A method for producing citric acid by fermentation
A citric acid, inoculation and fermentation technology, applied in the field of fermentation production of citric acid and citric acid production, can solve the problems of low utilization rate of saccharification enzyme, inactivation of saccharification enzyme, etc. low conversion rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] (1) Blending: 20 kg of corn flour is used as raw material, and 65 kg of water is added for blending, and the blending is controlled to a total sugar concentration of 160 g / L;
[0032] (2) Liquefaction: Add 10 ml of liquefying enzyme to the prepared slurry, liquefy at 98°C for 120 minutes, and then cool down to 70°C;
[0033] (3) Heating and sterilization: the liquefied slurry is heated and sterilized in the same way as the current citric acid production process.
[0034] (4) Inoculation fermentation: Inoculate the Aspergillus niger species during the normal temperature control process at 36°C, and ferment to obtain the fermentation liquid;
[0035] (5) Add glucoamylase: add 2 / 100,000 glucoamylase (calculated by the volume of the fermentation broth) after inoculation of the fermentation broth;
[0036] (6) Post-processing: Same as the current citric acid production process, citric acid is produced.
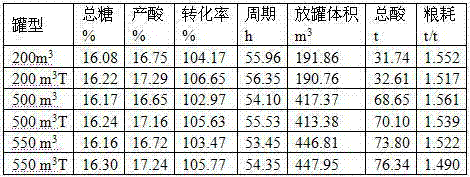
[0037] The results are shown in the table below:
[0038] Comparison...
Embodiment 2
[0043] (1) Blending: 20 kg of corn flour is used as raw material, and 65 kg of water is added for blending, and the blending is controlled to a total sugar concentration of 160 g / L;
[0044] (2) Liquefaction: Add 10 ml of liquefaction enzyme to the prepared slurry, liquefy at 95°C for 130 minutes, and then cool down to 70°C;
[0045] (3) Heating and sterilization: the liquefied slurry is heated and sterilized, which is the same as the current citric acid production process.
[0046] (4) Inoculation fermentation: Inoculate the Aspergillus niger species during the normal temperature control process at 37°C, and ferment to obtain the fermentation liquid;
[0047] (5) Add glucoamylase: add 1 / 100,000 glucoamylase (calculated by the volume of fermentation broth) after inoculation of the fermentation broth;
[0048] (6) Post-processing: Same as the current citric acid production process, citric acid is produced.
[0049] Results: The conversion rate of fermentation increased by 1.8...
Embodiment 3
[0051](1) Blending: 20 kg of corn flour is used as raw material, and 65 kg of water is added for blending, and the blending is controlled to a total sugar concentration of 160 g / L;
[0052] (2) Liquefaction: Add 10 ml of liquefying enzyme to the prepared slurry, liquefy at 99°C for 115 minutes, and then cool down to 70°C;
[0053] (3) Heating and sterilization: the liquefied slurry is heated and sterilized, which is the same as the current citric acid production process.
[0054] (4) Inoculation fermentation: Inoculate the Aspergillus niger species during the normal temperature control process at 38°C, and ferment to obtain the fermentation liquid;
[0055] (5) Add glucoamylase: add 0.5×10 -5 of glucoamylase (calculated by the volume of fermentation broth);
[0056] (6) Post-processing: Same as the current citric acid production process, citric acid is produced.
[0057] Results: The conversion rate of fermentation increased by 1.4%, and the grain consumption of fermentatio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com