Modified Keratinocyte growth factor gene and its expression in yeast
A keratinocyte and growth factor technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of low expression, protein change, difficulty in renaturation, etc., and achieve the effects of short cycle, low cost and easy technology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0063] 1. Gene synthesis
[0064] The KGF gene sequence is from Genebank, accession number NM_002009, and its sequence is modified as follows: (1) delete 69 nucleotides at the 5' end of the gene; (2) follow the codon preference of Pichia pastoris without changing the amino acid sequence (3) Whole gene synthesis of keratinocyte growth factor sequence.
[0065] 2. Construction of recombinant plasmids
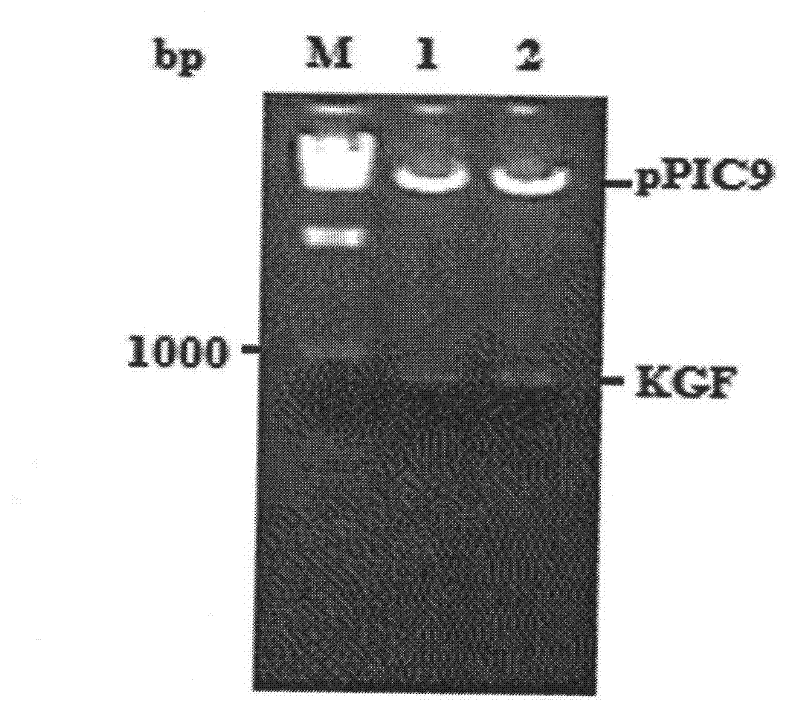
[0066] The pUC57-KGF plasmid was double cut with restriction endonucleases XhoI and EcoRI, the KGF target fragment was recovered by gel, and then ligated with the same cut pPIC9 plasmid. The ligation product was transformed into Escherichia coli JM109 competent cells, screened on LB plates (containing Amp), randomly selected strains to extract plasmids, and verified by XhoI / EcoRI double enzyme digestion (results are shown in the attached figure 1 ), after the verification is correct, further sequencing verification is carried out.
[0067] 3. Transformation and plate screening ...
Embodiment 2
[0076] 1. Gene synthesis
[0077] With embodiment 1.
[0078] 2. Construction of recombinant plasmids
[0079] The pUC57-KGF plasmid was double cut with restriction endonucleases XhoI and EcoRI, the KGF target fragment was recovered by gel, and then ligated with the pGAPZαA plasmid cut with the same enzyme to obtain the recombinant plasmid pGAPZαA-KGF. The recombinant plasmid pGAPZαA-KGF was transformed into Escherichia coli JM109 competent cells, and then plate screening, double enzyme digestion verification and sequencing verification were performed, and the next experiment was carried out after correctness.
[0080] 3. Transformation and plate screening of Pichia pastoris strain GS115
[0081] Recombinant plasmid pGAPZαA-KGF and blank plasmid pGAPZαA were digested with restriction endonuclease SacI, and 5 μg-20 μg of the plasmid was electroporated to transform Pichia pastoris GS115 competent cells. The specific method was the same as in Example 1.
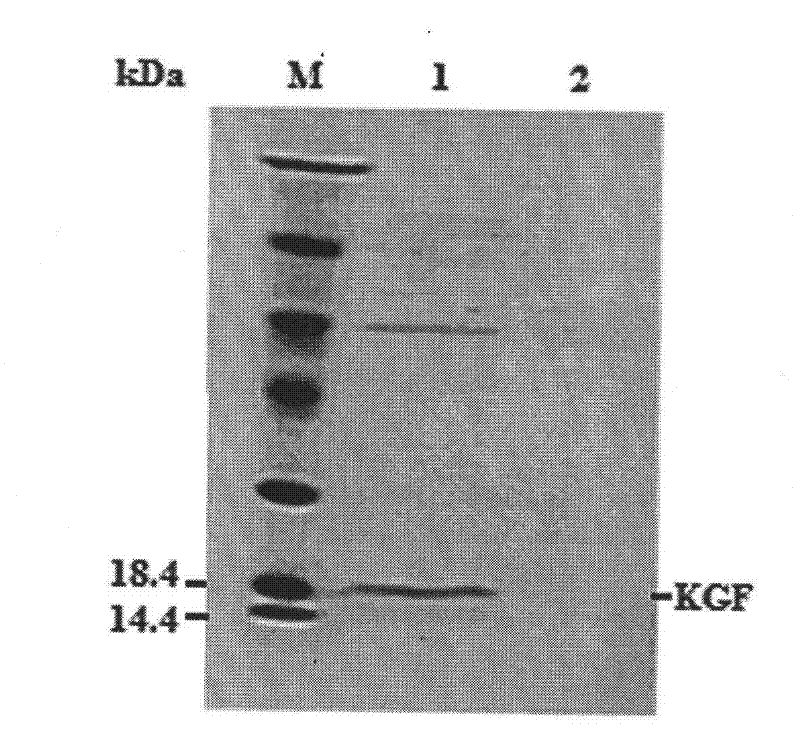
[0082] 4. Shake flask...
Embodiment 3
[0085] 1. Gene synthesis
[0086] With embodiment 1.
[0087] 2. Construction of recombinant plasmids
[0088] The pUC57-KGF plasmid was double cut with restriction endonucleases XhoI and EcoRI, the KGF target fragment was recovered by gel, and then ligated with the pPICZαA plasmid cut with the same enzyme to obtain the recombinant plasmid pPICZαA-KGF. The recombinant plasmid pPICZαA-KGF was transformed into Escherichia coli JM109 competent cells, then screened on LB plates containing Zeocin antibiotics, double enzyme digestion verification and sequencing verification, and the next experiment was carried out after correctness.
[0089] 3. Transformation and plate screening of Pichia pastoris strain GS115
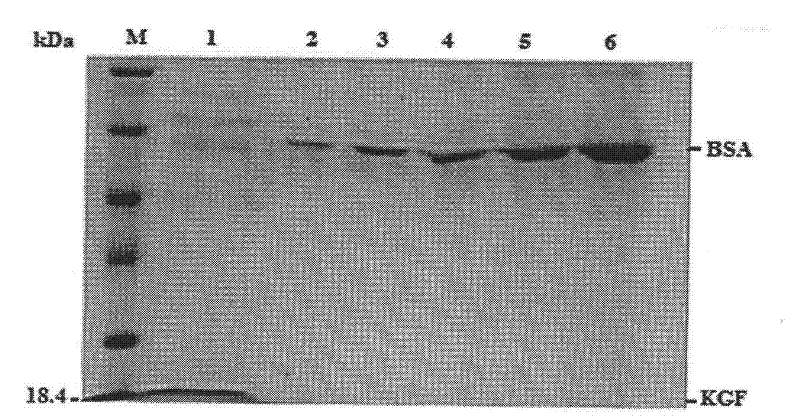
[0090] Recombinant plasmid pPICZαA-KGF and blank plasmid pPICZαA were digested with restriction endonuclease SacI, and 5 μg-20 μg of the plasmid was electroporated to transform Pichia pastoris GS115 competent cells. The specific method was the same as in Example 1, and the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com