Laser cladding technological method and alloy material for laser cladding
A technology of laser cladding and alloy materials, which is applied in the field of laser cladding technology and its alloy materials, journals, end faces of high-temperature and high-pressure valves, and can solve the problems of unsatisfactory mechanical properties, high process control requirements, and laser power. High density and other problems, to achieve good anti-cavitation performance, good process adaptability, simple and easy to operate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Embodiment 1: An alloy material for laser cladding, the chemical composition (weight percentage) of alloy elements is C: 0.85%; Cr: 35%; Fe: 5%; Si: 0.5%; W: 5.0%; Mo: 1.2%; Ni: 7%; V: 1.5%; Ti: 1.0%; B: 0.5%; Nb: 0.3%; Re: 0.6%; Co: balance.
[0023] The preparation method is as follows:
[0024] 1. Calculate the addition amount of various master alloys such as ferrochrome, ferrovanadium, ferrosilicon, and ferroboron (considering the different burning loss rates of each element when calculating).
[0025] 2. After weighing, bake in an oven at 200°C.
[0026] 3. Add high melting point and magnetic elements first, and then add elements that are easy to burn.
[0027] 4. After melting, remove slag, refine and add rare earth elements.
[0028] 5. Open the water and gas circuit, control the pressure and liquid level.
[0029] 6. Place the preheated middle leakage bag on the nozzle, and pour the alloy liquid in the furnace into the middle leakage bag.
[0030] 7. After ...
Embodiment 2
[0033] An alloy material for laser cladding, the chemical composition (weight percentage) of alloy elements is C: 0.95%, Cr: 42%, Fe: 3%, Si: 1.2%, W: 5.5%, Mo: 1.5% , Ni: 6%, V: 1.8%, Ti: 2.0%, B: 1.2%, Nb: 0.5%, Re: 1.0%, Co: balance.
[0034] The preparation method is the same as in Example 1.
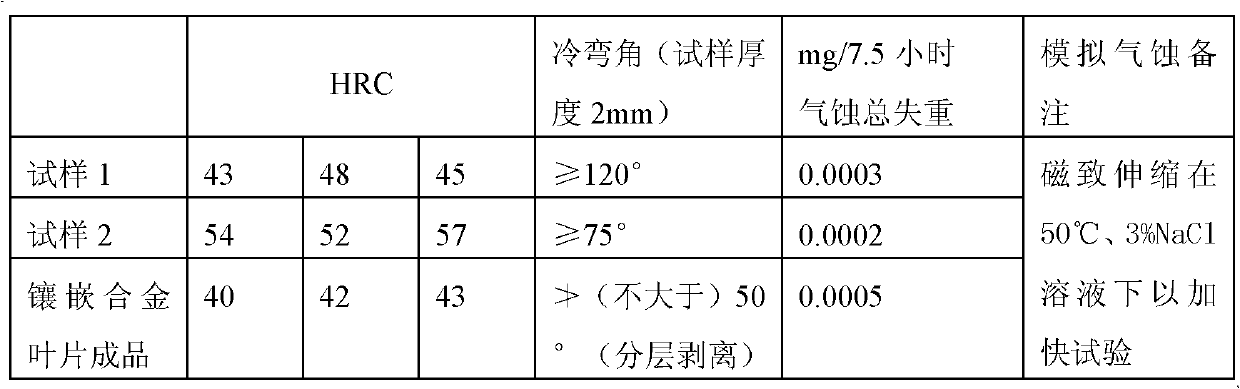
[0035] The hardness of the cladding layer prepared by laser cladding with this ratio of alloy powder is HRC52-57. In addition to being applied to steam turbine blades, it can also be applied to the repair of shaft journals and valve end faces, with the same performance and effect.
Embodiment 3
[0037] A laser cladding process method for substituting steam turbine blade inlaid alloy sheets, comprising the following steps:
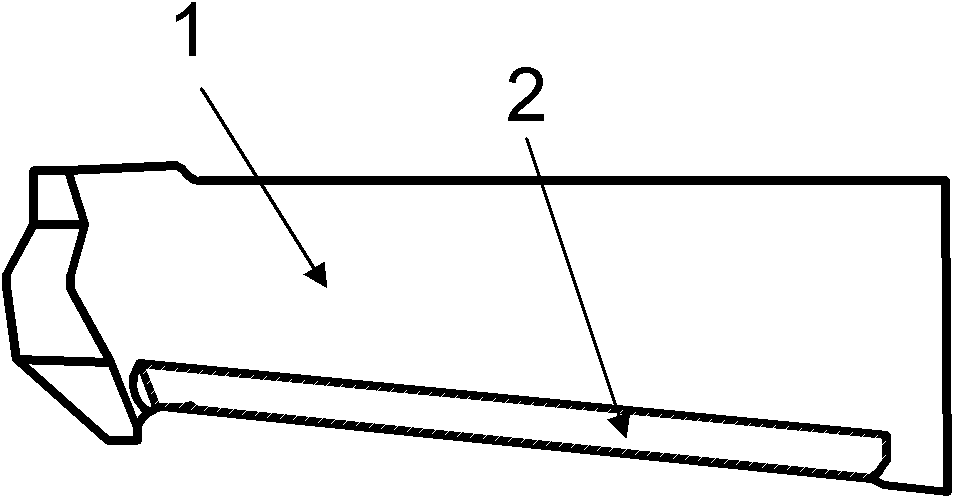
[0038] 1. If figure 1 As shown, the back arc of blade 1 (including the original R side) is milled off by 1 mm to form milling groove 2; the back arc side is milled off to 1 / 5 of the thickness, but the total depth does not exceed 1 mm; the forming knife can be used to complete it in one step by CNC milling machine .
[0039] 2. According to the size of the milled part, the robot motion track is compiled, and the overlap rate of cladding programming is 55%.
[0040] 3. Adopt optical fiber or semiconductor laser, select the powder of embodiment 1 and embodiment 2, and its particle size is -140+325 mesh (particles are lower than 140 mesh, higher than 325 mesh, and the particle size is within this range), dispatch The powder amount is 14g / min, and the powder is fed by inert gas; the spot diameter is 5mm, the power is adjusted to 1800W, the laser scann...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com