Method for treating scrapped molten salt generated in molten salt chlorination production method of TiCl4
A molten salt chlorination method, molten salt technology, applied in the direction of zirconia, process efficiency improvement, energy input, etc., can solve the problem of harmful chloride pollution to the environment, achieve considerable economic and social benefits, simple process effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
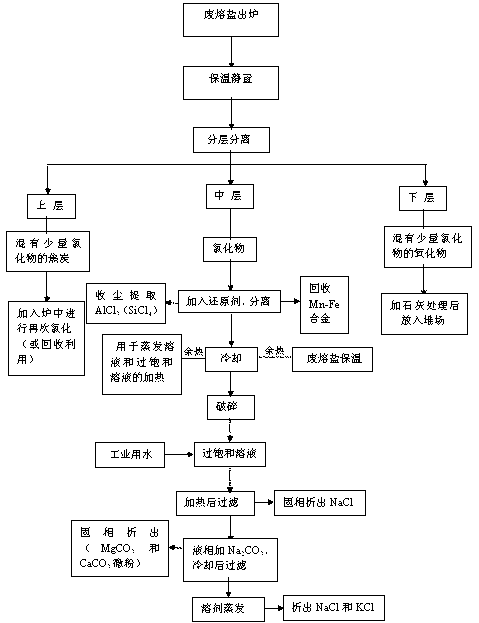
[0035] Such as the process flow of processing waste molten salt figure 1 As shown, the waste molten salt released from the furnace is directly kept at 500-900°C for 5-120 minutes, so that the waste molten salt is divided into three layers, namely the upper layer (floating layer), the middle layer (molten salt layer) and the lower layer ( sediment layer).
[0036] The upper layer is coke mixed with a small amount of molten salt. After the upper layer is separated from the middle layer and the lower layer, it is directly returned to the molten salt chlorination furnace for reuse under high temperature conditions (accounting for 13.0-16.0% of the total weight of the molten salt), or recycled coke.
[0037] The middle layer is mainly molten salt of chloride, and its composition is mainly MgCl 2 , KCl, CaCl 2 , NaCl and manganese and iron chlorides (accounting for 70.0-74.0% of the total weight of molten salt).
[0038] The lower layer (precipitated layer) is an oxide mixed with...
Embodiment 2
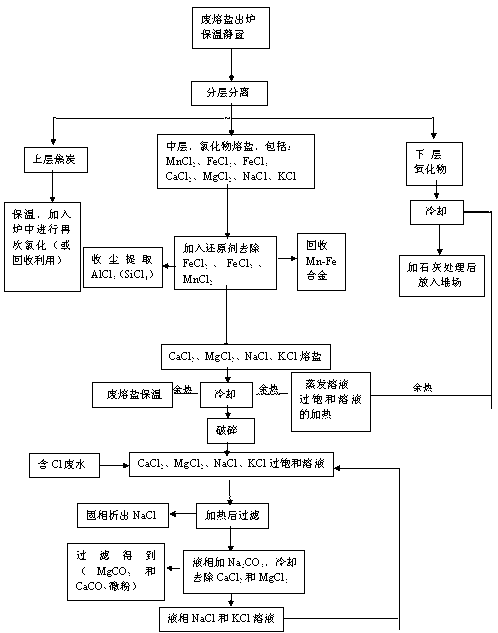
[0042] Such as the process flow of processing waste molten salt figure 2 As shown, after the waste molten salt is treated by thermal insulation and stratification, the chloride composition of the molten salt layer is: MgCl 2 +KCl+CaCl 2 +NaCl accounts for 76.0-80.0%, manganese and iron chlorides account for 20.0-24.0%, add silicon-calcium alloy powder (or its combination with silicon and silicon-iron alloy powder) of 2.5-3.5% of the weight of molten salt to remove manganese and iron Chloride, then pour out the spent molten salt from the crucible and cool to room temperature. This process can recycle Mn-Fe alloy (Mn content is 45.0-70.0%), and collect SiCl through dust removal system 4 , after removing manganese and iron, the MgCl of molten salt 2 , KCl, CaCl 2 And the content of NaCl is 95.3-98.0%.
[0043] Then take 100g of cooled and broken molten salt, add 45ml-70ml of waste water containing 10000ppmCl- to make a supersaturated solution, heat it to 25-100°C to form in...
Embodiment 3
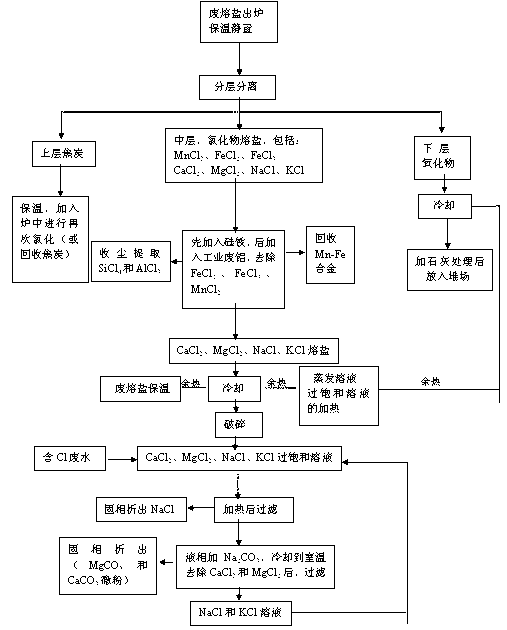
[0045] Such as the process flow of processing waste molten salt image 3 As shown, the process flow is basically the same as that of Example 2, the difference is that silicon powder (or ferrosilicon alloy powder) of 1.0-2.5% of the weight of the molten salt is first added to the middle molten salt to remove iron chloride, and the bottom of the crucible is taken out metal iron; then add 1.0-2.5% aluminum powder (or industrial waste aluminum and waste aluminum alloy powder) of molten salt weight, metal Mn can be recovered at the bottom of molten salt (Mn content is greater than 90.0%), and AlCl can be collected through the dust removal system 3 and SiCl 4 , this process removes manganese and iron chloride relatively completely, MgCl in molten salt after treatment 2 , KCl, CaCl 2 And the content of NaCl reaches 96.0-98.5%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com