Advanced treatment method for heavy alkylbenzene sulfonate (HABS) industrial wastewater
A technology of alkylbenzene sulfonate and production wastewater, applied in the field of water treatment, can solve problems such as unsatisfactory effect, and achieve the effects of easy automatic control, simple operation and low treatment cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
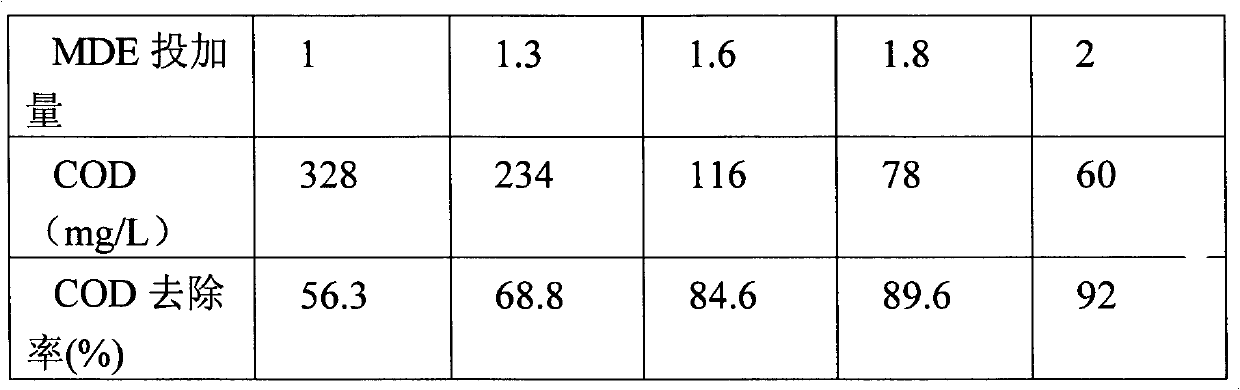
[0025] Specific implementation method: first adjust the pH value of the heavy alkylbenzene sulfonate wastewater treated by aeration and catalytic treatment to 2-4, adjust the current intensity of the regulated DC power supply to 2-10A, and process for 2-10min. For the iron plate. Let it settle for another half an hour, take the supernatant and adjust the pH to 7.5-9.5, then add microporous composite water treatment agent according to the mass ratio of 1-2g / L, stir for 2-3min, and take it out after standing for 1 hour. The COD value of the clear liquid was measured, and the microporous composite water treatment agent used was diatomite mixed with polyaluminum chloride (MDE1), ferrous sulfate heptahydrate (MDE2), aluminum sulfate octadecahydrate (MDE3), polyaluminum sulfate Iron (MDE4) is a water treatment agent compounded at a mass ratio of 3:1-6:1. Embodiment 1: Get 1L heavy alkylbenzene sulfonate wastewater through aeration catalytic oxidation and place in a beaker, adjust t...
Embodiment 2
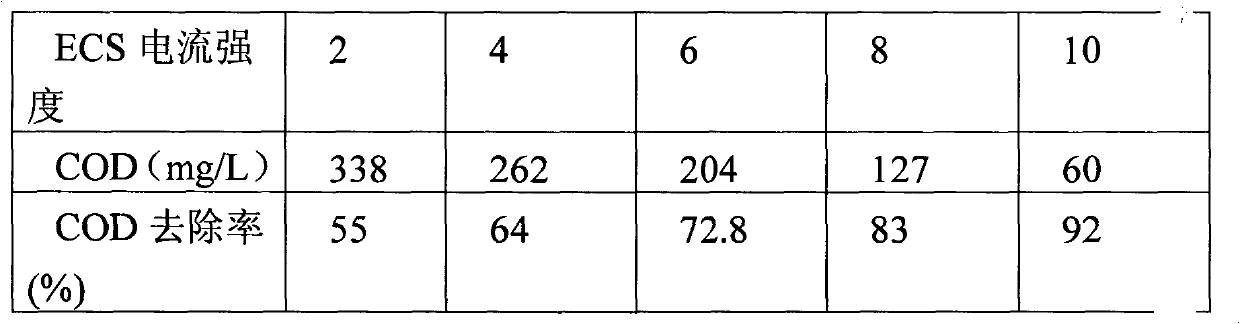
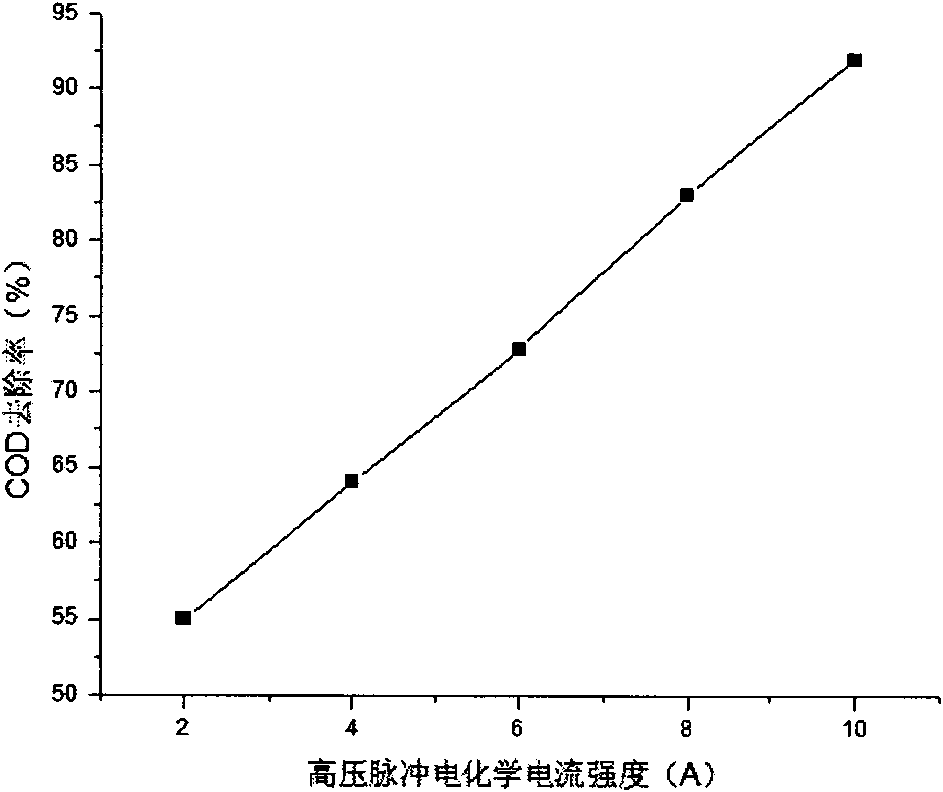
[0029] Using the method of Example 1, the pH was adjusted to 2.5 by sodium hydroxide, the current intensity was adjusted to 2A, 4A, 6A, 8A, and 10A, respectively, and the electrochemical treatment was performed for 8 minutes. After standing for half an hour, 200 mL of the supernatant was taken, and the pH was adjusted by sodium hydroxide. Adjust the pH of the effluent to 8.0, and the dosage of the microporous composite water treatment agent is 1g / L. The microporous composite water treatment agent used is a compound of purified diatomite and polyaluminum chloride at a mass ratio of 5:1. After adding the water treatment agent, stir rapidly for 2-3min, let it settle for 1h, take the supernatant to measure the COD value, the experimental results are shown in Table 2 and figure 2 shown.
[0030] Table 2 The influence of electrochemical current intensity on COD removal rate
[0031]
Embodiment 3
[0033] Using the method of Example 1, adjust the pH to 2.5 by sodium hydroxide, adjust the current intensity to 10A respectively, perform electrochemical treatment for 3min, 4min, 6min, 8min, and 10min, leave to stand for half an hour and take 200mL of the supernatant, and pass the sodium hydroxide Adjust the pH of the effluent to 8.0, and the dosage of the microporous composite water treatment agent is 1g / L. The microporous composite water treatment agent used is a compound of purified diatomite and polyaluminum chloride at a mass ratio of 5:1. After adding the water treatment agent, stir rapidly for 2-3min, let it stand for 1h, take the supernatant to measure the COD value, the experimental results are shown in Table 3 and image 3 shown.
[0034]Table 3 The influence of electrochemical treatment time on COD removal rate
[0035]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com