Preparation method of submicron-grade graph on sapphire substrate
A sapphire substrate, sub-micron technology, applied in electrical components, circuits, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve the problems affecting the performance of nitride LED devices, lattice constant mismatch and thermal expansion coefficient differences.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Step 1: Deposit a layer of 10nm silicon dioxide on the sapphire substrate as a photoresist adhesion layer for fine lithography on the sapphire substrate.
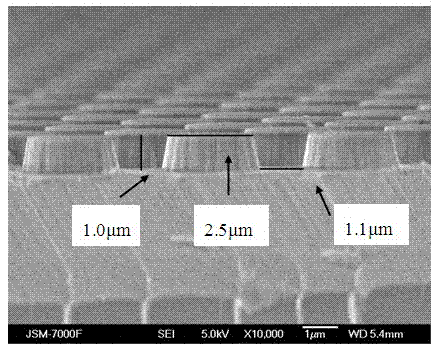
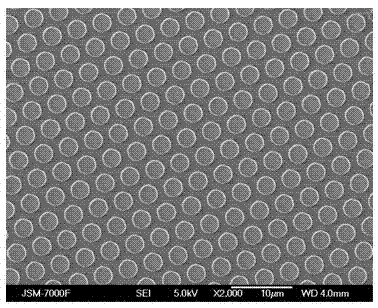
[0031] Step 2: Prepare a photoresist pattern mask layer with cylindrical holes with a diameter of 2.5 μm and an interval of 1 μm on the sapphire substrate prepared in step 1 by conventional photolithography technology.
[0032]Step 3: A four-layer metal structure consisting of a 10nm Ti layer, a 50nm Ni layer, a 10nm Al layer, and a 100nm Ni layer is sequentially evaporated on the sapphire substrate made in step 2 using vacuum evaporation equipment, as an etched sapphire substrate metal mask. Wherein, the thickness of each Ti layer and Al layer is 10 nm and 15 nm respectively, and the thickness of each metal Ni layer is 50 nm.
[0033] Step 4: Sonicate the sapphire substrate prepared in step 3 by immersing it in boiling acetone for 3 minutes to 15 minutes to carry out the photoresist stripping process, and then rins...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Step 1: Deposit a layer of 200nm silicon dioxide on the sapphire substrate as a photoresist adhesion layer for fine lithography on the sapphire substrate.
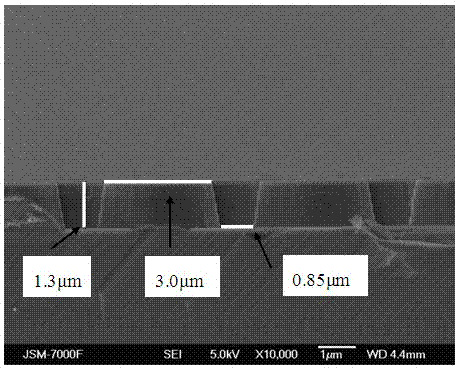
[0043] Step 2: Prepare a photoresist pattern mask layer with cylindrical holes with a diameter of 3 um and an interval of 1 um on the sapphire substrate produced in step 1 by conventional photolithography technology.
[0044] Step 3: Use vacuum evaporation equipment to sequentially vapor-deposit a four-layer metal structure of 10nm Al layer, 100nm Ni layer, 10nm Au layer, and 100nm Ni layer on the sapphire substrate prepared in step 2, as the metal for etching the sapphire substrate mask,
[0045] Wherein, the thicknesses of the Au layer and the Al layer are 20nm and 35nm respectively, and the thickness of each metallic Ni layer is 5nm.
[0046] Step 4: Immerse the sapphire substrate prepared in step 3 into boiling acetone for 3 minutes to 15 minutes and perform the photoresist stripping process, and then rinse it ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com