Device and process for monitoring oceanic planktonic microorganism content in real time and early warning red tide
A technology for microbial biomass and real-time monitoring, applied in analytical materials, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient comprehensiveness, high cost and slow speed, etc., and achieve the effect of improving the utilization rate of light energy and improving the oxidation capacity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
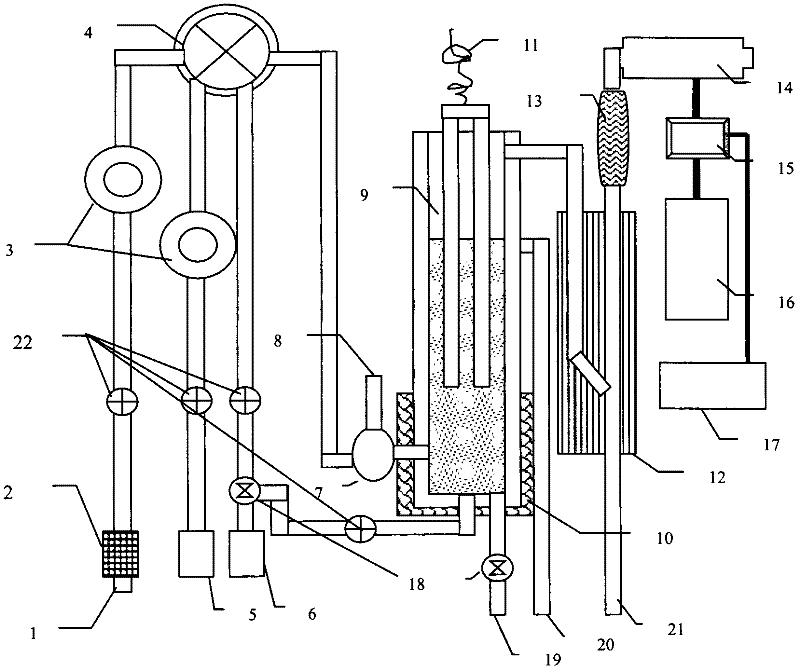
[0032] Embodiment 1 Marine planktonic biomass real-time monitoring and red tide early warning device, which mainly includes sequentially connected sampler, acidifier 4, gas-water separator 7, oxidation reactor 9, condensation dehydrator 12, ion trap 13 and infrared CO 2 Detector 14, the gas-water separator 7 is provided with an exhaust port 8, the condensation dehydrator is provided with a drain pipe 21, the oxidation reactor 9 is provided with an ultraviolet lamp 11 and an electric heating jacket 10, and the sampler It mainly includes sampling port 1, reagent bottle 5, and carrier gas bottle 6. Sampling port 1 is connected to acidifier 4 through filter 2, flow sensor 22, peristaltic pump 3, and reagent bottle 5 is connected to acidifier through flow sensor 22, peristaltic pump 3. 4 are connected, and the carrier gas cylinder 6 is divided into two paths through a three-way solenoid valve, one of which is connected with the acidifier 4.
[0033] The inner diameter of the sampli...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Example 2 is a real-time monitoring and red tide warning device for marine planktonic microbial biomass. The difference from Example 1 is that the inner diameter of the sampling tube between the sampling port and the acidifier is 2.0 mm. The mesh size of the filter is 3.0 mm. The acidifying agent in the reagent bottle is sulfuric acid, the oxidizing agent is ammonium persulfate, and the mass ratio of sulfuric acid to ammonium persulfate is 4:1.
experiment example 1
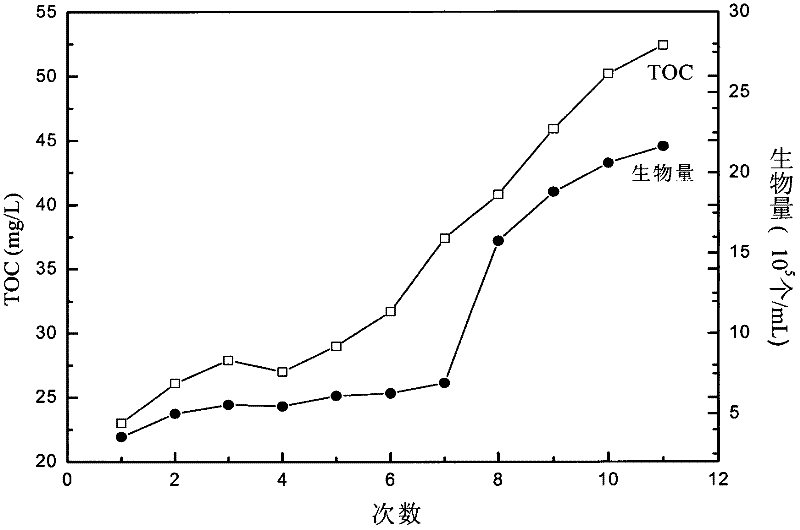
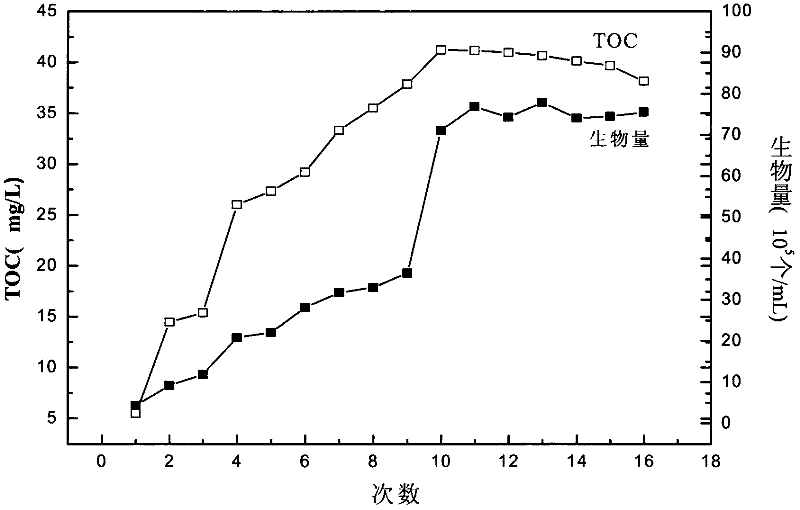
[0049] In Experimental Example 1, Papua viridis, Salina and Chlorella were respectively selected for cultivation. The culture container is a 20L transparent glass container. The cultivation process is as follows: first soak the glass container with 1:5 HCl, then rinse with distilled water and double distilled water, and finally wash and steam sterilize (121°C, 0.56kg·cm -2 , 30min) and dried before use, to keep the sterility of the container, so that the cultured algae grow more beneficial. Select seawater for cultivating algae and filter it through a filter membrane with a pore size of 0.45 μm, then boil and sterilize it in a pressure cooker (121°C, 0·56kg·cm -2, 30min), after standing for 24 hours to balance, the nutrient solution was prepared according to the f / 2 formula to improve the favorable nutritional environment for algae. The experimental algae species were cultivated under light conditions with light intensities of 10000lx and 15000lx (400-700nm) respectively, wi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The inside diameter of | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The inside diameter of | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com