Method for recovering lead in waste lead-acid storage battery filler by using wet process
A waste lead-acid battery, wet process technology, applied in the improvement of process efficiency, photography process, instruments and other directions, can solve the problems of low lead recovery rate, long process, great harm to human body and environment, etc. The effect of simplifying the process flow and improving the efficiency of electrolysis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
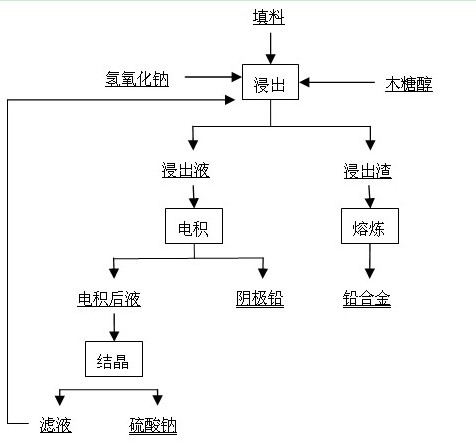
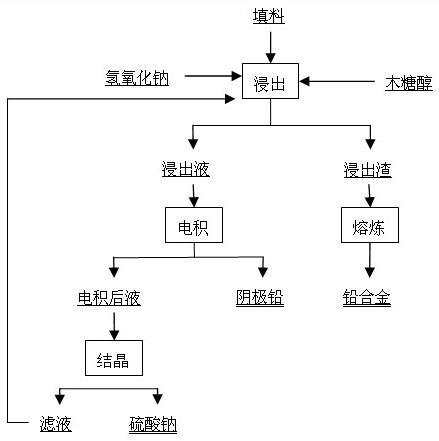
[0038] Weigh 150 g of sodium hydroxide (analytically pure), add 180 g of xylitol (food grade) into 1.5 L of water, stir and dissolve to obtain a solution for leaching, and use the lead paste part selected after the waste lead-acid battery is broken as the leaching raw material. After drying and grinding, pass through a 200-mesh sieve, and add 200 g to the obtained solution for leaching. Stir magnetically at 85°C for 4 h, filter, and the filtrate is the electrolyte, in which the concentration of lead ions is 92 g / L. The electrolysis temperature was controlled at 45°C, the current density was 200 A / m2, and the pole distance was 4 cm. Both the cathode plate and the anode plate were stainless steel plates with an area of 9.7 cm×9.9 cm. The electrolyte circulation rate was 30 mL / min, and the electrolysis time was 10 h. The average cell voltage is 1.62V, the current efficiency is 96.12%, and the cathode energy consumption is 436.07 kWh / t Pb. The cathode lead purity is higher than...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Weigh 200 g of sodium hydroxide (analytical pure), add 180 g of xylitol (food grade) into 1.5 L of water, stir and dissolve to obtain a solution for leaching, and use the lead paste part selected after the waste lead-acid battery is broken as the leaching raw material. After drying and grinding, pass through a 200-mesh sieve, and add 250 g to the obtained solution for leaching. Stir with magnetic force at 75°C for 4 h, filter, and the filtrate is the electrolyte solution, in which the concentration of lead ions is 115 g / L. The electrolysis temperature was controlled at 50°C, the current density was 250 A / m2, and the pole distance was 4 cm. Both the cathode plate and the anode plate were stainless steel plates with an area of 9.7 cm×9.9 cm. The electrolyte circulation rate was 25 mL / min, and the electrolysis time was 10 h. The average cell voltage is 1.70V, the current efficiency is 96.52%, and the cathode energy consumption is 455.70 kWh / t Pb. The cathode lead purity...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Weigh 150 g of sodium hydroxide (analytically pure), add 180 g of xylitol (food grade) into 1.5 L of water, stir and dissolve to obtain a solution for leaching, and use the lead paste part selected after the waste lead-acid battery is broken as the leaching raw material. After drying and grinding, pass through a 200-mesh sieve, and add 200 g to the obtained solution for leaching. Stir magnetically at 85°C for 4 h, filter, and the filtrate is the electrolyte, in which the concentration of lead ions is 92 g / L. The electrolysis temperature was controlled at 55°C, the current density was 400 A / m2, and the pole distance was 4 cm. Both the cathode plate and the anode plate were stainless steel plates with an area of 9.7 cm×9.9 cm. The electrolyte circulation rate was 30 mL / min, and the electrolysis time was 10 h. The average cell voltage is 1.85V, the current efficiency is 97.45%, and the cathode energy consumption is 491.18 kWh / t Pb. The cathode lead purity is higher than...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com