Method for improving corrosion resistance performance of magnesium-based hydrogen storage alloy by using ion nitriding method
A magnesium-based hydrogen storage alloy, ion nitriding technology, applied in alkaline battery electrodes, metal material coating process, coating and other directions, can solve unseen, unreported problems, etc., to improve capacity or energy density, The effect of improved corrosion resistance and abundant resources
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Embodiment 1: Preparation of hydrogen storage alloy powder
[0027] Table 1Mg a R b Ni c co d Al e Composition examples of hydrogen storage alloys
[0028] Mg 2 Ni
[0029] According to the atomic ratio of the metal elements in the alloys in Table 1, weigh the corresponding metals and put them into the crucible. Put it in a tube furnace protected by argon, raise the temperature to 800°C under the protection of argon, keep it at 800°C for 2 hours and then cool to room temperature to obtain the corresponding bulk calcium-based or magnesium-based hydrogen storage materials. Broken by mechanical crushing method, the particles with a particle size of less than 2 mm were obtained by screening, placed in a stainless steel reactor, heated to 350 ° C, and vacuumed to a reactor pressure of 10 -3Below Torr, then hydrogenation is added and the pressure is increased to 40 atmospheres for hydrogenation. When the hydrogen pressure in the reactor no longer drops, the ...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Embodiment 2: Hydrogen storage alloy nitriding treatment
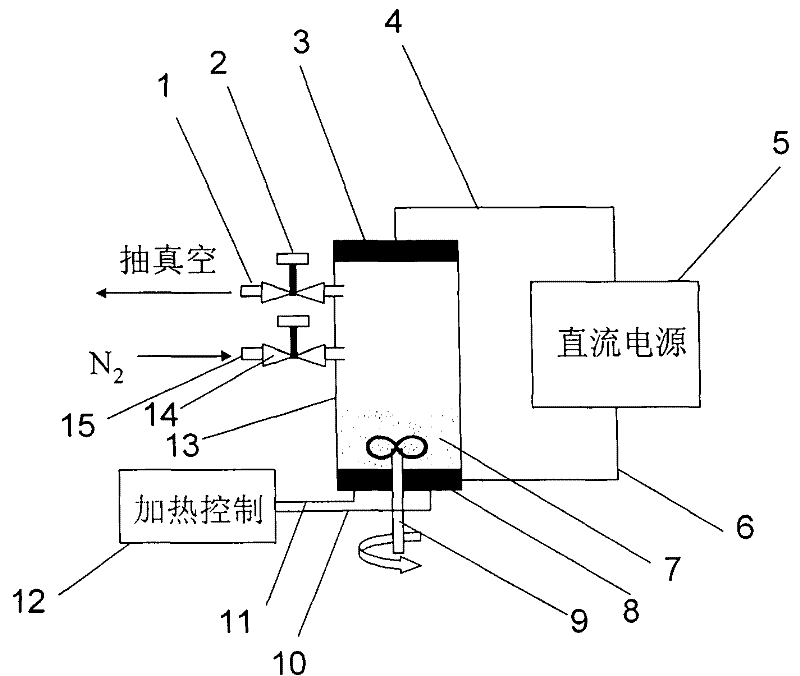
[0031] Select some alloys in Example 1 for nitriding treatment, take 100 grams of magnesium-based hydrogen storage alloy powder, grind it to 200 mesh to 400 mesh, place it on the cathode at the bottom of the ion nitriding furnace, and place the anode on the furnace top; Apply a DC voltage of 200-800 volts between the cathode and anode, and continuously stir the alloy powder placed at the bottom of the furnace at a stirring speed of 10-200rpm; control the heating rate at 1-10°C / min, and control the temperature of the alloy powder at 300 ~600℃, the treatment time is 0.2~2 hours. The boronizing treatment process conditions are listed in Table 2.
[0032] Table 2 Hydrogen Storage Alloy Nitriding Treatment Process Conditions
[0033] Magnesium base alloy
Embodiment 3
[0034] Embodiment 3: Evaluation of nitriding treatment effect
[0035] Get the magnesium-based alloy Mg in embodiment 2 1.9 La 0.1 Ni 0.7 co 0.2 Al 0.1 Powder, screened particle size 200 mesh to 400 mesh. Mg 1.9 La 0.1 Ni 0.7 co 0.2 Al 0.1 Powder, nickel powder, and PVA aqueous solution (5wt.%) were mixed at a mass ratio of 1:0.5:3 to form a slurry, which was applied to nickel foam, dried at room temperature, and pressed into shape as a comparative electrode.
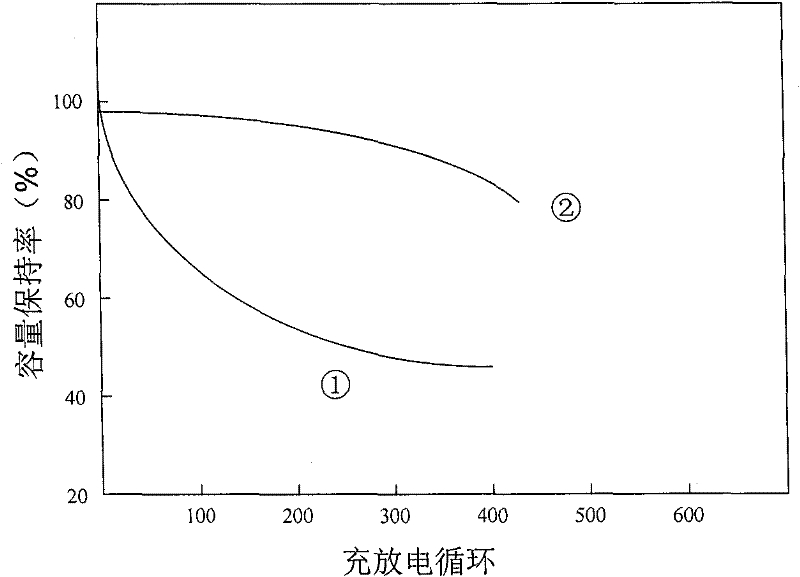
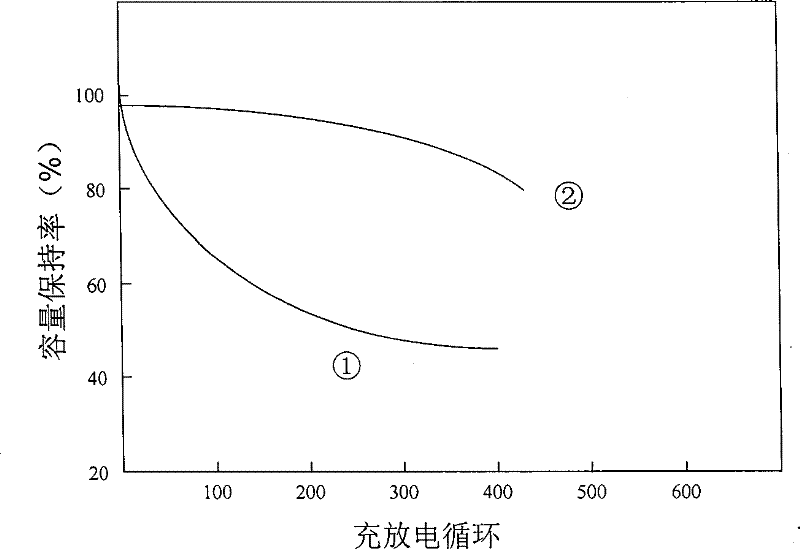
[0036] figure 2 Mg before and after nitriding 1.9 La 0.1 Ni 0.7 co 0.2 Al 0.1 Compare the capacity fade behavior of the electrodes. It can be seen from the figure that the nitriding treatment greatly increased the Mg 1.9 La 0.1 Ni 0.7 co 0.2 Al 0.1 Electrode charge-discharge cycle stability.
[0037] The corrosion resistance of the magnesium-based alloy was evaluated by the charge-discharge capacity retention rate of 200 charge-discharge cycles. The higher the capacity retention rate, the better t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com