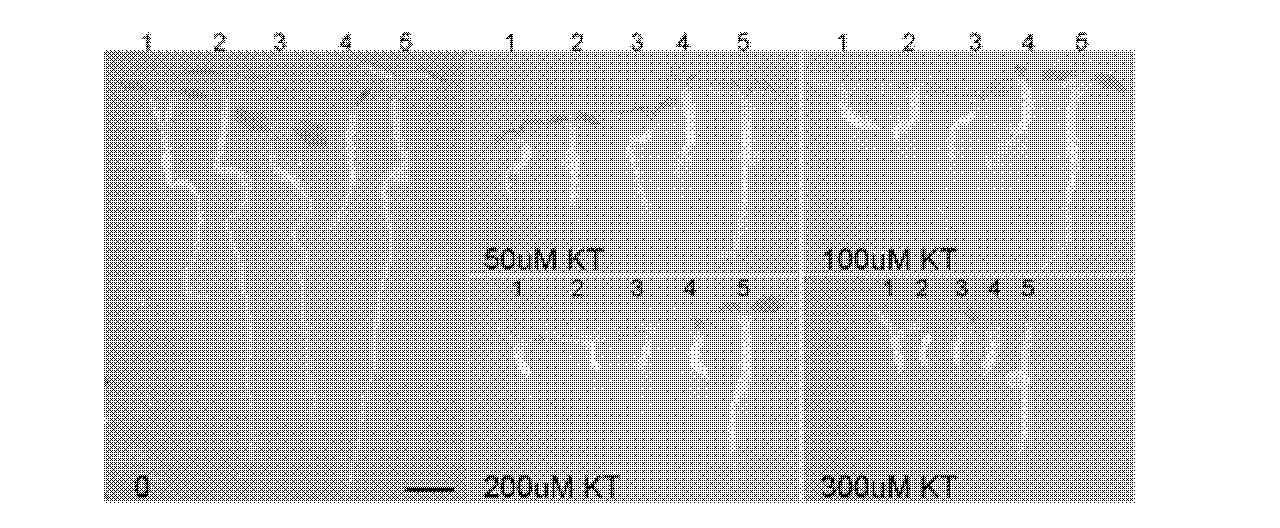Applications of adenine phosphoribosyltransferase (APRT) family genes in phytocytomine toxicity aspect
A technology of cytokinin and plant cells, which is applied in the field of application of APRT family genes in plant cytokinin toxicity, can solve the problems of sensitive and invisible cytokinin toxicity, and achieve the effect of reducing toxic and side effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Example 1 Application of the Arabidopsis gene APT1 and its homologous genes APT2, APT3, APT4 and / or APT5 in the regulation of plant cytokinin toxicity and cytokinin metabolism
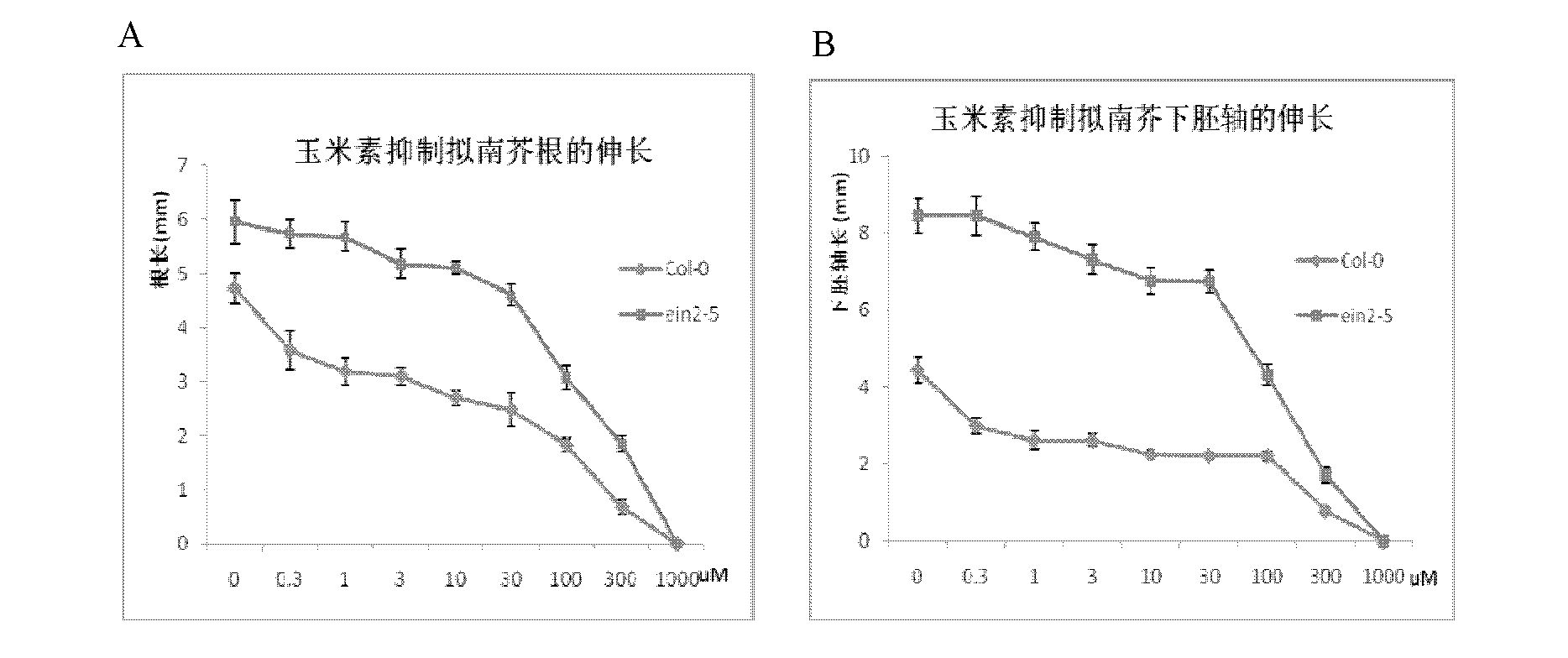
[0043] First, a new screening system for cytokinin mutants was established. Because the previous mutant screening is often screened under low-concentration cytokinin conditions, the mutants of the ethylene synthesis pathway and the ethylene signal transduction pathway are often obtained. For this reason, the present invention has carried out a concentration gradient experiment to find a suitable cytokinin Treatment concentration. Hypocotyl and root elongation of dark-grown wild-type seedlings were strongly inhibited by treatment with high concentrations of zeatin (greater than 100 μM), as did ethylene-insensitive mutants, suggesting a role for cytokinins at this concentration Mainly through a pathway independent of ethylene signal transduction ( figure 1 ). Both the high-concentration cytokin...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Example 2 Application of Arabidopsis gene APT1, its homologous genes APT2, APT3, APT4 and / or APT5 in cultivating adenine and / or cytokinin-regulated transgenic plants
[0057] The full length of APT1, APT2, APT3, APT4 and / or APT5 genes was amplified by PCR method, and constructed on the binary expression vector pDr by molecular cloning method, and then transformed into Arabidopsis thaliana by Agrobacterium infection method to obtain excess Transgenic plants expressing APT1, APT2, APT3, APT4 and / or APT5 genes ( Figure 12 ).
[0058] The results showed that the transgenic plants had different cytokinin resistance. The transgenic plants grown under normal conditions were not significantly different from the wild type, but under the treatment of cytokinin, the phenotypes of the five genes were more differentiated, supporting the functional differentiation of the five genes. APT1 is the most sensitive to cytokinin toxicity, APT3 and APT4 are obviously hypersensitive but we...
Embodiment 3
[0059] Example 3 Knockout of APRT Family Genes to Enhance Plant Cytokinin Resistance or Reduce Toxic Side Effects
[0060] The ethylene-insensitive Arabidopsis mutant ein2-9 tt4 was used as the background for EMS mutagenesis and screening, and it was insensitive to high concentration (300 μM) kinetin. At this concentration, the root development and cotyledon greening process of the wild type were strongly inhibited. A mutant C9 was found to grow normally under this treatment condition ( image 3 ). The corresponding mutation site was found by map-based cloning, and the mutation site of C9 was found to be located in an adenine ribose phosphotransferase APT1 (At1g27450).
[0061] The other three allelic mutants of apt1 (apt1-1, apt1-2, apt1-3) were found to be insensitive to high concentrations of cytokinin, cotyledons could turn green, and roots could elongate ( Figure 4 ). like Image 6 As shown, the dark-grown apt1 mutant was no longer sensitive to zeatin above 30 μM, a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com