Method for removing heavy metal lead and cadmium in gracilaria seaweed
A technology of heavy metals and Gracilaria, applied in the removal of heavy metals lead and cadmium from Gracilaria seaweed, and the field of removing heavy metals lead and cadmium, which can solve the problems that the research on heavy metal removal has not been reported yet
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] ① Take Gracilaria from Tiaoshun Island, Zhanjiang, and rinse it thoroughly with clear water to remove impurities such as sediment, broken shells, and insects in Gracilaria, rinse it, drain, and set aside;
[0022] ② Take 1000g of Gracilaria treated above, add 6 liters of 0.2mol / L citric acid solution to soak, make sure that Gracilaria is immersed in the liquid, the treatment temperature of citric acid solution is 30°C (room temperature), shake in water bath for 24 hours;
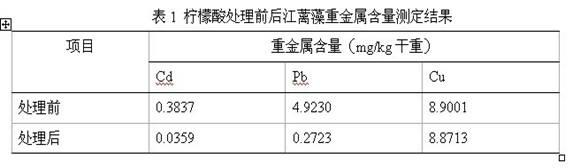
[0023] ③ The determination of heavy metal ions in this experiment was determined by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry in GB17378.6~1998 "Marine Monitoring Specifications", and the measurement results are shown in the following table;
[0024]
[0025] GB2760~2005 limits of pollutants in food, lead in leafy vegetables ≤ 0.3mg / kg, cadmium ≤0.2mg / kg, Table 1 shows that neither cadmium nor lead in Gracilaria before treatment meets the limits of pollutants in GB2762~2005 in food Vegetable ...
Embodiment 2
[0030] ① Take Gracilaria from Tiaoshun Island, Zhanjiang, and rinse it thoroughly with clear water to remove impurities such as sediment, broken shells, and insects in Gracilaria, rinse it, drain, and set aside;
[0031] ② Take 1000g of Gracilaria treated above, add 6 liters of 18% acetic acid solution to soak, make sure that Gracilaria is immersed in the liquid, the treatment temperature of the acetic acid solution solution is 30°C (room temperature), and shake in a water bath for 24 hours;
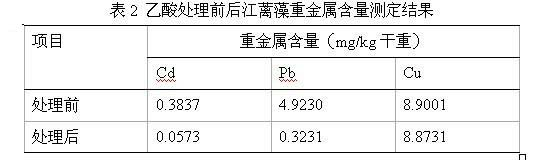
[0032] ③ The determination of heavy metal ions in this experiment was determined by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry in GB17378.6~1998 "Marine Monitoring Specifications". The measurement results are as follows:
[0033]
[0034] The concentration of Cd in Gracilaria algae samples before treatment was 0.2869 mg / kg, and the concentration of Cd in this test sample after treatment with 18% acetic acid was 0.0573 mg / kg, and the removal rate of Cd was 85.0%, which was a good r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com