Method for rapidly detecting and screening staphylococcus aureus
A staphylococcus, golden yellow technology, applied in the direction of measuring devices, instruments, scientific instruments, etc., can solve the problems of difficult simultaneous analysis of multiple components, molecular weight analysis, shortened detection time, etc., to achieve low requirements for supporting equipment, high efficiency and rich Set, good effect of reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
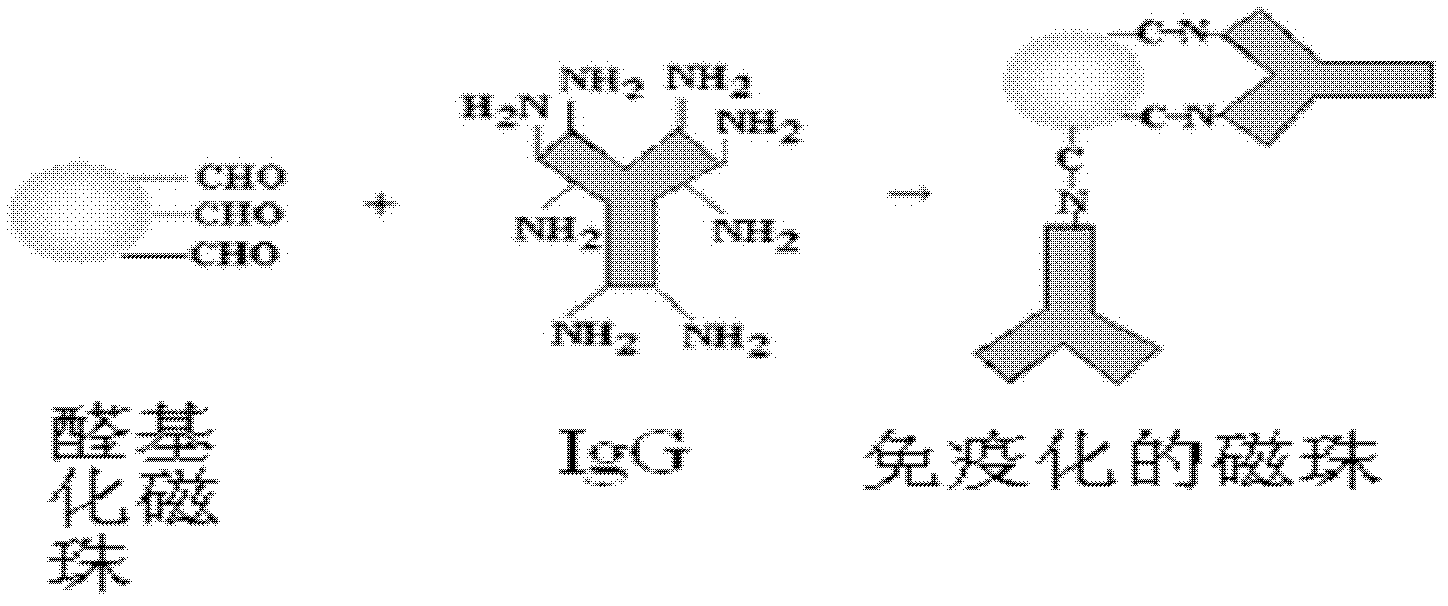
[0032] Example 1 Preparation of Immunized Superparamagnetic Nanomagnetic Beads
[0033] 1. Preparation of aldylated superparamagnetic nano-magnetic beads
[0034]Mix 0.06 g of magnetic beads with ferric oxide as the magnetic core and 6.0 g of polyethylene glycol, add to 6 mL of double distilled water, and disperse for 30 minutes. The mixture was transferred to a shaker flask at room temperature with continuous stirring. 115 mL of dispersion medium ethanol / double distilled water (V:V=3:2) was added to the bottle. 8mL (0.68g) of acrolein, 15mL (13.5g) of styrene, 0.3mL (0.28g) of divinylbenzene, and 6.0g of benzoyl peroxide were added in sequence, and stirred for 30min. The temperature was raised to 65°C, and the reaction was continued for 10 hours to obtain a light brown emulsion. Wash several times with 0.1M hydrochloric acid and double distilled water, and separate by magnetic field. Aldehyde functionalized magnetic beads were obtained.
[0035] 2. Linkage of aldylated m...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Example 2 Connection of fluorescent quantum dots to human immunoglobulin IgG
[0038] 1-Ethyl-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC·HCL) was used as a cross-linking agent, N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) was used as a protective agent, and the Quantum dots modified with carboxyl groups on the surface (QDs-COOH) cross-link with the terminal amino groups on the antibody (Ab) to generate amide bonds, and then immune quantum dots are obtained. The molar ratio of antibody to quantum dot is 1:10 to 1:30.
[0039] The specific method is: 60ul (7.8*10 -6 mol) QDs (red light) stock solution was added to the mixture of phosphate buffer solution PBS (0.01mol / L, pH 7.2) and 6mg EDC·HCL (final concentration 20mg / mL), and the mixture was vortexed at room temperature for 5min. React for another 15-20min to fully activate the free carboxyl groups on the QDs; similarly, 1.5mg NHS (final concentration: 5mg / mL) was added to the above mixture, vortexed at room temperature fo...
Embodiment 3
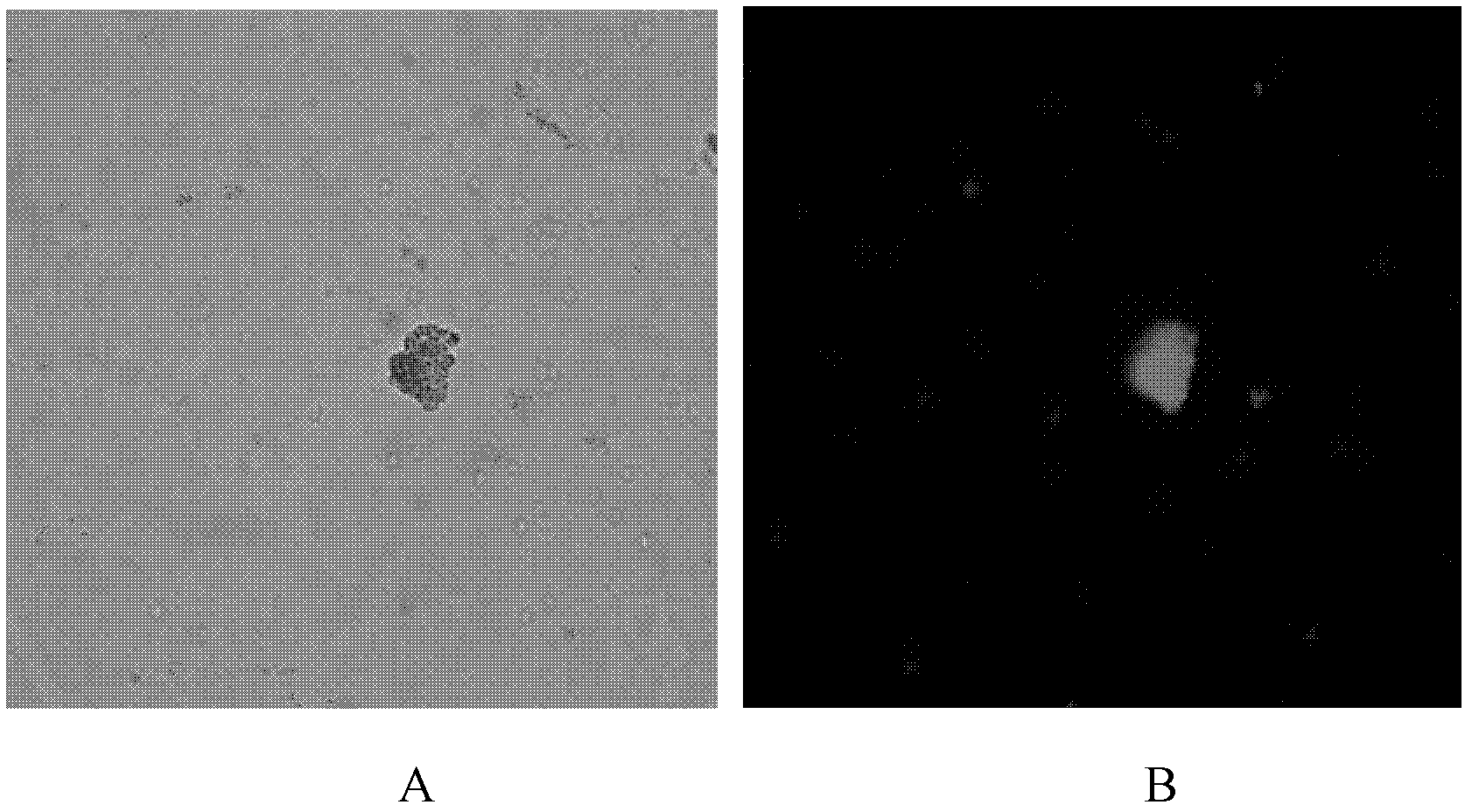
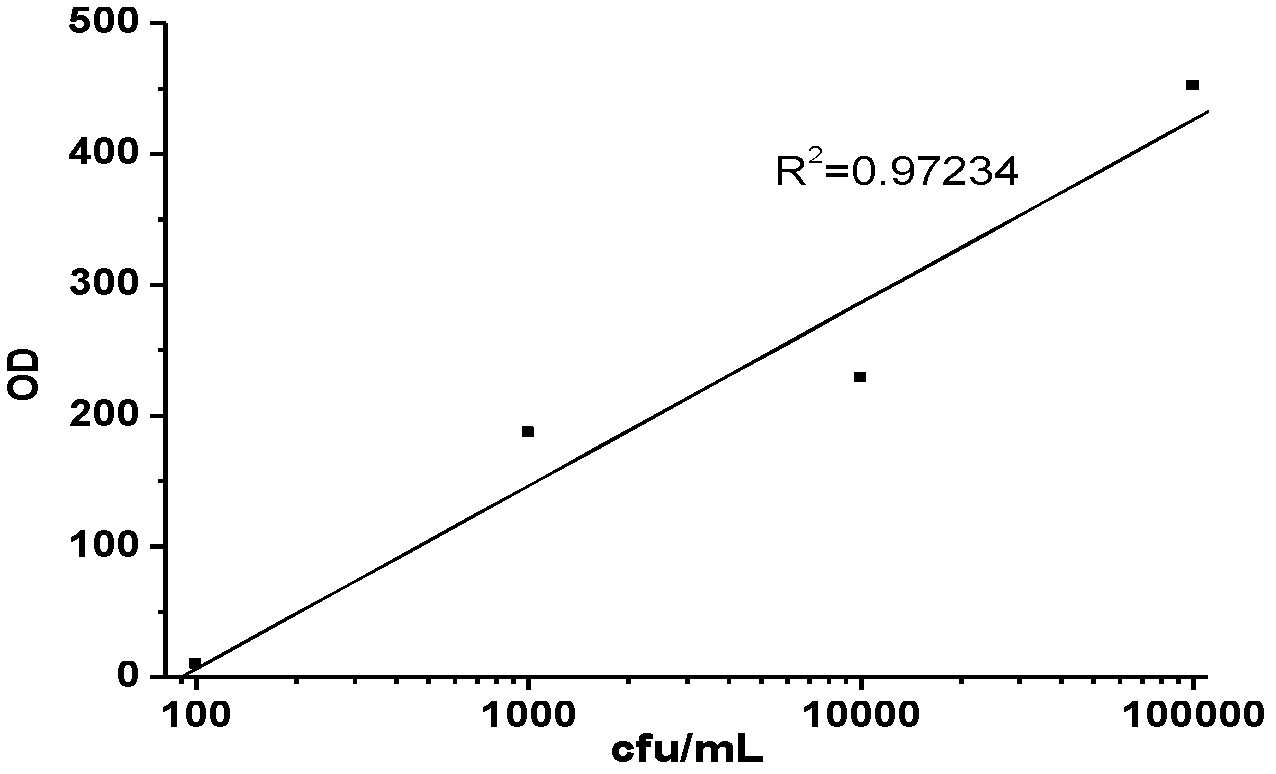
[0040] The detection of embodiment 3 samples
[0041] The principle of detection is as figure 1 shown. The immunized superparamagnetic nano-magnetic beads prepared in Example 1 were dispersed in phosphate buffer (0.01 mol / L, pH=7.2) (concentration is mg / ml, and 50 μL of immuno-magnetic beads were used dropwise into 3mL different concentrations (10 5 cfu / mL, 10 4 cfu / mL, 10 3 cfu / mL, 10 2 cfu / mL, 10cfu / mL) in the sample liquid of Staphylococcus aureus. Shake at room temperature to fully react for 0.5h. Under the action of an external magnetic field, wash with phosphate buffer (0.01mol / L, pH 7.2) for 2 to 3 times, and dilute to 0.2mL to obtain "magnetic beads-Salmonella" Complex.
[0042] Then, 50uL of the immunized quantum dots prepared in Example 2 were added dropwise to the washed system, and shaken for 0.5h under a shaker at room temperature, so that the antigen on the surface of Staphylococcus aureus and the IgG antibody connected to the quantum dots were fully For ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com