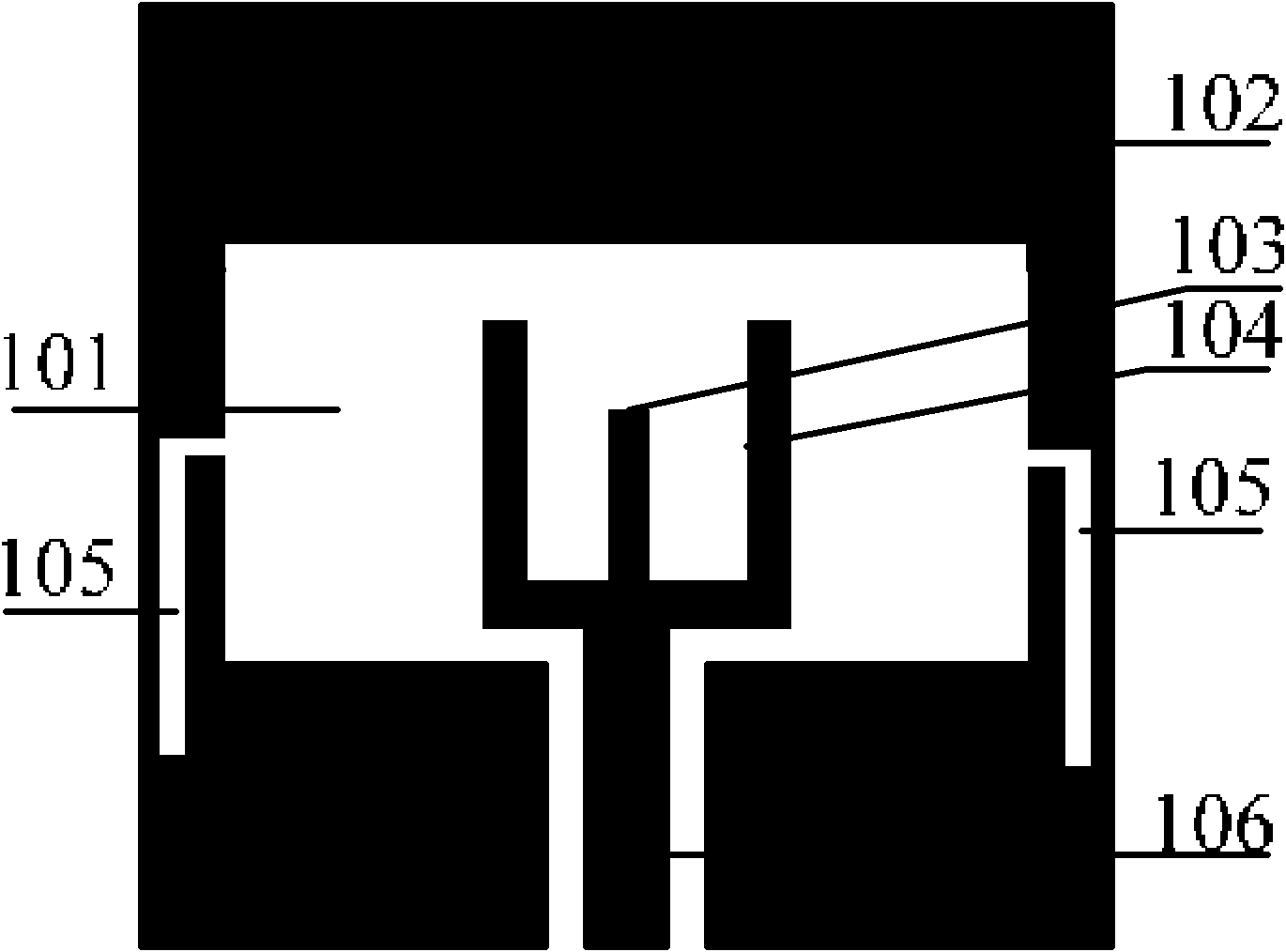Ultra-wideband antenna
A technology of ultra-wideband antenna and microstrip line, which is applied in the direction of antenna, antenna grounding device, radiation element structure, etc. It can solve the problems of electromagnetic wave leakage, limited antenna bandwidth, and reduce system performance, so as to suppress unnecessary frequency bands and achieve good Impedance bandwidth and the effect of reducing the size of the antenna
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
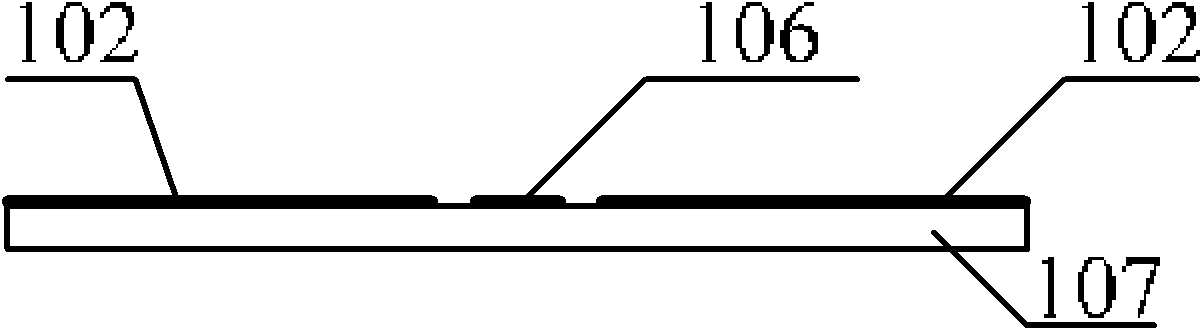
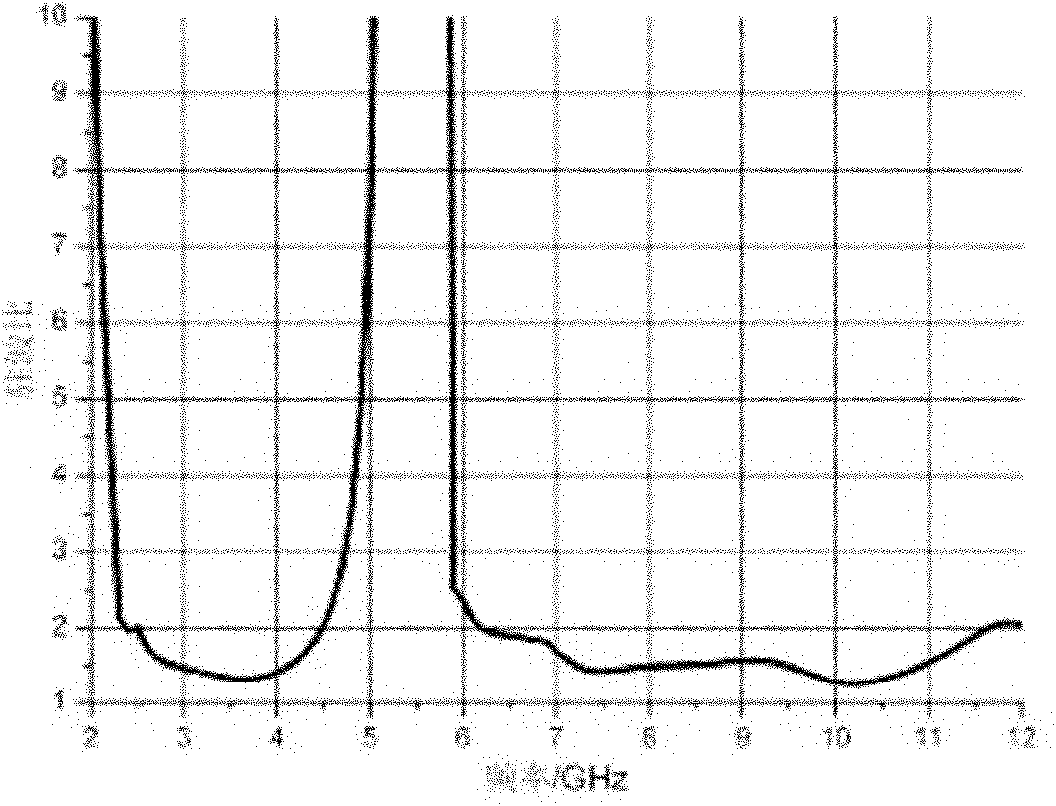
[0040] An example of the invention is figure 1 with figure 2 Shown. It is composed of a dielectric substrate 107, a radiation unit 104, a coplanar waveguide feeding signal strip line 106, a tuned microstrip line 103, a wide slot 101, two inverted L-shaped slots 105 and a coplanar waveguide ground plane 102. The lower end of the coplanar waveguide feeding signal strip line 106 of the antenna is connected to the SMA inner conductor. The outer conductor of the SMA is connected to the coplanar waveguide ground plane 102. according to figure 1 with figure 2 The structure shown can meet its ultra-wideband operating characteristics and notch characteristics as long as the appropriate size is selected.
[0041] Parameter setting:
[0042] 1. Tuning microstrip line
[0043] The notch characteristics of the antenna are mainly realized by inserting an open-circuit tuning microstrip line between the fork-shaped radiating elements. The tuning microstrip line is equivalent to a band rejection...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Such as Figure 7 As shown, another embodiment of the present invention is that the antenna does not have two inverted L-shaped slots, and the antenna radiating unit 204, the coplanar waveguide feeding signal strip line 206, the tuning microstrip line 203, and the wide slot 201 are composed. The entire antenna is printed on a dielectric substrate with a dielectric constant of 2.65. The lower end of the coplanar waveguide feeding signal strip line 206 of the antenna is connected to the SMA inner conductor. The outer conductor of the SMA is connected to the coplanar waveguide ground plane 202. according to Figure 7 The structure shown can meet its ultra-wideband operating characteristics and notch characteristics as long as the appropriate size is selected. The notch characteristics of the antenna are still realized by the tuning microstrip line. By adjusting the length and width of the tuning microstrip line, the center frequency of the notch and the bandwidth of the no...
Embodiment 3
[0055] Such as Picture 9 As shown, another embodiment of the present invention is that the radiating unit is directly composed of fork-shaped patches, without two inverted L-shaped grooves and tuning microstrip lines. The antenna radiation unit 304, a coplanar waveguide feeding signal strip line 306, and a wide slot 301 are composed. The entire antenna is printed on a dielectric substrate with a dielectric constant of 2.65. The lower end of the coplanar waveguide feeding signal strip line 306 of the antenna is connected to the SMA inner conductor. The outer conductor of the SMA is connected to the ground plane 302 of the coplanar waveguide. according to Picture 9 The structure shown can meet its ultra-wideband operating characteristics as long as the appropriate size is selected.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com