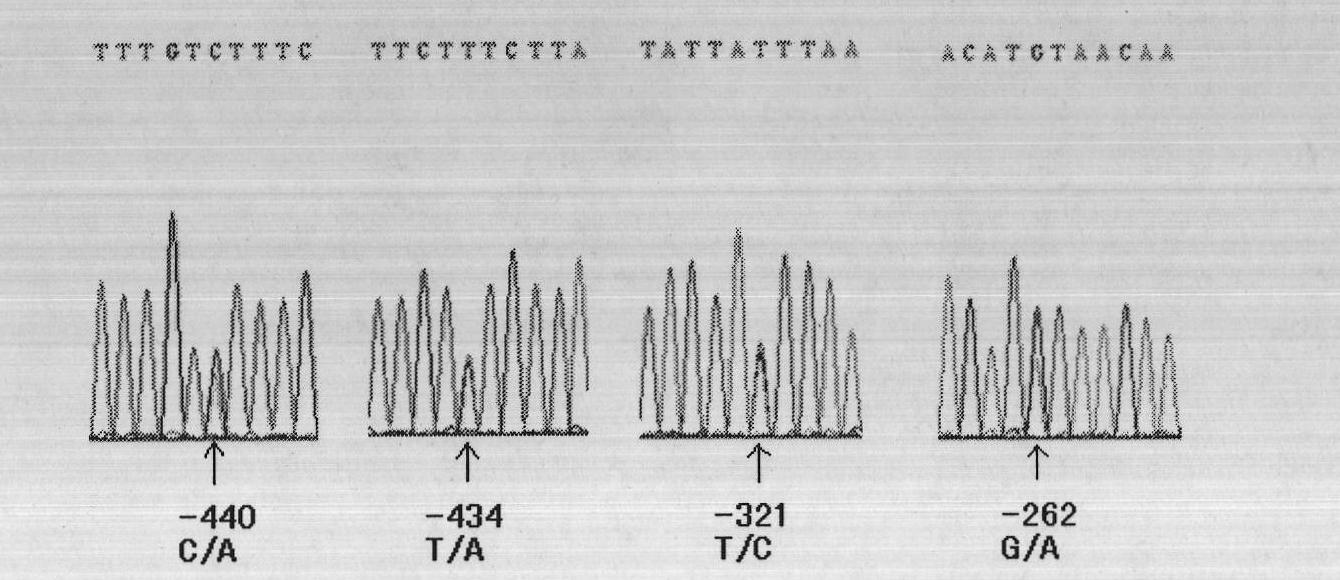
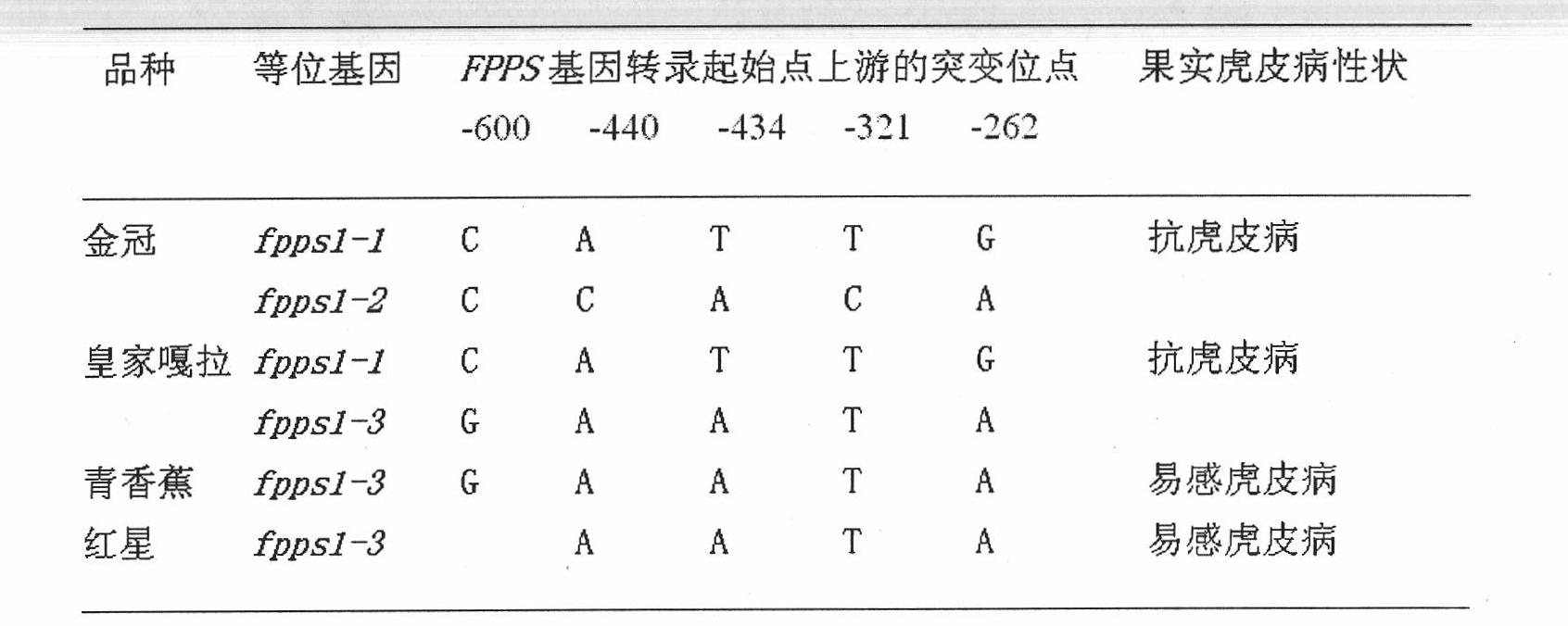
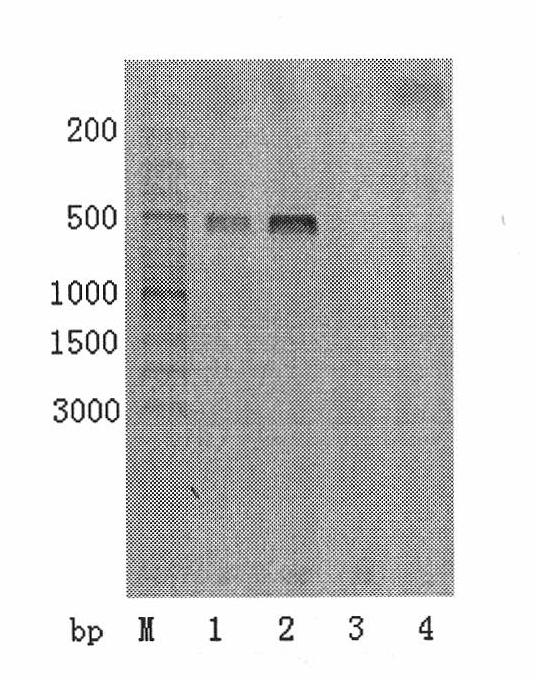
Three mutations of FPPS gene of Malus domestica Borkh. and identification method thereof
A technology of apples and genes, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of finding alleles and base mutation research reports, etc., and achieve the effect of saving management and screening costs and saving costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] Example 1: Specific primer molecular labeling method to detect mutations and identify apple varieties or fruit tiger skin disease traits of hybrid offspring
[0048] Step 1, test materials: leaves or flowers of four apple varieties, Guoguang, Green Banana, Golden Delicious and Royal Gala, among which Royal Gala is a hybrid offspring of Jinguan.
[0049] Step 2, genomic DNA extraction: Immediately after grinding the test material, add 0.6mL 2% CTAB extraction buffer [2% CTAB, 100mmol / L Tris-HCl (pH8.0), 20mmol / L EDTA, 1.4 mol / L NaCl, 2% PVP-40, 2% β-mercaptoethanol], extracted in a 65°C water bath for 30min, during which time the sample tube was gently inverted 3 times. Take out and add 0.6mL of chloroform:isoamyl alcohol (24:1), turn over gently, mix well, and centrifuge at 12000rpm for 10min. Transfer the supernatant to another new test tube, add an equal volume of isopropanol pre-cooled at -20°C, shake gently, centrifuge at 12000rpm for 10min, and remove the supern...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Example 2: Using the sequencing method to obtain the base information of the mutation site to identify the tiger skin disease traits of apple varieties or hybrid progeny
[0054] Step 1, test material: leaves or flowers of five apple varieties: Fuji, Guoguang, Green Banana, Red Star, and Golden Delicious, among which Fuji is a hybrid offspring of Guoguang.
[0055] Step 2, genomic DNA extraction: the same as the aforementioned molecular marker method.
[0056] Step 3, PCR amplification: perform PCR amplification with f3x as forward primer and f4x as reverse primer. The PCR reaction solution (20 μL) contained 0.5 μL (25 ng) of genomic DNA and 19.5 μL of reaction mixture, and one part of the mixture consisted of 0.4 μL of dNTPs (10 mmol / L), 2 μL of 10x Taq buffer, 0.5 μL of forward primer (10 μmol / L), 0.5 μL of reverse primer (10 μmol / L), 0.25 μL (5 U) of Taq DNA polymerase and 15.85 μL of water. The PCR reaction was performed for 35 cycles, each cycle including denat...
Embodiment 3
[0061] Example 3: Using CAPS molecular markers to detect mutations and identify tiger skin disease traits in apple varieties
[0062] Step 1, test materials: leaves or flowers of six common apple varieties: Golden Delicious, Royal Gala, Fuji, Guoguang, Red Star, and Green Banana.
[0063] Step 2, genomic DNA extraction: the same as the aforementioned molecular marker method.
[0064] Step 3, PCR amplification: perform PCR amplification with f3x as forward primer and f4x as reverse primer. The PCR reaction solution (20 μL) contained 0.5 μL (25 ng) of genomic DNA and 19.5 μL of reaction mixture, and one part of the mixture consisted of 0.4 μL of dNTPs (10 mmol / L), 2 μL of 10x Taq buffer, 0.5 μL of forward primer (10 μmol / L), 0.5 μL of reverse primer (10 μmol / L), 0.25 μL (5 U) of Taq DNA polymerase and 15.85 μL of water. The PCR reaction was performed for 35 cycles, each cycle including denaturation at 94°C for 30 s, annealing at 56°C for 1 min and primer extension at 72°C fo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com