Method for preparing light porous inorganic gelled material product from gel particles
A technology of inorganic cementitious materials and gel particles, applied in the field of porous lightweight materials, can solve the problems of low pressure bearing capacity, floating and uneven distribution of pores, high energy consumption, etc., to achieve good thermal insulation performance, easy to control And the effect of good adjustment and pressure bearing performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
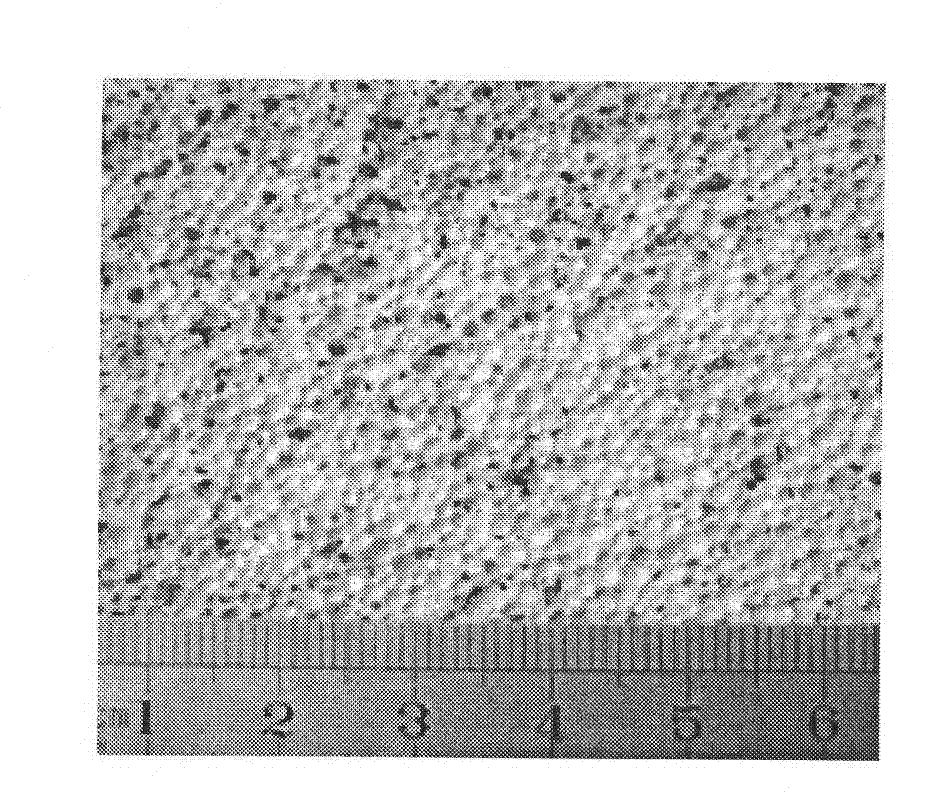
[0021] (1) Preparation of pore-forming agent particles
[0022] 1. Sodium alginate is a natural linear polysaccharide polymer with good water solubility and acts as a gelling mother liquor. Prepare a sodium alginate aqueous solution with a concentration of 0.7% to 1.3% according to mass percentage: mechanically stir the sodium alginate at 20 to 80°C to dissolve it in water, (the comprehensive effect of stirring and dissolving at 60°C is the best, ) to form a uniform and transparent sodium alginate aqueous solution, which was cooled to room temperature for use.
[0023] 2. Calcium chloride is used as the gelling cross-linking agent. Prepare a 0.5-1.5mol / L calcium chloride solution and store it for later use.
[0024] 3. Spray the sodium alginate solution obtained in step 1 into the calcium chloride solution obtained in step 2 with a spray device to form gel particles with high water content, and these gel particles react in the calcium chloride solution for 5 ~ 20 minutes, t...
Embodiment 1
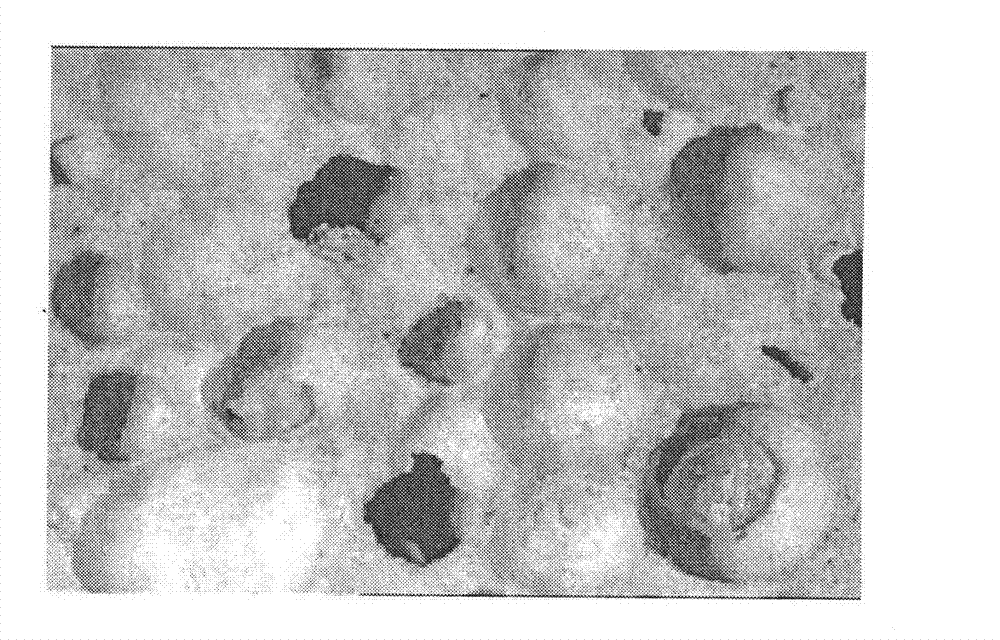
[0031] Use pore-forming agent particles as aggregates (with a particle size between 2 and 3 mm), and add them to the cement slurry according to different volume percentages. After stirring, injection molding, and curing, the lightweight porous concrete test blocks are made. The comparison and test results are shown in the table below:
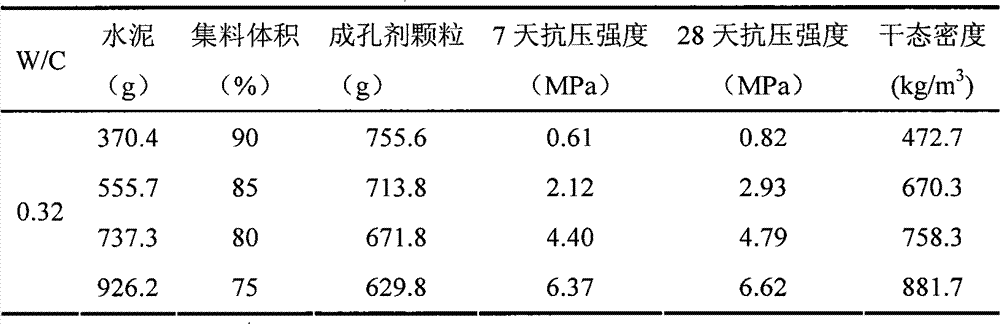
[0032] Table 1 Concrete formula and performance with aggregates as pore-forming agent particles
[0033]
[0034] 1. W / C in the table is water-cement ratio.
[0035] 2. Aggregate volume refers to the volume percentage of pore-forming agent particles or compound aggregates when they are piled up in the mould.
[0036] The prepared lightweight porous concrete test block has a 7-day compressive strength of 0.61-6.37Mpa, a 28-day compressive strength of 0.82-6.62Mpa, and a dry density of 472.7-881.7kg / m 3 between.
Embodiment 2
[0038] The pore-forming agent particles and expanded perlite particles are compounded as aggregates, and added to the cement slurry in different proportions and volume percentages. After stirring, injection molding and curing, the lightweight porous concrete test block is prepared. The specific proportion and the properties of the made lightweight porous concrete test block are shown in Table 2 and Table 3 below:
[0039] Table 2 Concrete ratio table with aggregates composed of pore-forming agent particles (A) and expanded perlite particles (B)
[0040]
[0041] Table 3 Concrete properties of aggregates composed of pore-forming agent particles (A) and expanded perlite particles (B)
[0042]
[0043] The 7-day compressive strength of the prepared lightweight porous concrete test block is between 2.33-5.71Mpa, the 28-day compressive strength is between 0.89-7.03Mpa, and the dry density is 534.5-896.73kg / m 3 between.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com