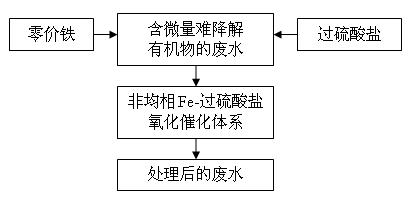
Method for treating track non-degradable organisms in water by aid of heterogenous sulfate radical oxidation
A technology for refractory organic matter and oxidation treatment, applied in the field of environmental pollution control, can solve the problems of reducing the rate of oxidation degradation, etc., and achieve the effect of easy parameters, easy acquisition, and fast activation efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Such as figure 1 Shown, adopt the method of the present invention to handle the waste water that contains trace p-chloroaniline.
[0026] Add 100 mL of phosphate buffer solution containing a trace amount of p-chloroaniline to the reactor to adjust the pH to 4, wherein the initial concentration of p-chloroaniline is 50 μmol / L; add sodium persulfate and zero-valent iron to the reactor to make sodium persulfate The initial concentration is 2.5mmol / L, and the initial concentration of zero-valent iron is 0.7g / L; zero-valent iron continues to produce Fe in water 2+ , Fe 2+ Activation of sodium persulfate produces sulfuric acid free radicals, which oxidize and degrade trace amounts of p-chloroaniline in water.
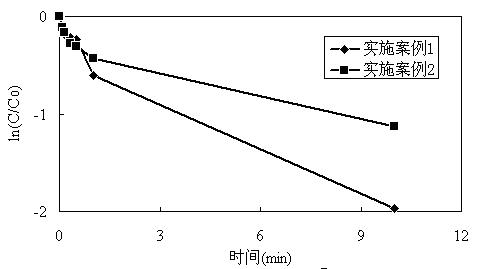
[0027] The effect of treatment was detected by high performance liquid chromatography, such as figure 2 As shown, at 25°C, the degradation rate of p-chloroaniline reached more than 99.9% within 10 minutes.
Embodiment 2
[0029] Such as figure 1 Shown, adopt the method of the present invention to process the waste water that contains trace aniline.
[0030] Add 100 mL of phosphate buffer solution containing a small amount of aniline to the reactor to adjust the pH to 4, wherein the initial concentration of aniline is 50 μmol / L; add sodium persulfate and zero-valent iron to the reactor to make the initial concentration of sodium persulfate 2.5 mmol / L, the initial concentration of zero-valent iron is 2g / L; zero-valent iron continuously produces Fe in water 2+ , Fe 2+ Activation of sodium persulfate produces sulfuric acid free radicals, which oxidize and degrade trace amounts of aniline in water.
[0031] Use high-performance liquid chromatography to detect the treatment effect, at 25 ° C, such as figure 2 Shown, the degradation rate of aniline in 10min reaches more than 87%.
Embodiment 3
[0033] Such as figure 1 Shown, adopt the method of the present invention to handle the waste water that contains trace p-chloroaniline.
[0034] Add 100 mL of phosphate buffer solution containing a trace amount of p-chloroaniline to the reactor to adjust the pH to 7, wherein the initial concentration of p-chloroaniline is 50 μmol / L; add sodium persulfate and zero-valent iron to the reactor to make sodium persulfate The initial concentration is 2.5mmol / L, and the initial concentration of zero-valent iron is 5g / L; zero-valent iron continues to produce Fe in water 2+ , Fe 2+ Activation of sodium persulfate produces sulfuric acid free radicals, which oxidize and degrade trace amounts of p-chloroaniline in water.
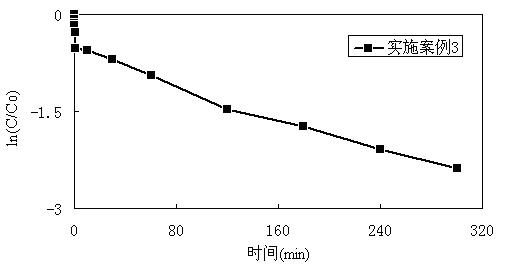
[0035] The effect of treatment was detected by high performance liquid chromatography, such as image 3 As shown, at 25°C, the degradation rate of p-chloroaniline reached over 90.8% within 5 hours.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com