Application of protein acetylation enzyme SIRT1 (Silent Mating type Information Regulation 2Homolog1) in promoting proliferation and delaying senility of mesenchymal stem cells
A deacetylase and stem cell technology, which is applied in the application of protein deacetylase SIRT1 in promoting the proliferation of mesenchymal stem cells and delaying aging, and can solve problems such as cell aging and MSC proliferation stagnation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
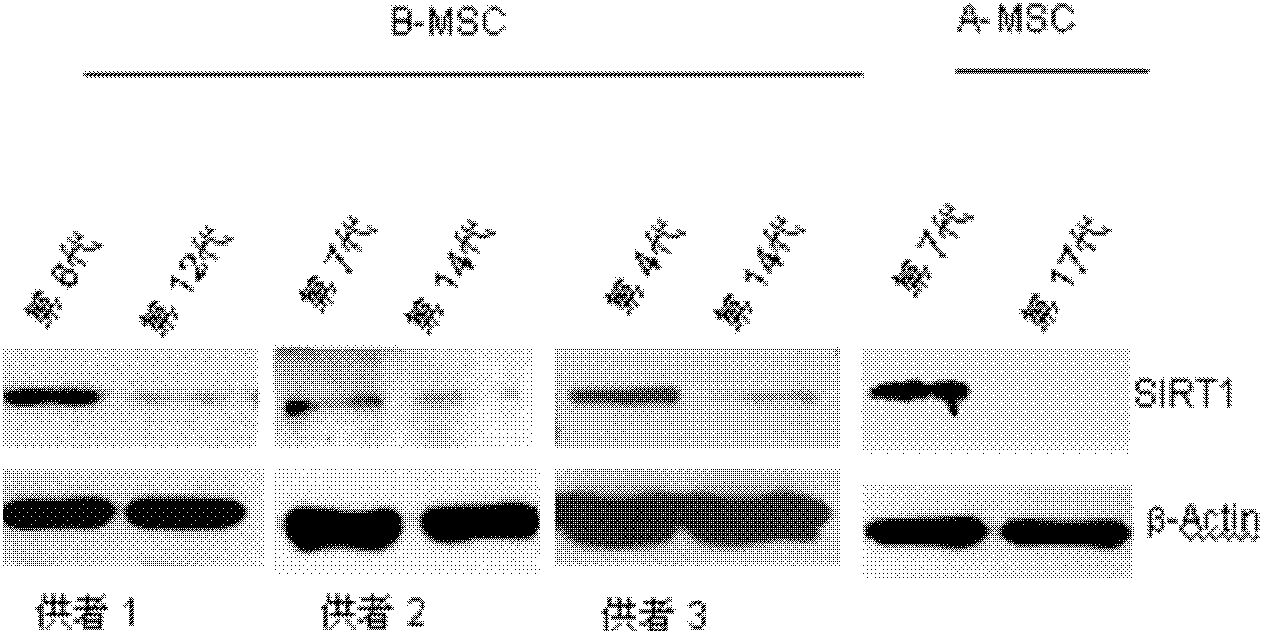
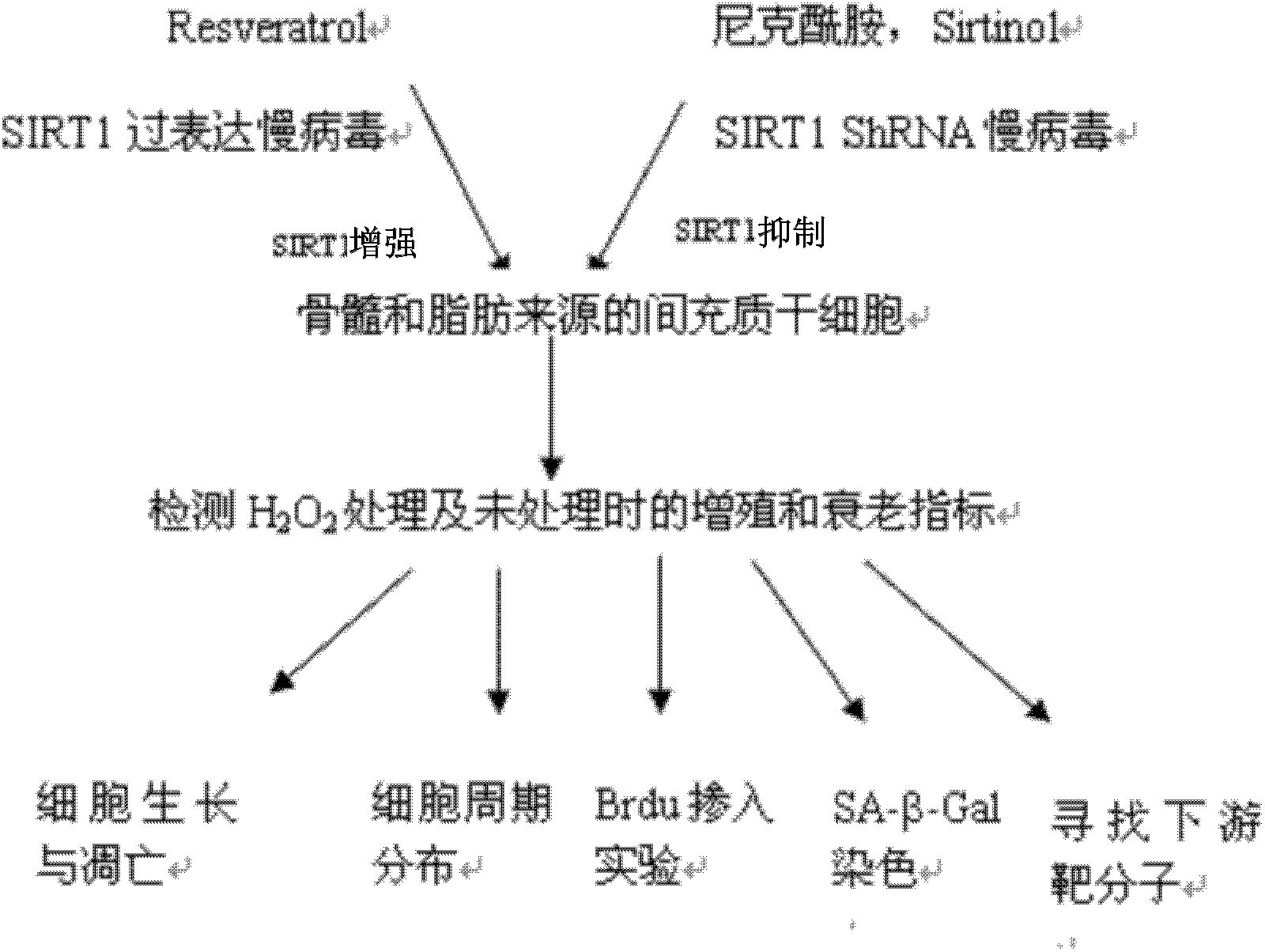
[0031] Example 1. Regulation of SIRT1 on proliferation and aging of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs)
[0032] 1. Detection of the relationship between the expression level of SIRT1 and the proliferation and senescence of MSCs
[0033] MSCs were isolated and amplified from human bone marrow and adipose tissue by conventional density gradient centrifugation combined with adherent culture, and continued to be subcultured in vitro until aging. Different donors (donors 1, 2, 3) and different passages (4, 3) were collected. 7, 8, 12, 14, and 17 generations) cells, the expression of SIRT1 was detected (the expression level was detected by Western Blot method, the primary antibody was rabbit anti-human SIRT1 antibody (purchased from Epitomics), and the secondary antibody was goat anti-rabbit antibody ( purchased from Zhongshan Jinqiao Company) and MSC proliferation (cell count, PI staining and Brdu staining) and senescence (SA-β-Gal staining) indicators to analyze whether there is a corr...
Embodiment 2
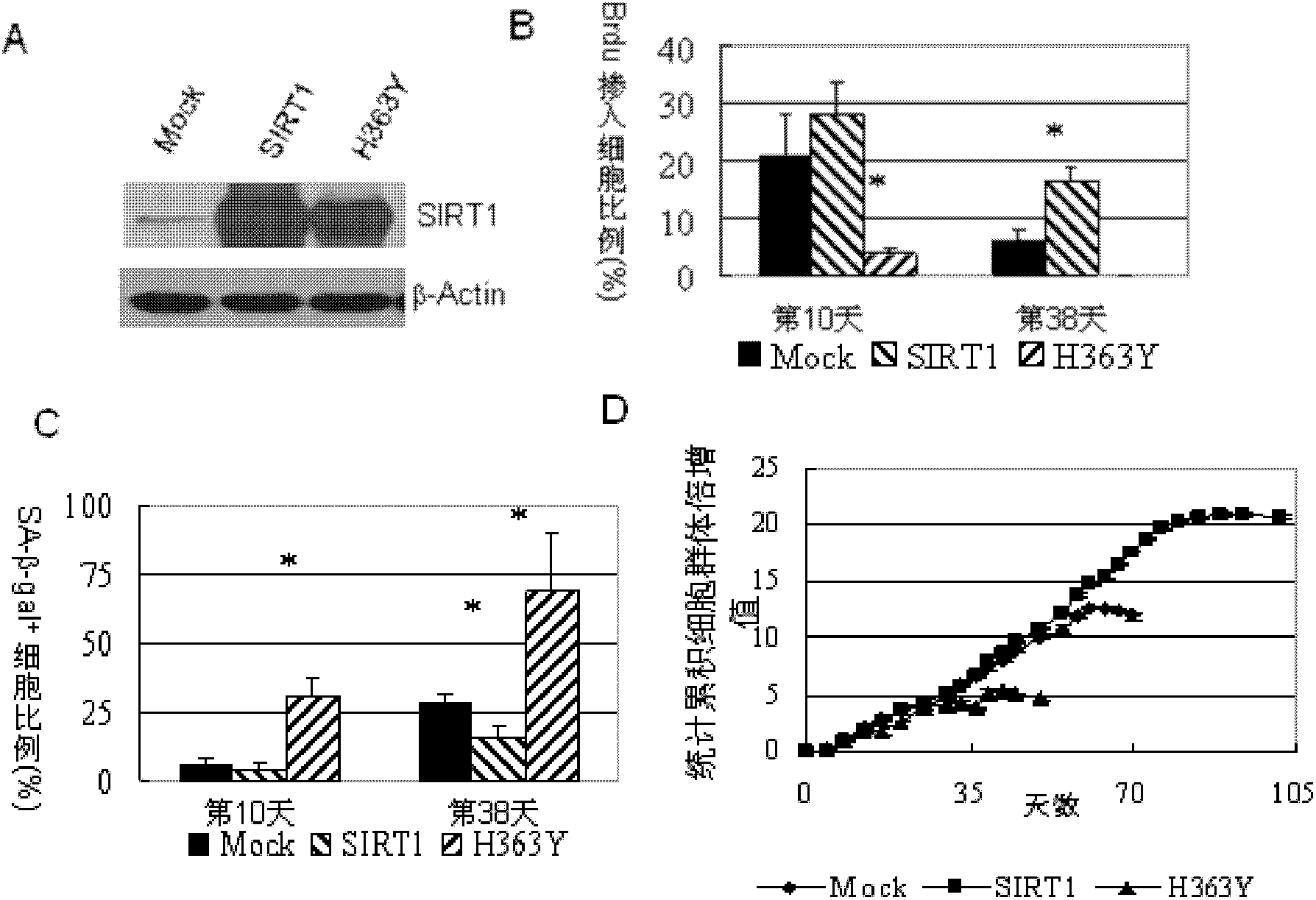
[0104] Example 2. Regulatory mechanism of SIRT1 on mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) proliferation and aging
[0105] Figure 6 The mechanism of cell senescence known so far is reviewed: pathway 1: telomere shortening, oncogene activation and reactive oxygen species cause DNA damage, damage signal activates p53, p53 activates p21Cip1, p21 Cip1 inhibits CDK2 and leads to pRb dephosphorylation; Certain senescence signals in one pathway activate p15INK4b or p16INK4a, and p15INK4b or p16INK4a inhibit CDK4 / 6 leading to dephosphorylation of pRb. It is already known that dephosphorylated pRb and acetylated pRb bind to the transcription factor E2F on the one hand to inhibit the transcription of proliferation-promoting genes, and on the other hand affect the chromatin structure of proliferation-promoting genes to shut down their expression, while hyperphosphorylated pRb and deacetylated pRb The ability of acetylated pRb to bind to E2F is reduced, allowing E2F to be released to promote the t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com