Silicon-base ceramic core added with cristobalite
A technology of ceramic cores and additives, applied in the direction of cores, molds, and mold components, can solve the problem of failure to meet the requirements of directional casting of blades, high temperature creep resistance has not been reported, and deterioration of ceramic cores. Core performance and other issues, to achieve the effect of improving high temperature creep resistance, improving high temperature creep resistance, and improving high temperature deformation resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
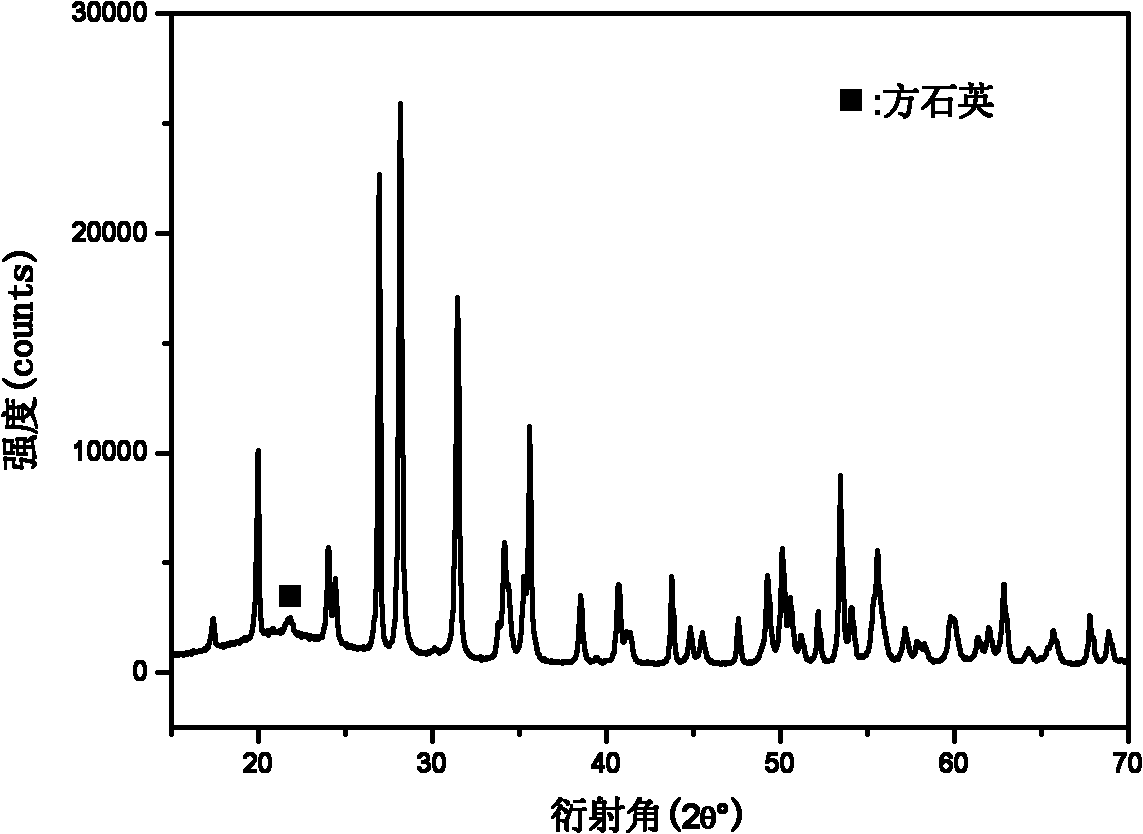
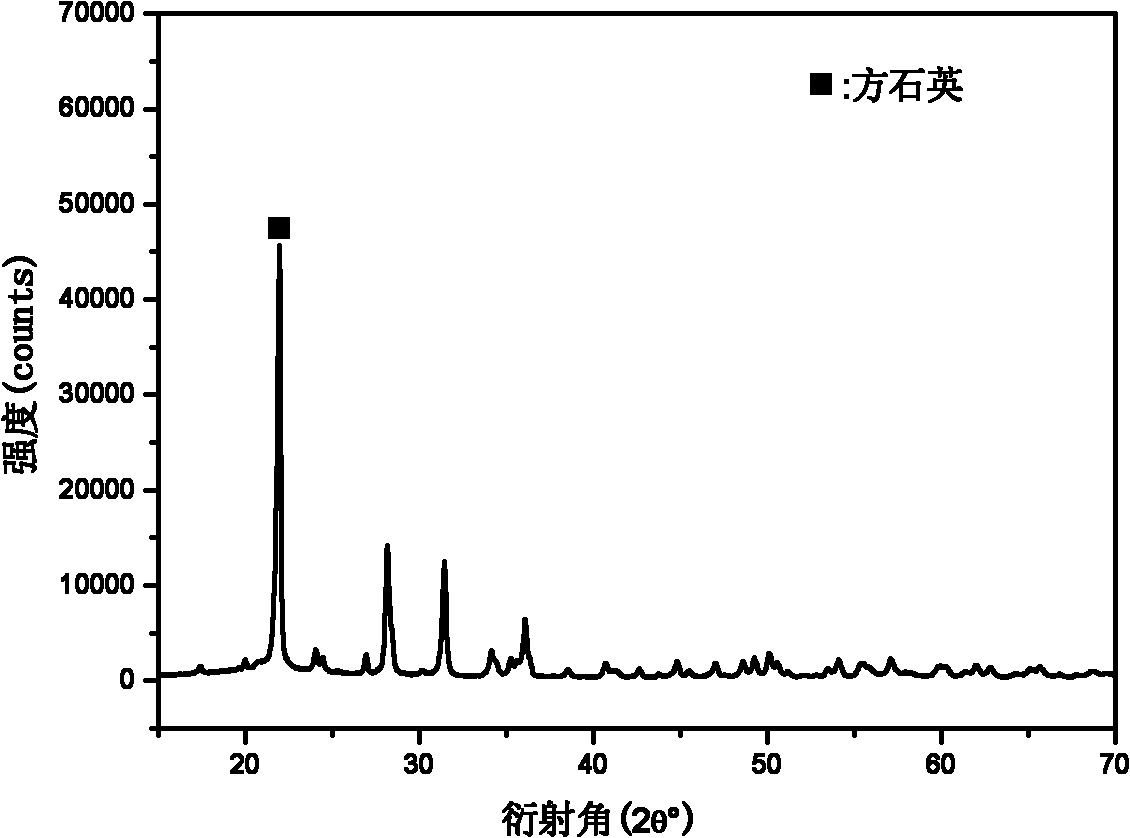
[0037] The ceramic core composition is 74% quartz glass, 10% cristobalite, and 16% zirconia. The purity of the quartz glass is greater than or equal to 99.59%, and the purity of zirconia is greater than or equal to 99.96%. The cristobalite is calcined from quartz glass and pressed into a standard sample. Sample. According to the process, the temperature is raised to 1250 ° C for 4 hours, and after roasting, it is strengthened with ethyl silicate aqueous solution and epoxy resin / polyamide. X-ray quantitative analysis shows that the amount of cristobalite in the ceramic core is 21%. Compared with the ceramic core without adding cristobalite, the crystallization rate is obviously increased, and the high temperature deformation resistance is improved. The performance index of the core is as follows: the bending strength at room temperature is 73MPa, the high temperature deflection (30min at 1550°C) is 16mm, and the shrinkage rate is 2.3%.
Embodiment 2
[0039] The ceramic core composition is 74% quartz glass, 10% cristobalite, and 16% zirconia. The purity of the quartz glass is greater than or equal to 99.59%, and the purity of zirconia is greater than or equal to 99.96%. The cristobalite is calcined from quartz glass and pressed into a standard sample. Sample. According to the process, the temperature is raised to 1300 ° C for 4 hours, and after roasting, it is strengthened with ethyl silicate aqueous solution and epoxy resin / polyamide. X-ray quantitative analysis shows that the amount of cristobalite in the ceramic core is 40%. Compared with the ceramic core in Example 1, the amount of cristobalite transformation increases, indicating that the increase in sintering temperature is beneficial to the crystallization of quartz glass. The ability of the core to resist high temperature deformation is greatly improved. The performance index of the core is as follows: the bending strength at room temperature is 72MPa, the high tem...
Embodiment 3
[0041] The ceramic core composition is 44% quartz glass, 40% cristobalite, and 16% zirconia. The purity of the quartz glass is greater than or equal to 99.59%, and the purity of zirconia is greater than or equal to 99.96%. The cristobalite is calcined from quartz glass and pressed into a standard sample. Sample. According to the process, the temperature is raised to 1250 ° C for 4 hours, and after roasting, it is strengthened with ethyl silicate aqueous solution and epoxy resin / polyamide. X-ray quantitative analysis shows that the amount of cristobalite in the ceramic core is 47%. Compared with the ceramic core without adding cristobalite, the crystallization rate is significantly increased, and the high temperature deformation resistance is significantly improved. The performance index of the core is as follows: the bending strength at room temperature is 60MPa, the high temperature deflection (30min at 1550°C) is 0.6mm, and the shrinkage rate is 1.14%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Granularity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Granularity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Granularity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com