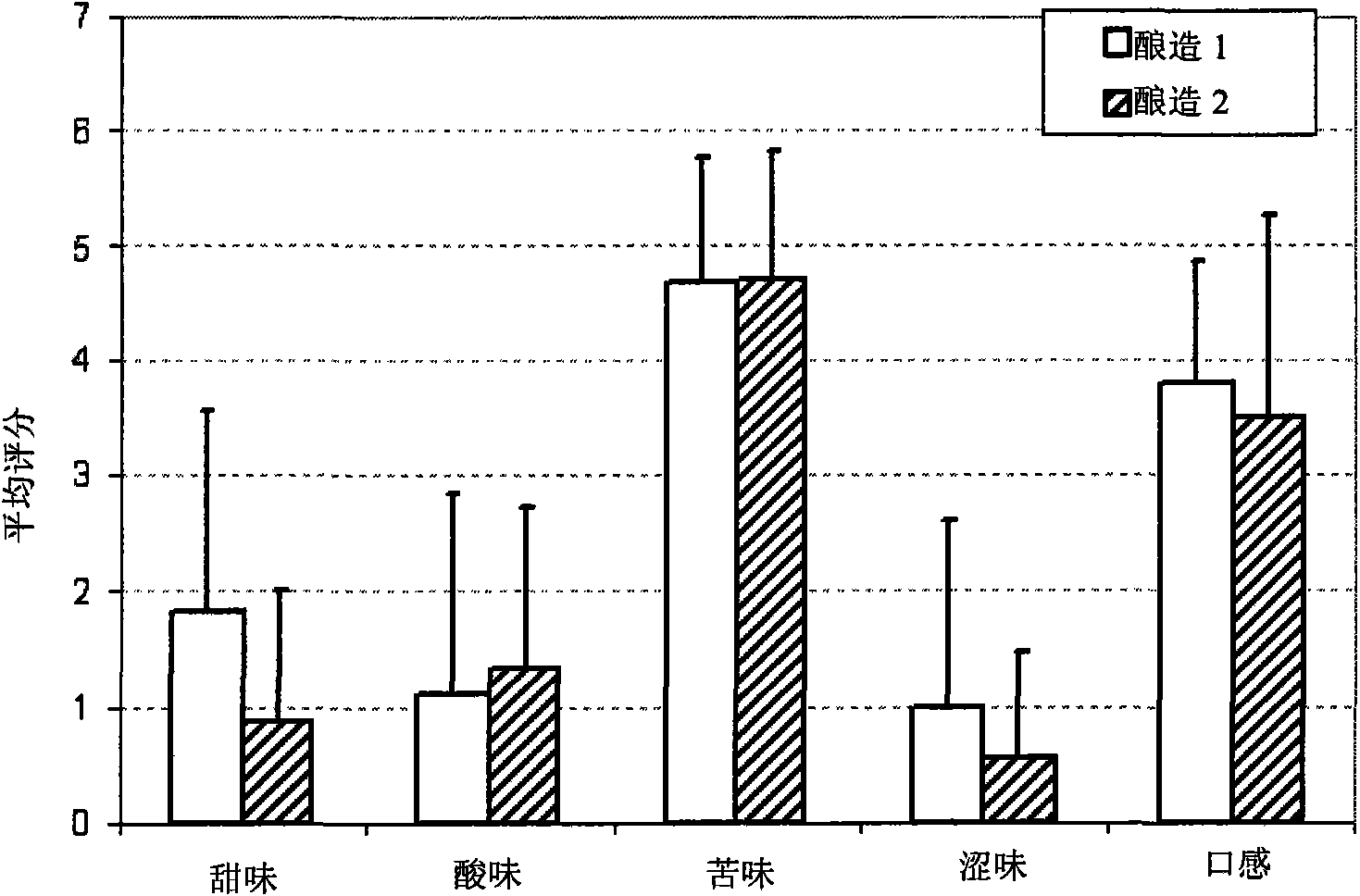
[0056] Example 1: Clarified bottom fermented beer with bran as extender
[0057] Material
[0058] Pilsner malt was purchased from MA company (Mouterij Albert) (Puurs, Belgium). Wheat and rye bran were obtained from DMB (Dossche Mills & Bakery) (Deinze, Belgium) and MG (Molens Goethals (Gent, Belgium), respectively. The carbohydrate composition of the bran fraction shown in Table 1 was determined by the method of Courtin et al., 2000, in which carbohydrates were first hydrolyzed into monosaccharides by acid hydrolysis, and the resulting monosaccharides were detected by gas chromatography as acetic aldols. Termamyl 120L (a thermostable α-amylase preparation), Attenuzyme (a amyloglucosidase preparation) and Promozyme (a pullulanase preparation) were purchased from Novozymes (Bagswald (Bagsvaerd), Denmark).
[0059] analytical skills
[0060] The alcohol content of the beer samples was determined with a near-infrared spectroscopic microscope (AlcolyzerPlus from Anton Paar) an...
Embodiment 2
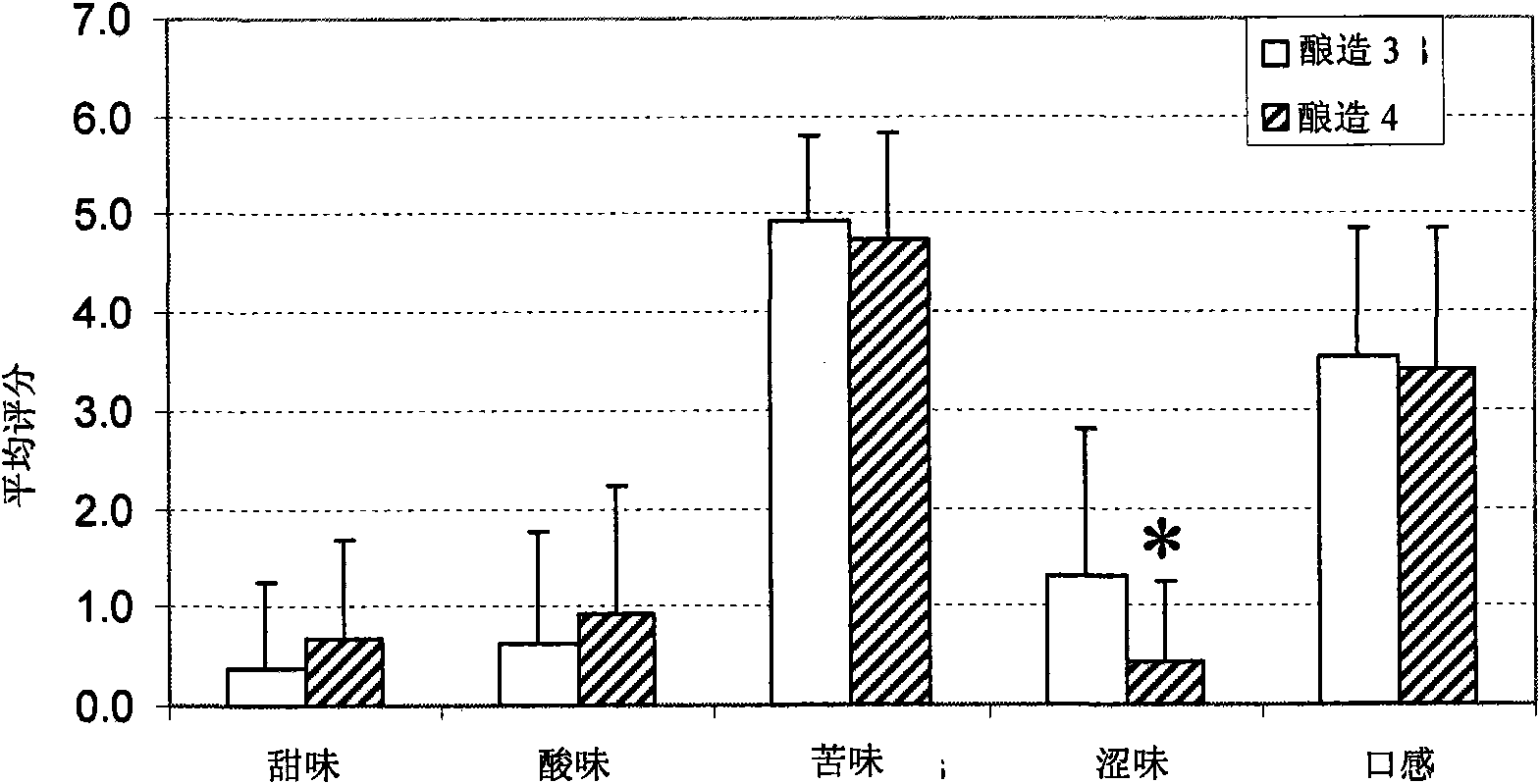
[0070] Example 2: Analysis of below fermented beers made with bran as extender
[0071] Material
[0072] Beers 3 and 4 were prepared as Brews 3 and 4 as described in Example 1. Commercial beers were purchased from local shops.
[0073] Analysis of total ferulic acid and free ferulic acid
[0074] Beer samples (90ml) were sonicated in an ultrasonic bath and then lyophilized. Total ferulic acid (total bound and free ferulic acid) content was determined on 10-50 mg samples suspended in sodium hydroxide (5 ml, 2M, anaerobic). The headspace above the solution was purged with nitrogen, and the bound ferulic acid was hydrolyzed for 18 hours at room temperature. o-coumaric acid (100 μl, 50 mg / 100 ml) was added as an internal standard and the solution was acidified with hydrochloric acid (4 ml; 4M). Then, the solution was extracted three times with ethyl acetate (3 ml each), and the organic phases were combined and dried with nitrogen. The residue was dissolved in methanol (5 ml...
Embodiment 3
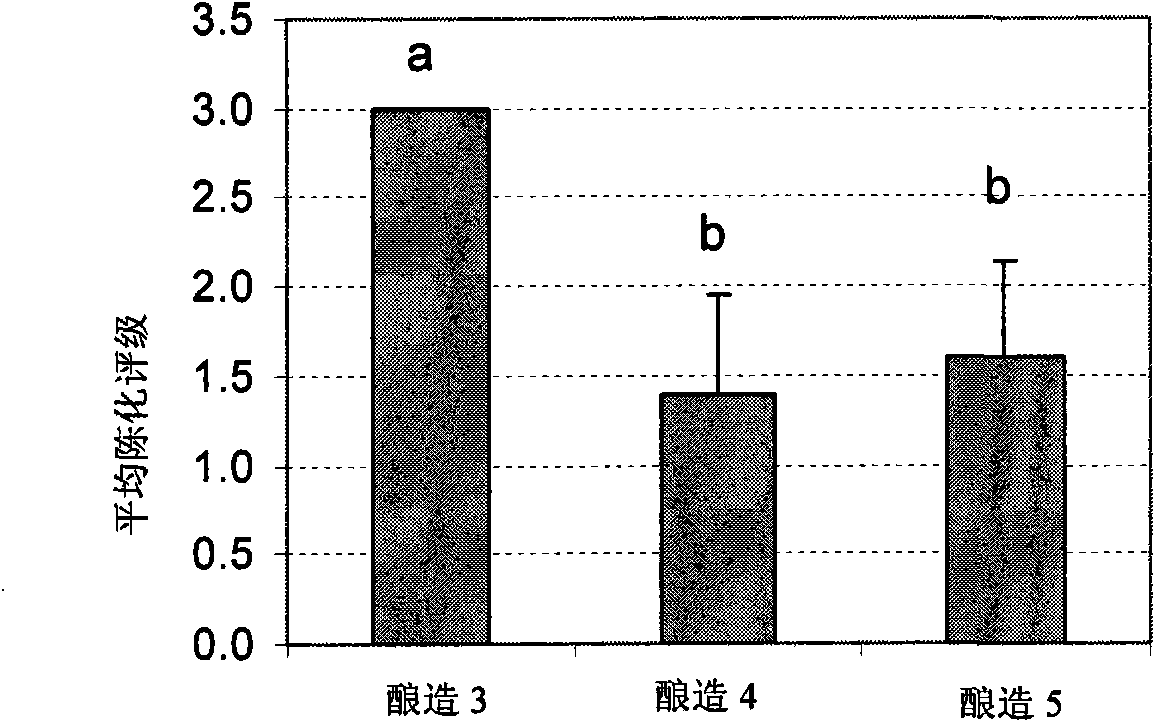
[0106] Example 3: Effect of pH on underfermented beer produced with bran as extender
[0107] Two beers were prepared by adding wheat bran to the grain as described in Brew 4 of Example 1. One beer was prepared at pH 5.6 during the mashing step and the other at pH 5.2 using lactic acid as the acidulant. The analysis revealed that taste-altering compounds associated with lipoxygenase were reduced in beer prepared at pH 5.2 compared to beer prepared at pH 5.6.
[0108] Table 1 : Carbohydrate composition of wheat bran and rye bran used in the brewing experiments described in Example 1 (expressed as % w / w of monosaccharides obtained after acid hydrolysis on dry matter basis). The glucose mainly reflects the starch content and does not account for the cellulose content, which cannot be hydrolyzed by the acid hydrolysis method used.
[0109] Monosaccharides (% dm after acid hydrolysis)
[0110] Table 2: Composition of the mash for brews 1 and 2. The saccharification tem...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com