Lactobacillus plantarum and application thereof in fermenting and ensiling sweet potato stem and leaf
A Lactobacillus plantarum, stem and leaf technology, applied in the directions of application, microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems of rapid loss of nutrients, pollution, waste, etc., and achieve the effect of low cost and high efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
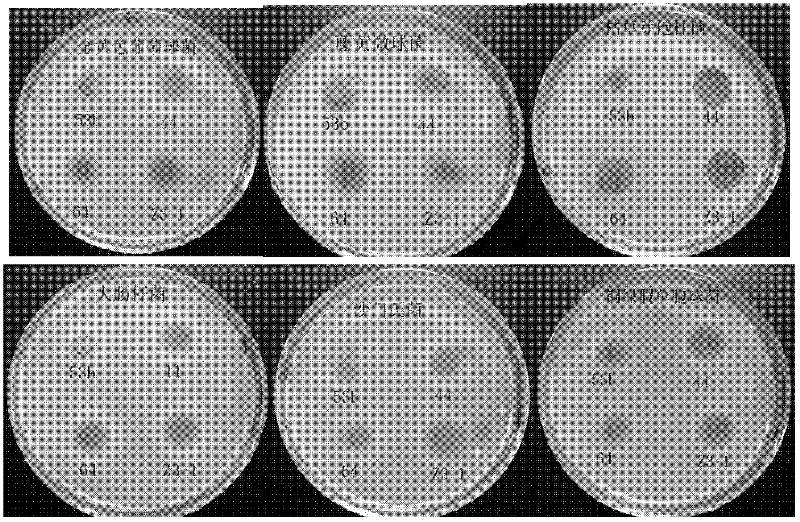
[0043] Example 1. Isolation, purification and identification of Lactobacillus plantarum Z3-1CGMCC No.5027
[0044] Take 10g of silage corn stalks in Zhengzhou, Henan, add 90mL of distilled water, shake with a shaker for 5min, 10 -1 -10 -5Gradient dilution. Take 20 μL from each gradient dilution solution and spread it on the MRS solid medium, let it stand for anaerobic culture for 48 hours, pick a single colony with obvious differences in colony shape, size, color and gloss, and repeat the streaking until the obtained Pure colonies. The strains were inoculated in MRS liquid medium and cultured at 30°C for 24 h, centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 10 min, and 20 μL of the supernatant was taken to inoculate Micrococcus luteus, Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis ), Salmonella enterica, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli were respectively used as indicator bacteria, and the bacteriostasis test was carried out by the Oxford cup double plate method, as figure 1 As shown,...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Embodiment 2, the growth of Lactobacillus plantarum (Lactobacillus plantarum) Z3-1CGMCC No.5027 under different pH, temperature and salt concentration environmental conditions
[0052] Adjust the initial pH of the MRS medium to 2.0, 3.0, 3.5, 4.0, 4.5, 5.0, 5.5, 6.0, 7.0, 8.0, 9.0, and 30°C with 1 mol / L hydrochloric acid and 1 mol / L sodium hydroxide, respectively Cultivate Lactobacillus plantarum (Lactobacillus plantarum) Z3-1CGMCC No.502724h at a constant temperature, without adjusting the acid during the cultivation process, and measure the light absorption value at 600nm with a spectrophotometer (OD 600 ). The results are shown in Table 2, the Z3-1 strain can grow under the conditions of initial pH2.5-pH9.0.
[0053] Inoculate the activated Lactobacillus plantarum (Lactobacillus plantarum) Z3-1CGMCC No.5027 strain into MRS liquid medium and culture them at 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 42, 50°C and other temperatures 24h, the light absorption value (OD) at 600nm w...
Embodiment 3
[0058] Embodiment 3, plant Lactobacillus (Lactobacillus plantarum) Z3-1CGMCC No.5027 fermentation sweet potato stem and leaf
[0059] Preparation of bacterial suspension: under sterile conditions, take Lactobacillus plantarum (Lactobacillus plantarum) Z3-1CGMCCNo.5027, inoculate it in MRS liquid medium and cultivate it at 30°C to obtain a Z3-1 content of 10 8 ~10 9 cfu / mL bacterial suspension.
[0060] Method I
[0061] 1. Set up 2 treatments (each treatment is repeated 3 times, and the results are expressed as mean values):
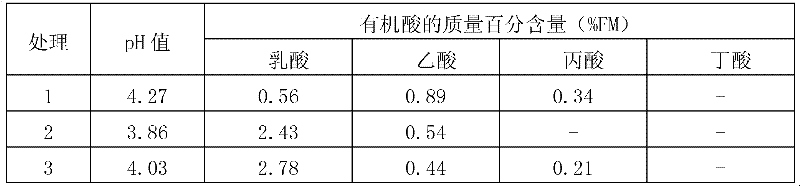
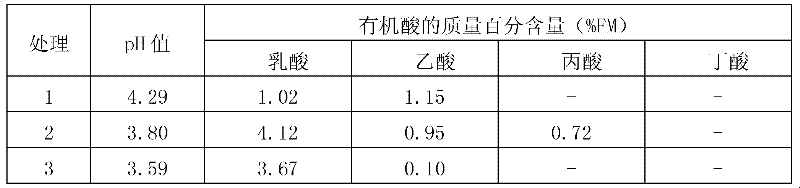
[0062] Treatment 1 (inoculated with Z3-1 for fermentation): Take 200g sweet potato stems and leaves, 50g water and 2.5gNaCl and mix them, then add 10 per gram of sweet potato stems and leaves 5 The ratio of cfu Z3-1 was added to the above-mentioned Z3-1 bacterial suspension, the obtained mixture was put into a silage bag and mixed evenly, and after the air was pumped (the air pressure in the bag was zero), it was placed anaerobically at 25°C for 3 day...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com