Method for controlling morphology and performance of ferriferrous oxide
A technology of ferroferric oxide and morphology, applied in the field of inorganic materials, to achieve the effects of concentrated particle size distribution, high purity, and strong product controllability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
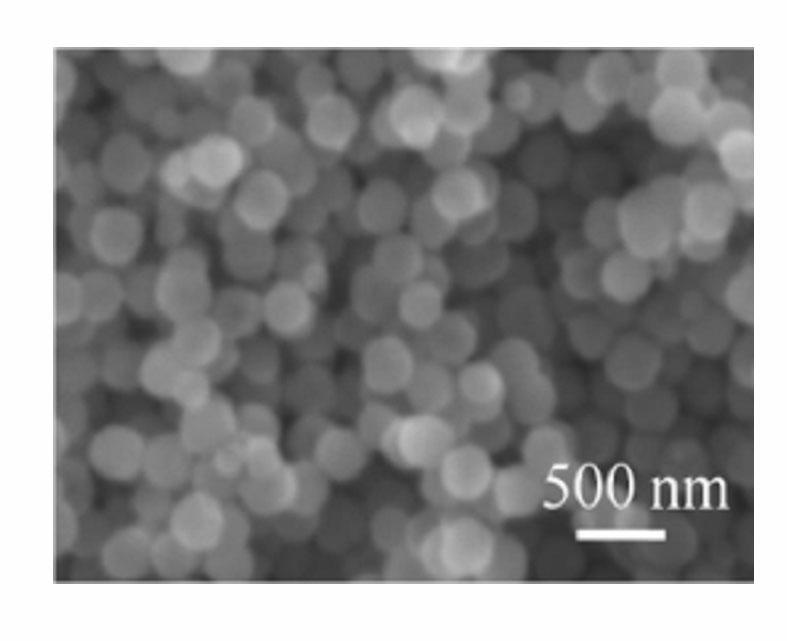
[0025] According to the preparation process, 1.2 g FeCl 3 ·6H 2 O and 0.834 g of tetrabutylammonium chloride were added to 30 mL of ethylene glycol, and magnetically stirred to completely dissolve ferric chloride hexahydrate and tetrabutylammonium chloride to obtain a clear solution. 3.6 g of urea was added to the above clear solution, and under the action of magnetic stirring, it was fully mixed to obtain a reddish-brown clear solution. The solution was sealed and placed in a polytetrafluoroethylene-lined reactor with a volume of 50 mL, and the reactor was placed in an oven, heated to 180 °C, and reacted for 36 h. After the reaction, the obtained black precipitate was washed by centrifugation with deionized water and absolute ethanol three times, and then dried at 60°C for 12 h to obtain ferric oxide particles. Scanning electron microscope observation and magnetic performance test results see figure 1 . The characterization shows that the morphology of the product is sphe...
Embodiment 2
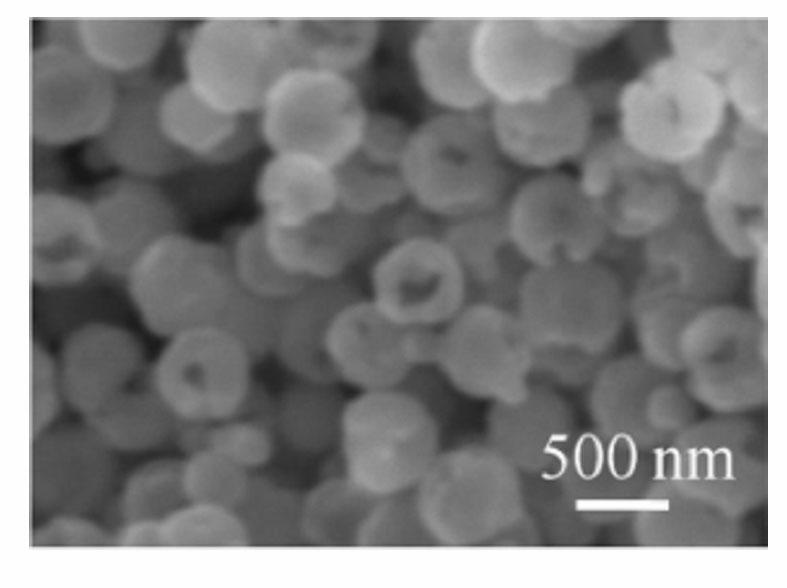
[0027] According to the preparation process, 1.2 g FeCl 3 ·6H 2 O and 0.834 g of tetrabutylammonium chloride were added to 30 mL of ethylene glycol, and magnetically stirred to completely dissolve ferric chloride hexahydrate and tetrabutylammonium chloride to obtain a clear solution. 3.6 g of urea was added to the above clear solution, and under the action of magnetic stirring, it was fully mixed to obtain a reddish-brown clear solution. The solution was sealed and placed in a polytetrafluoroethylene-lined reactor with a volume of 50 mL, and the reactor was placed in an oven, heated to 220 °C, and reacted for 36 h. After the reaction, the obtained black precipitate was washed by centrifugation with deionized water and absolute ethanol three times respectively, and then dried at 60°C for 12 h to obtain ferric oxide particles. Scanning electron microscope observation and magnetic performance test results see figure 2 . The characterization shows that the morphology of the p...
Embodiment 3
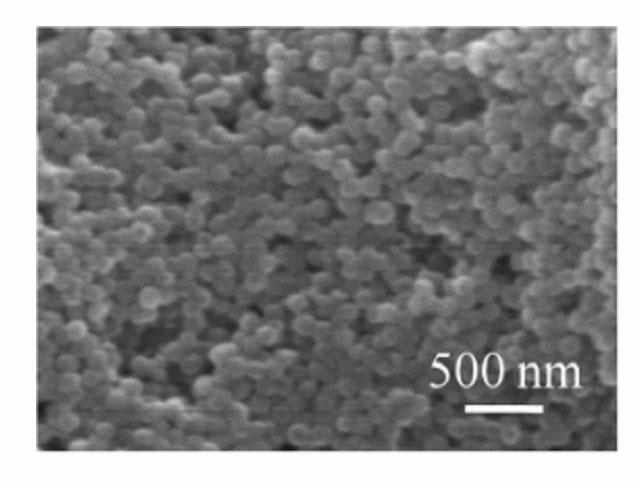
[0029] According to the preparation process, 1.2 g FeCl 3 ·6H 2 O and 0.834 g of tetrabutylammonium chloride were added to 30 mL of ethylene glycol, and magnetically stirred to completely dissolve ferric chloride hexahydrate and tetrabutylammonium chloride to obtain a clear solution. 3.6 g of urea was added to the above clear solution, and under the action of magnetic stirring, it was fully mixed to obtain a reddish-brown clear solution. The solution was sealed and placed in a polytetrafluoroethylene-lined reactor with a volume of 50 mL, and the reactor was placed in an oven, heated to 200 °C, and reacted for 8 h. After the reaction, the obtained black precipitate was washed by centrifugation with deionized water and absolute ethanol three times respectively, and then dried at 60°C for 12 h to obtain ferric oxide particles. Scanning electron microscope observation and magnetic performance test results see image 3 . The characterization shows that the morphology of the pro...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Saturation magnetization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Saturation magnetization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Saturation magnetization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com