Porous bioceramic with calcium phosphate nanorods on surface layer and formation method for same
A technology of bioceramics and porous ceramics, applied in the fields of bioceramics and its preparation, porous bioceramics, and the composition of porous bioceramics. Ceramic bonding is weak and other problems, achieving high repeatability, avoiding mechanical strength, and simple method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] The reaction vessel used is a hydrothermal reaction kettle.
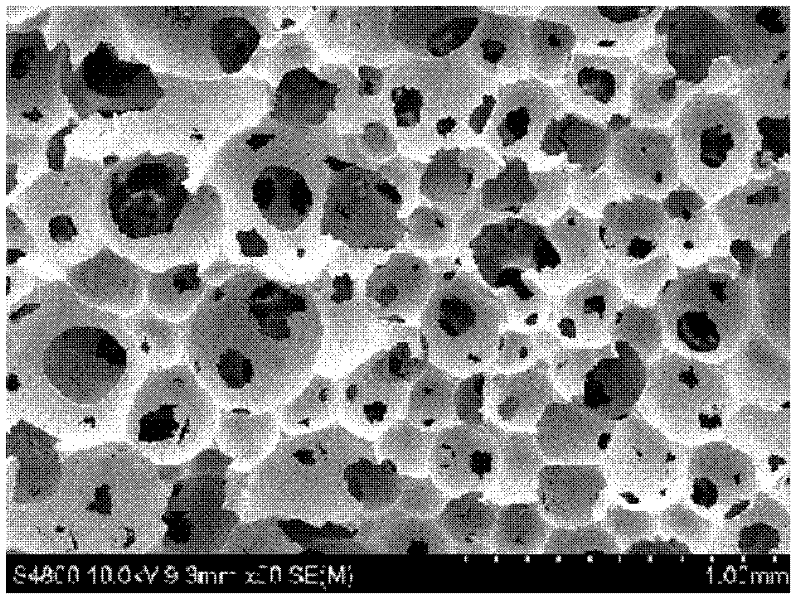
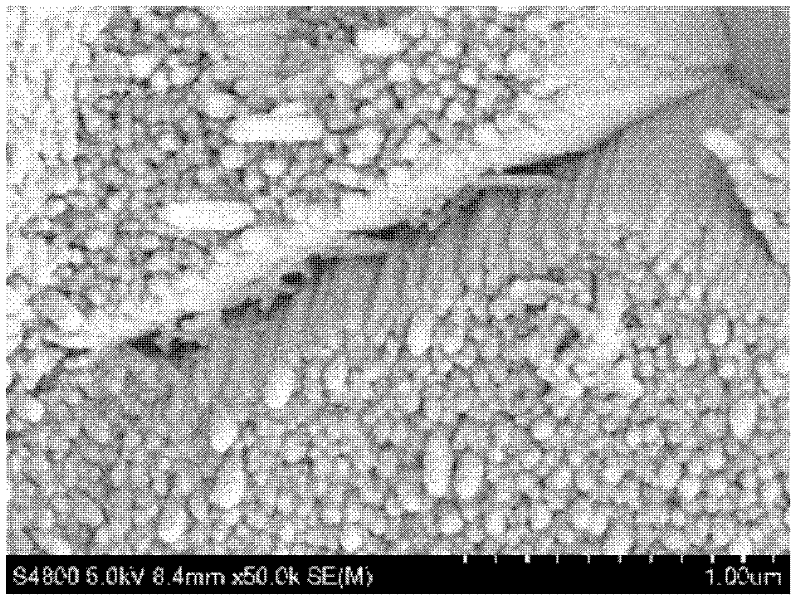
[0028] Prepare a 0.8 mol / liter aqueous urea solution in a hydrothermal reactor, and mix the prepared urea aqueous solution with 0.167 mol / liter Ca(NO 3 ) 2 4H 2 O and 0.1 mol / L (NH 4 ) 2 HPO 4 Mix to obtain a mixed solution, the Ca:P ratio of which is 1.67, then use nitric acid and ammonia water to adjust the pH of the prepared mixed solution to 4, and add 2 cm in diameter and 0.5 cm in thickness to the mixed solution after the pH value is stable. , a porous ceramic whose component is hydroxyapatite, undergoes a hydrothermal reaction at a temperature of 120° C. for 10 hours, and obtains a porous ceramic with hydroxyapatite nanorods on the surface. Wherein the average diameter of calcium phosphate nanorods is 60 nanometers, and the average length is 1200 nanometers, such as figure 2 The surface layer shown is a SEM photograph of a porous biohydroxyapatite ceramic with apatite nanorods.
Embodiment 2
[0030] A 0.2 mol / L aqueous urea solution was prepared in a hydrothermal reactor, and the other preparation conditions were the same as in Example 1 to obtain a porous ceramic with hydroxyapatite nanorods on the surface. Its hydroxyapatite nanorods have an average diameter of 50 nanometers and an average length of 1000 nanometers.
Embodiment 3
[0032] A 1.0 mol / L aqueous urea solution was prepared in a hydrothermal reactor, and the other preparation conditions were the same as in Example 1 to obtain a porous ceramic with hydroxyapatite nanorods on the surface. Its calcium phosphate nanorods have an average diameter of 55 nanometers and an average length of 1100 nanometers.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com