Method for detection of trace impurities in polished subsurface damage layer of optical glass
A technology of sub-surface damage and optical glass, applied in the direction of color/spectral characteristic measurement, etc., can solve the problems of unrealistic detection, high detection cost, limited detection area, etc., to achieve flexible and controllable detection area, fast detection process and low detection cost low effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
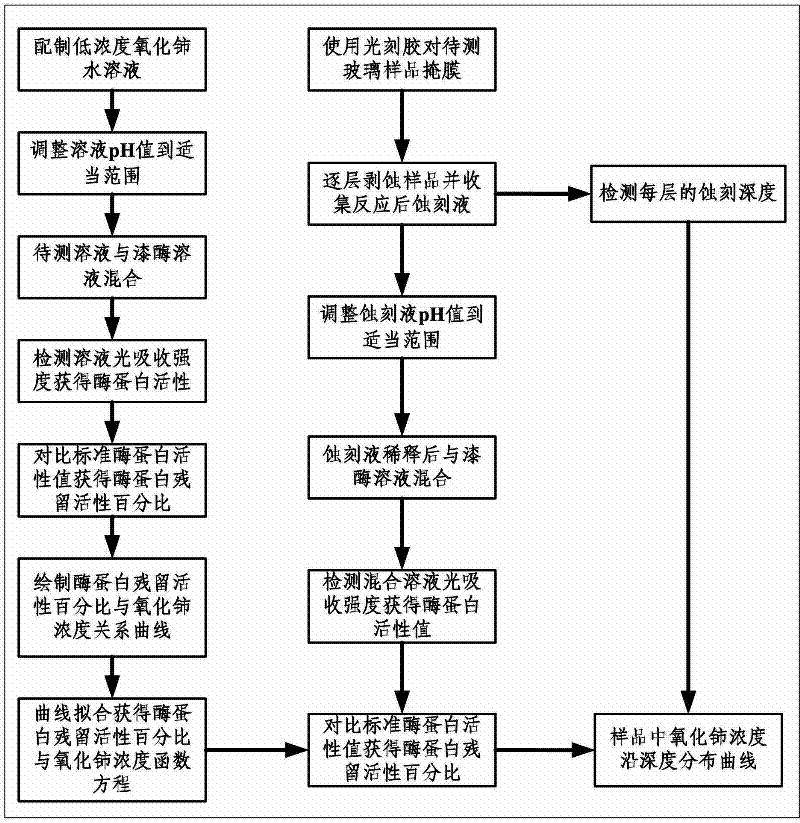
[0027] a kind of like figure 1 The detection method of trace impurity in the optical glass polishing subsurface damage layer of the present invention shown, comprises the following steps:
[0028] (1) Solution preparation: five different concentrations of cerium oxide (CeO 2 ) aqueous solution (concentration values are 10 -7 ppm, 10 -4 ppm, 10 -3 ppm, 10 -2 ppm and 10 -1 ppm), and adjust the pH value of each cerium oxide aqueous solution to 4.5; take 3 mL of each of the five different concentrations of cerium oxide aqueous solutions, and then mix them with an equal volume of laccase solution, which contains 0.6 mL of crude enzyme (the fermented broth was centrifuged at 10000r / min for 10min and the supernatant was taken as the crude enzyme solution), 1mmol / L guaiacol substrate and 50mmol / L sodium succinate buffer solution to obtain five different solution samples;
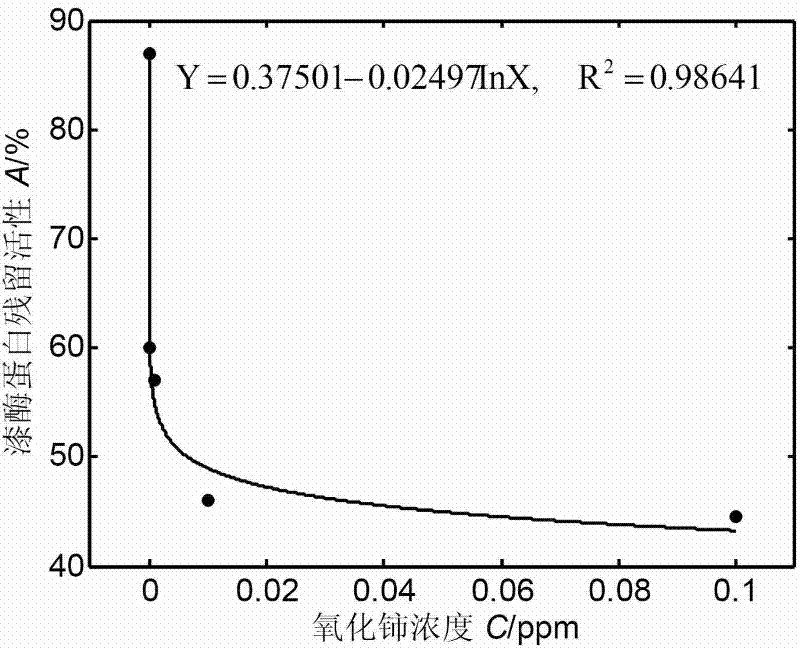
[0029] (2) Determination of the residual activity percentage of the enzyme protein: put a series of solut...
Embodiment 2
[0035] a kind of like figure 1 The detection method of trace impurity in the optical glass polishing subsurface damage layer of the present invention shown, comprises the following steps:
[0036] (1)-(3): Steps (1)-(3) of this embodiment are the same as those of Embodiment 1;
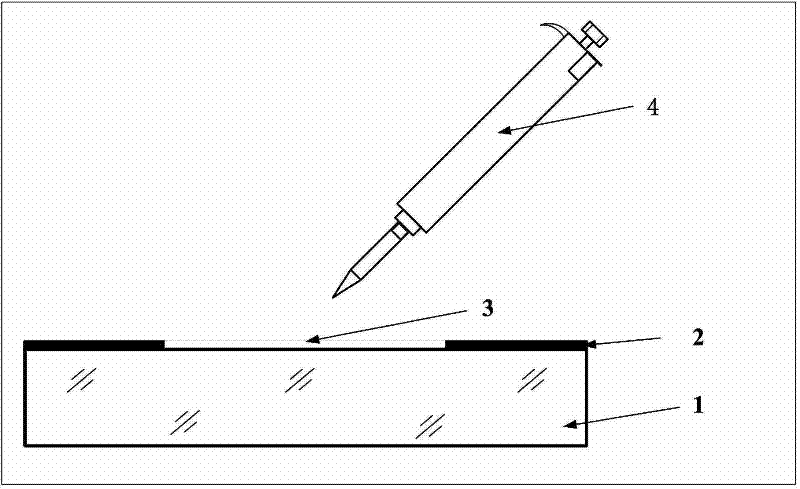
[0037] (4) Etching the glass to be tested: such as image 3 As shown, the K9 glass sample of Φ100mm×10mm polished by cerium oxide is selected as the glass sample 1 to be tested, and the photoresist 2 is used to mask the glass sample 1 to be tested, and the unmasked circular area with a central diameter of 50mm is used as the area to be tested 3. Then use the pipette 4 to introduce 10mL of etching solution into the unmasked area 3 of the glass sample to be tested 1, take it out for cleaning after an interval of 1min, and use a profiler to detect each etching of the glass sample to be tested depth, and collect the residual etching solution after each etching reaction;
[0038] (5) Detection of residua...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com