Marine aerobic denitrifying halomonas strain HGMN422 and application thereof
A technology of Halomonas and nitrifying salt, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve problems such as high cost and achieve the effect of high-efficiency denitrification capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0017] The screening method of embodiment 1 marine aerobic denitrification bacterial strain:
[0018] 1. Material preparation
[0019] 1. Bacterial source and experimental wastewater
[0020] (1) Bacterial source: sediments from the seawater fish cage farm area of Dapengao, Shenzhen, which has a breeding history of more than 20 years.
[0021] (2) Experimental wastewater A (high concentration of nitrate nitrogen (NO 3 - -N) Seawater): 2.6g sodium nitrate, 36g glucose, 0.5g yeast extract, 1000mL aged seawater, pH7.6-8.2, sterilized at 121°C for 20min.
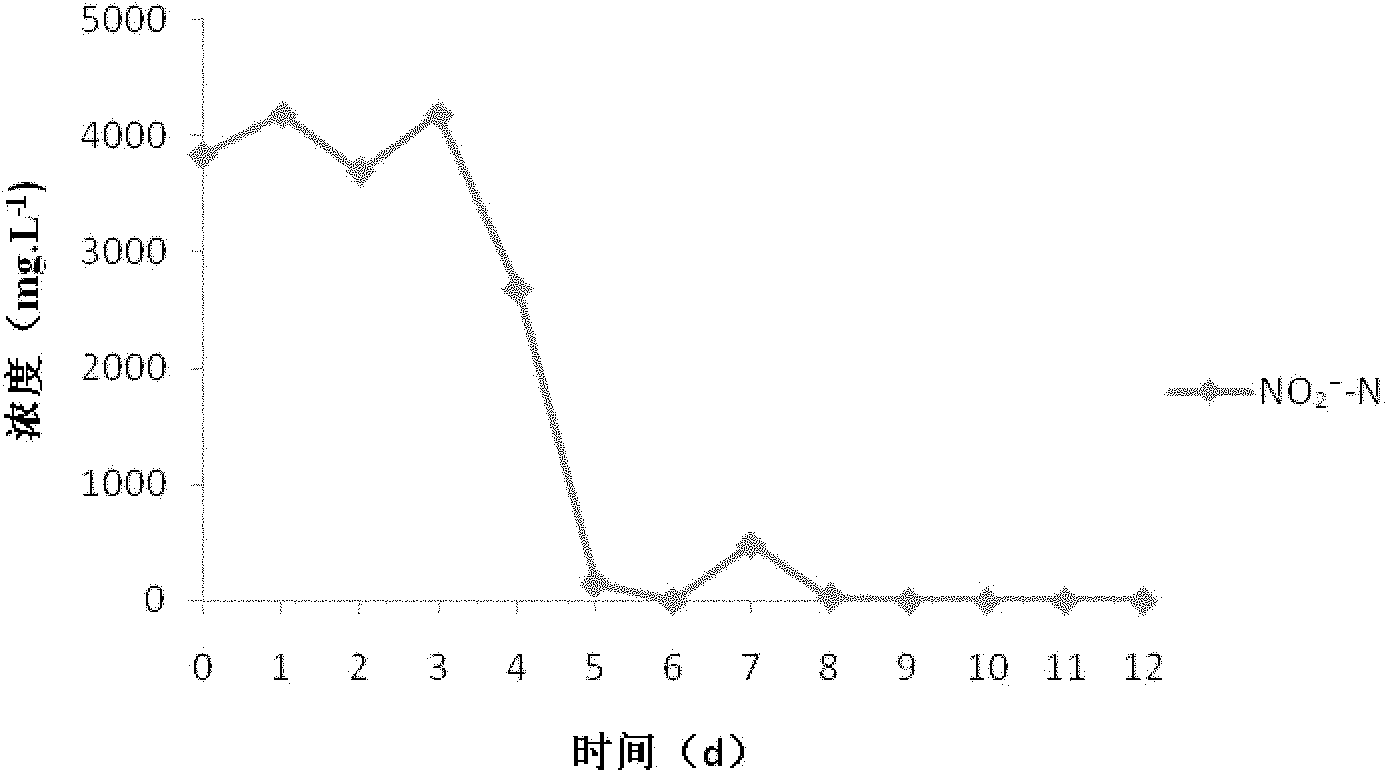
[0022] (3) Experimental wastewater B (high concentration of nitrite nitrogen (NO 2 - -N) Seawater): sodium nitrite 2.1g, glucose 36g, yeast extract 0.5g, aged seawater 1000mL, pH7.6-8.2, sterilized at 121°C for 20min.
[0023] 2. Medium
[0024] (1) Selection medium: glucose 24g, sodium citrate 14.7g, potassium nitrate 6.7g, ammonium chloride 4.7g, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 1.8g, aged sea water 1000mL, sterilized a...
Embodiment 2
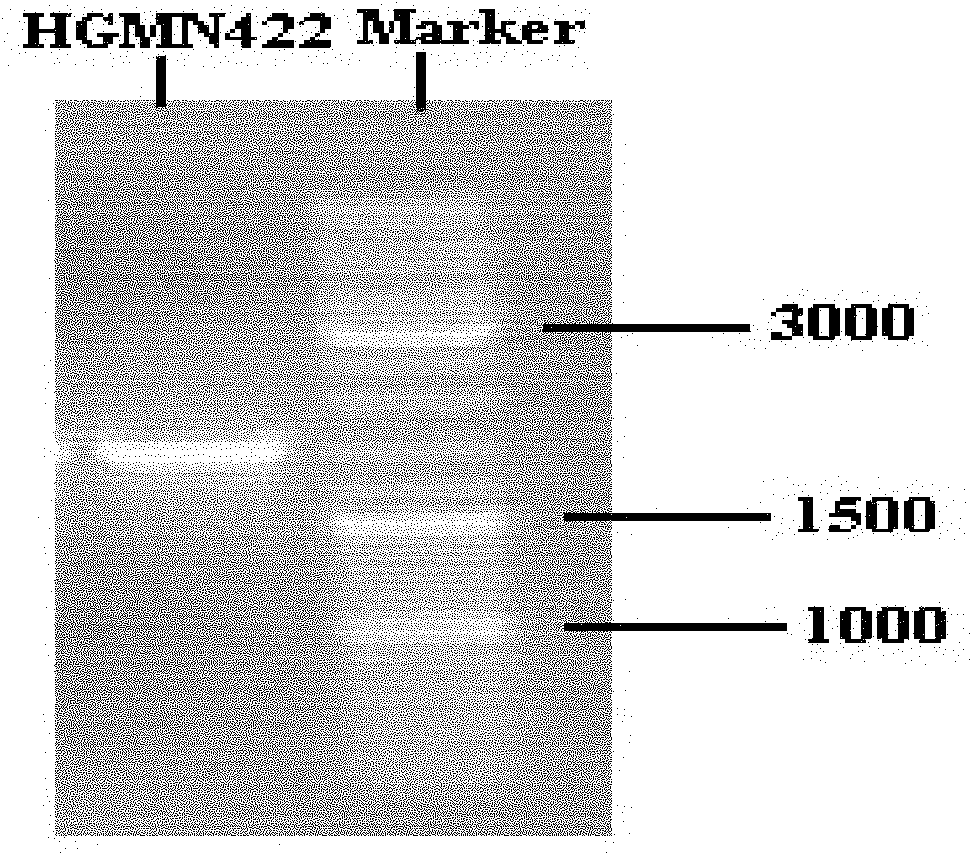
[0051] Example 2 Identification of marine aerobic denitrification strain HGMN422
[0052] 1. Identification of marine aerobic denitrification strain HGMN422
[0053] The marine aerobic denitrifying strain HGMN422 was identified by physiology and biochemistry and 16S rDNA molecules, and the species of the strain was determined from the molecular level, combined with the analysis of bacterial morphological characteristics and physiological and biochemical characteristics.
[0054] 16S rDNA sequence analysis mainly follows the following steps:
[0055] ① Extraction of bacterial nuclear DNA:
[0056] 1) Pick a single colony with an autoclaved toothpick and inoculate it in the expansion medium overnight, take 1.5ml of the bacterial solution into an Eppendorf tube, centrifuge at 8000rpm for 5min at room temperature, and remove the supernatant completely.
[0057] 2) Add 1.5ml of STE buffer solution to wash once, centrifuge to discard the supernatant, then add 0.6ml TE solution to ...
Embodiment 3
[0106] Example 3 Colony Morphological, Physiological and Biochemical Characteristics of Marine Aerobic Denitrifying Bacteria Strain HGMN422
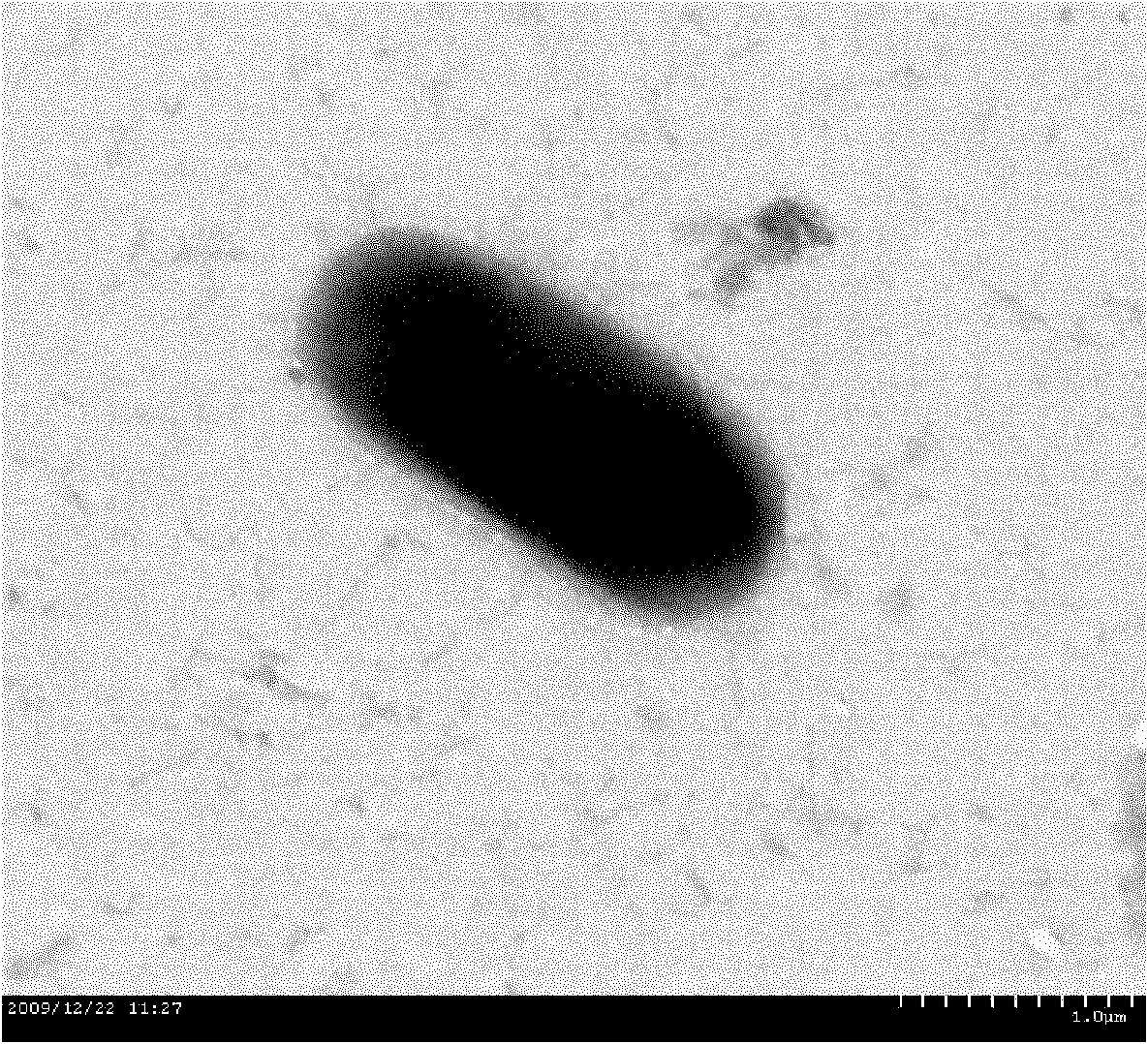
[0107] The colony morphology, physiological and biochemical characteristics of the marine aerobic denitrifying strain HGMN422 are shown in Table 1-1; the cell morphology is shown in figure 1 .
[0108] Table 1-1 Colony morphology and main physiological and biochemical characteristics of marine aerobic denitrifying strain HGMN422
[0109]
[0110] Note: "+": more than 90% of the strains are positive, "-": more than 90% of the strains are negative.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com