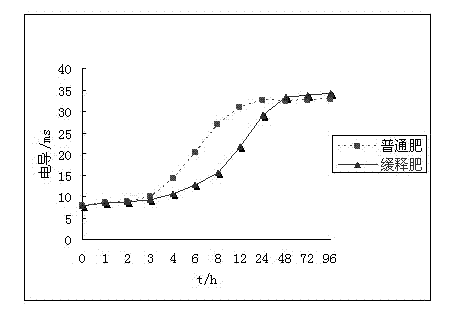
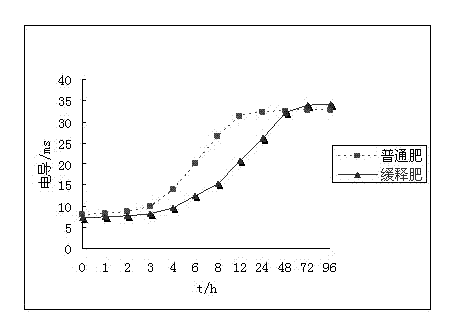
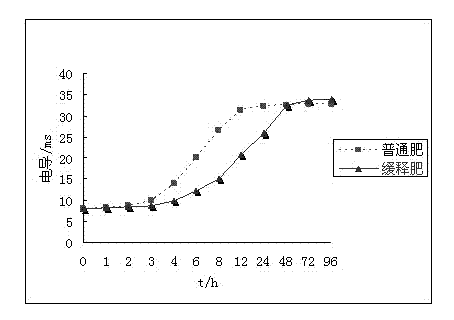
Polymer emulsion coated slow release fertilizer taking nanomaterial as carrier and preparation method thereof
A technology of polymer emulsion and nanomaterials, which is applied in the field of polymer emulsion-coated slow-release fertilizer and its preparation, can solve the problems of low fertilizer efficiency and no slow-release effect, and achieve the effect of improving the soil aggregate structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0077] Embodiment 1, a polymer emulsion coated slow-release fertilizer with nanomaterials as the carrier, which is composed of the following components in weight ratio: nanometer soil material 18, moderately fermented bacteria residue 12, moderately fermented manure 20, moderately fermented green manure 14. Coal washing slime 15, NPK fertilizer 9, oxidized starch 5, silicone modified acrylate emulsion 10, crosslinking agent 0.02.
[0078] The moderately fermented bacteria residue is composed of the following components by weight ratio before fermentation: waste bacteria residue 70, bacteria species 3, fly ash 0.5, organic nitrogen source 9, auxiliary materials 17.5.
[0079] The cross-linking agent is borax.
[0080] Described strain is ferment bacterium.
[0081] The auxiliary material is straw.
[0082] The method for preparing the above-mentioned slow-release fertilizer coated with a polymer emulsion using nanomaterials as a carrier comprises the following steps:
[0083...
Embodiment 2
[0091] The special treatment liquid is composed of components in the following weight ratio: sulfuric acid: calcium fluorophosphate 3Ca 3 (PO 4 )2CaF 2 : Phosphogypsum CaSO 4 2H 2 The weight ratio of O: water: straw powder: nitrogen fertilizer compound is 2.2: 0.9: 1.2: 2.7: 0.7: 0.4. Embodiment 2, a polymer emulsion coated slow-release fertilizer with nanomaterials as the carrier, which is composed of the following components in weight ratio: nano-soil material 16, moderately fermented bacteria residue 12, moderately fermented manure 22, moderately fermented green manure 14. Coal washing slime 15, NPK fertilizer 9, oxidized starch 5, silicone modified acrylate emulsion 10, crosslinking agent 0.02.
[0092]The moderately fermented bacteria dregs are composed of the following components in weight ratio before fermentation: 75% of waste dregs, 1 strain, 1.5% of fly ash, 5% of inorganic nitrogen sources, and 17.5% of auxiliary materials.
[0093] The crosslinking agent is zi...
Embodiment 3
[0105] The special treatment liquid is composed of components in the following weight ratio: sulfuric acid: calcium fluorophosphate 3Ca 3 (PO 4 )2CaF 2 : Phosphogypsum CaSO 4 2H 2 The weight ratio of O: water: straw powder: nitrogen fertilizer compound is 2.1: 0.6: 0.8: 1.7: 0.9: 2.2. Embodiment 3, a polymer emulsion coated slow-release fertilizer with nanomaterials as the carrier, which is composed of the following components in weight ratio: nano-soil material 16, moderately fermented bacteria residue 22, moderately fermented manure 22, moderately fermented green manure 14. Coal washing slime 16, NPK fertilizer 8, oxidized starch 5, silicone modified acrylate emulsion 10, crosslinking agent 0.02.
[0106] The moderately fermented bacteria residue is composed of the following components by weight ratio before fermentation: 80 waste bacteria residues, 3 strains, 2 fly ash, 2 organic nitrogen sources, and 13 auxiliary materials.
[0107] The crosslinking agent is a combine...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com