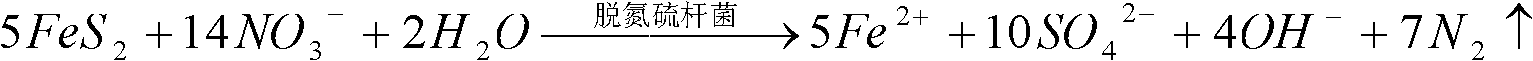Nitrogen and phosphorus removal method by using pyrite as biochemical filling
A technology for nitrogen and phosphorus removal and pyrite removal, which is applied in the direction of anaerobic digestion treatment, can solve problems such as poor results, and achieve the effects of easy engineering promotion and application, low effluent hardness, and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Embodiment 1: the start-up of reactor
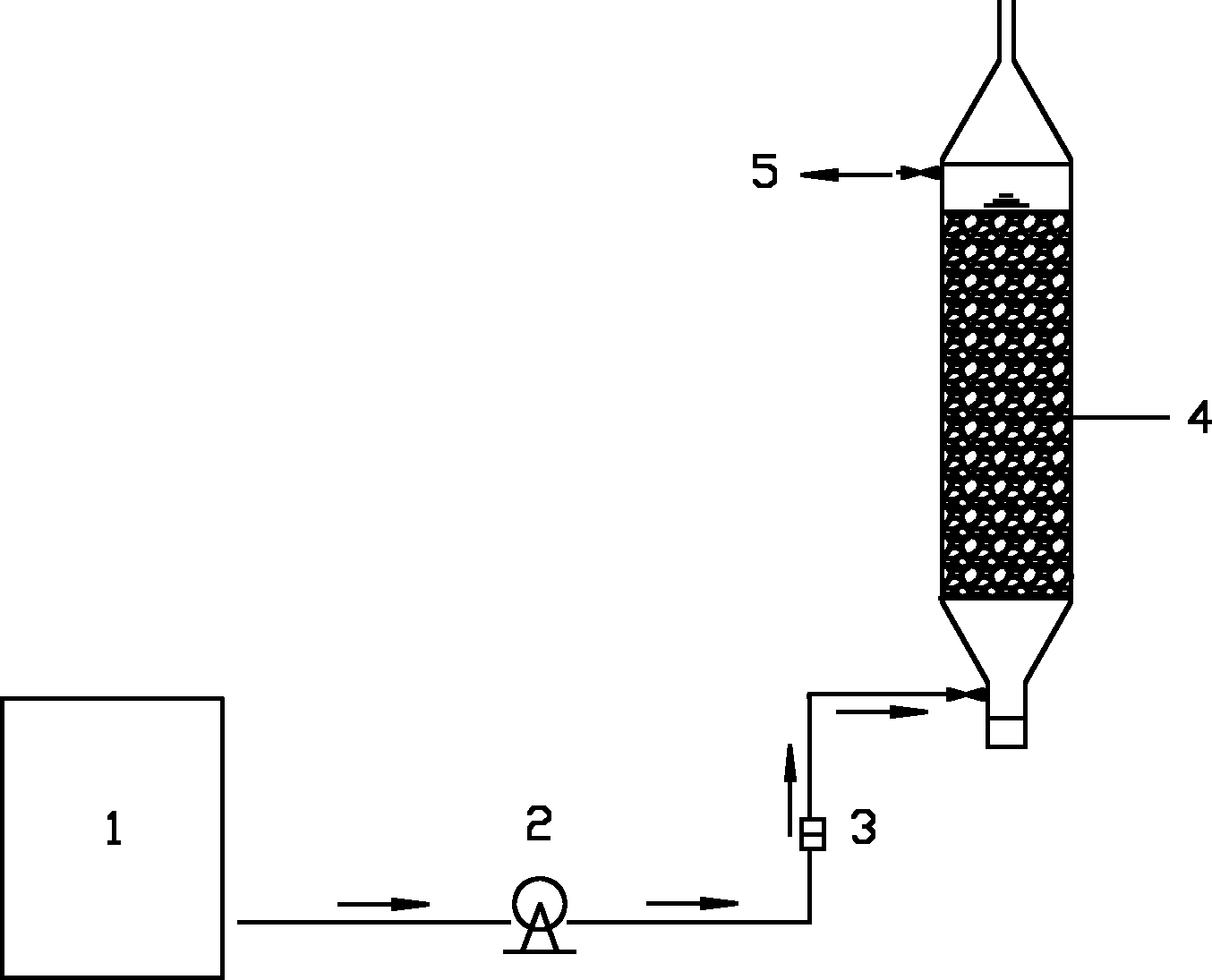
[0033] The process used in the test is as figure 1 As shown, the waste water to be treated is located in the water tank 1, enters the reactor through the peristaltic pump 2, the inflow flow is measured by the liquid flow meter 3, and the treated water is discharged from the water outlet 5.
[0034] (1) Preparation of reactor packing: screening pyrite with a particle size of 2 to 5 mm and limestone with a particle size of 1 to 2 mm, with a mass ratio of 4:1 and a bed porosity of about 50%, are directly filled into the reaction device;
[0035] (2) In order to start the reactor as soon as possible, the start of the reactor is divided into three stages:
[0036] a. First inoculate the anaerobic sludge from the sewage plant into the reactor, feed the culture solution of Thiobacillus denitrificans into the reactor, set the hydraulic retention time to 8h, and regularly detect NO 3 - -N concentration, NO measured for 3 consecutive ti...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Example 2: Denitrification and dephosphorization of artificially prepared domestic sewage
[0043] The experiment was continued on the basis of the start-up of the Example 1 reactor.
[0044] The test water is artificial water, and the influent NO 3 - -N concentration is 29.52mg / L, TP is 15.37mg / L, pH=7.18, water temperature is 30°C.
[0045] The waste water to be treated is circulated into the reactor after the start-up, and the hydraulic retention time is 5 days, so that the microorganisms can fully contact with the treated waste water; water samples are taken every 24 hours to measure the water quality indicators. The results are shown in the table below, the effluent NO 3 - -N below 1mg / L, NO 2 - -N was not detected; while TP was lower than 0.05mg / L. It can be seen that the treated effluent is better than the first-level discharge standard of pollutant discharge standards for urban sewage treatment plants in my country, and the device operates stably.
[004...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Example 3: Denitrification and dephosphorization of artificially prepared domestic sewage
[0048] The experiment was continued on the basis of the start-up of the Example 1 reactor.
[0049] The test water is artificial water, and the influent NO 3 - -N concentration is 30.14mg / L, TP is 14.19mg / L, pH=5.03, water temperature is 20°C.
[0050] The waste water to be treated is circulated into the reactor after the start-up, and the hydraulic retention time is 5 days, so that the microorganisms can fully contact with the treated waste water; water samples are taken every 24 hours to measure the water quality indicators. The results are shown in the table below.
[0051] Sampling times
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com