Preparation method of Marbofloxacin
A technology for marbofloxacin and compounds, applied in the field of preparing marbofloxacin, can solve the problems of unfavorable commercial production, long reaction time and high production cost, achieve good social and economic benefits, improve product purity and yield, and reduce The effect of production costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Embodiment 1: Preparation of the compound shown in the intermediate formula (IV) of marbofloxacin
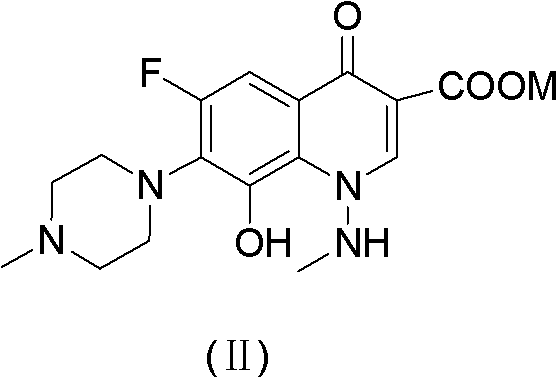
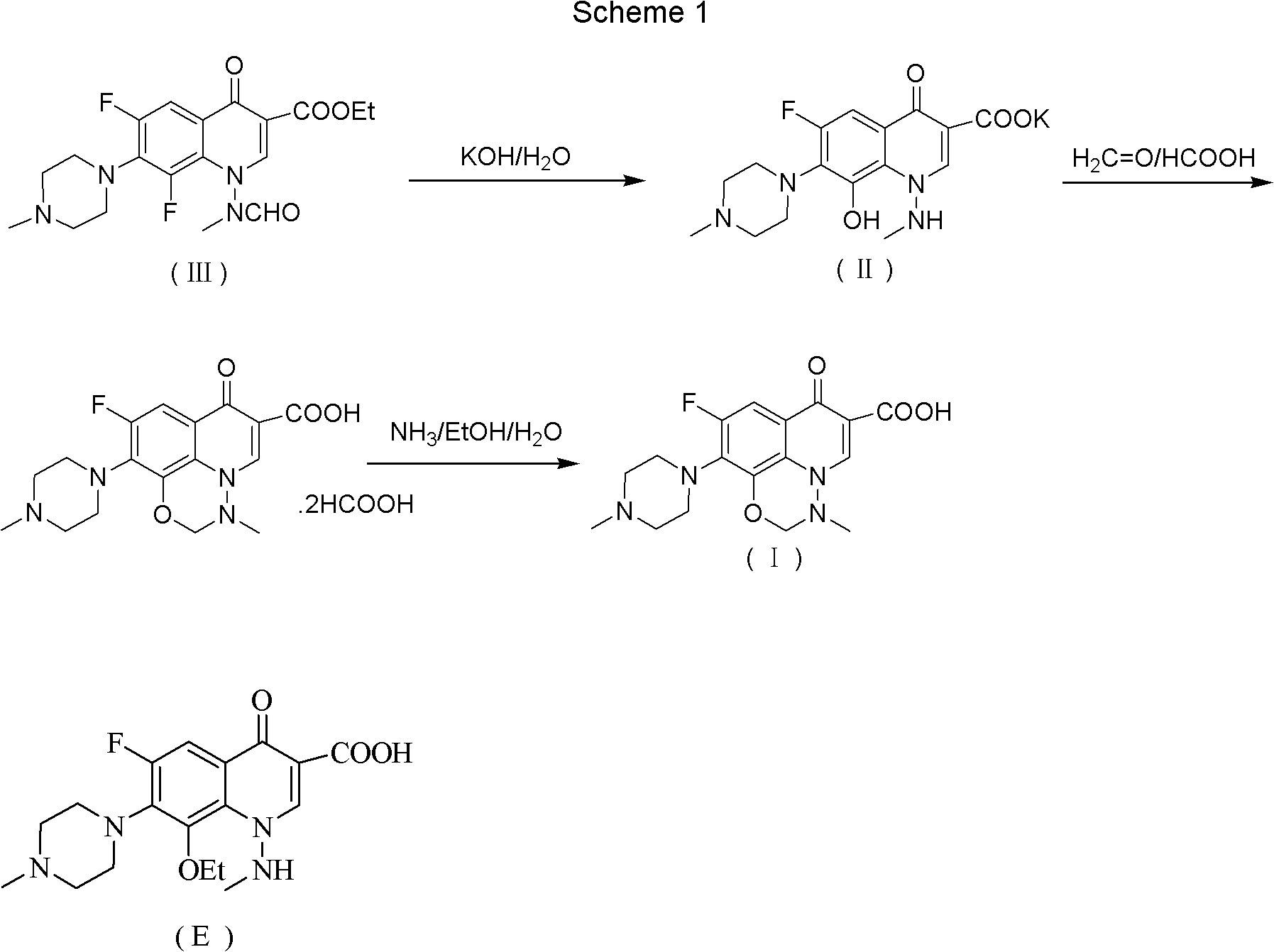
[0032] Add 200 g of toluene, 21.5 g of N-methylpiperazine, and 17 g of triethylamine to the flask successively, and then drop into 50 g of 6,7,8-trifluoro-1,4-dihydro-1-(N-methyl Formamido)-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid ethyl ester, heat up to reflux, react for 12 hours, then cool down to room temperature (25°C), add 250g of purified water and 23.5g of potassium hydroxide, and then heat up to React at 90°C for 3 hours, cool down to 25°C, separate the aqueous phase, adjust the pH value to 7.0 with 6 mol equivalent hydrochloric acid, then extract with 250mL of dichloromethane, dry the organic phase with anhydrous sodium sulfate, filter, and concentrate under reduced pressure to obtain 6 , 8-difluoro-1,4-dihydro-1-(N-methylamino)-7-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid 32.1 g.
[0033] (Molar yield: 74.41%, HPLC: 99.79%)
Embodiment 2
[0034] Embodiment 2: Preparation of the compound shown in the intermediate formula (IV) of marbofloxacin
[0035] Add 350 g of toluene, 30 g of N-methylpiperazine, and 30 g of triethylamine in sequence in the flask, and then drop in 50 g of 6,7,8-trifluoro-1,4-dihydro-1-(N-methyl formylamino)-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid ethyl ester, warming up to reflux, reacting for 8 hours, then cooling down to room temperature (25°C), adding 350g of purified water and 40g of potassium hydroxide, then warming up to React at 60°C for 5 hours, cool down to 25°C, separate the water phase, and adjust the pH value to 7.0 with 6 mol equivalent hydrochloric acid. It was then extracted with dichloromethane, the organic phase was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, filtered, and concentrated under reduced pressure to give 6,8-difluoro-1,4-dihydro-1-(N-methylamino)-7-(4 -Methyl-1-piperazinyl)-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid 32.1 g.
[0036] (Molar yield: 77.65%, HPLC: 99.85%)
Embodiment 3
[0037] Embodiment 3: the preparation of marbofloxacin
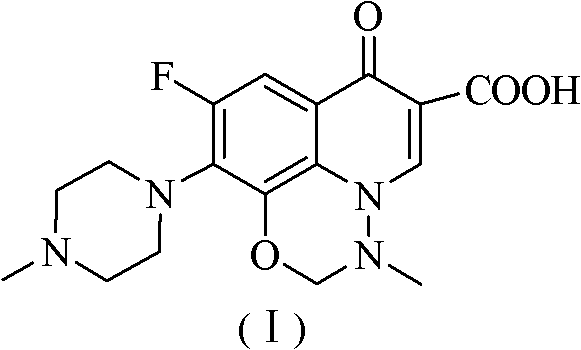
[0038] The 6,8-difluoro-1,4-dihydro-1-(N-methylamino)-7-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-4-oxo Put 25g of substituted-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid into a 500mL stainless steel kettle, add 60mL of purified water and 28.6g of potassium hydroxide, the reaction temperature is 125°C, the internal pressure is 0.1Mpa, react for 12 hours; cool down to 50°C, add dropwise 45mL of 94% Formic acid and 10.8mL 37% formaldehyde, after dropping, heat up to 75°C and react for 6 hours, then cool down to 0°C, filter, wash with purified water, put the filter cake into a 500mL flask and add 150mL purified water, dissolve, and use the mass concentration Adjust the pH value to 8.5 with 24% ammonia water, extract with dichloromethane, dry the organic phase with anhydrous sodium sulfate, filter, and distill the filtrate under reduced pressure to obtain 17.97g of crude marbofloxacin, crystallize with 720mL of 50% ethanol solution 16.75 g of marbofloxacin w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com