Anti-fog coating composition
A technology of anti-fog coating and composition, which is applied in coating, lighting and heating equipment, transportation and packaging, etc. It can solve the problems of reducing the brightness of car lights, affecting the appearance of lenses, and making users unhappy, so as to improve the suppression effect and improve The effect of hydrophilicity and excellent adhesion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0055] [Manufacturing method of copolymer (A)]
[0056] The copolymer (A) is produced by copolymerizing a monomer mixture containing the above-mentioned monomers (A1), (A2), (A3) and optionally (A4). The structure of the copolymer can be any structure of random copolymer, alternating copolymer, block copolymer and graft copolymer, but it can improve the anti-fog performance of the anti-fog coating composition, and at the same time From the viewpoint of being able to easily prepare an anti-fog coating composition, a random copolymer is preferable. As a polymerization method for obtaining a copolymer, various well-known polymerization methods such as radical polymerization, cationic polymerization, anionic living polymerization, and cationic living polymerization can be used, but the ease of industrial productivity and product performance vary. From the viewpoint of chemicalization, radical polymerization is particularly preferred. As the radical polymerization method, block p...
Embodiment 1
[0100] The following compounds were placed in a reaction vessel equipped with a stirring device, a nitrogen gas introduction pipe, and a condenser, and heated to 65° C. while blowing nitrogen gas.
[0101] 240g n-propanol (hereinafter referred to as NPA) as polymerization solvent;
[0102] 10g of N-methylolacrylamide (hereinafter referred to as N-MAA) as monomer (A1);
[0103] 10g of 2-acrylamide-2-methylpropanesulfonic acid (hereinafter referred to as AMPS) as monomer (A2);
[0104] 60g methyl methacrylate (hereinafter referred to as MMA), 20g n-butyl acrylate (hereinafter referred to as BA) as monomer (A3);
[0105] 20g N,N-dimethylacrylamide (hereinafter referred to as DMAA) as monomer (A4);
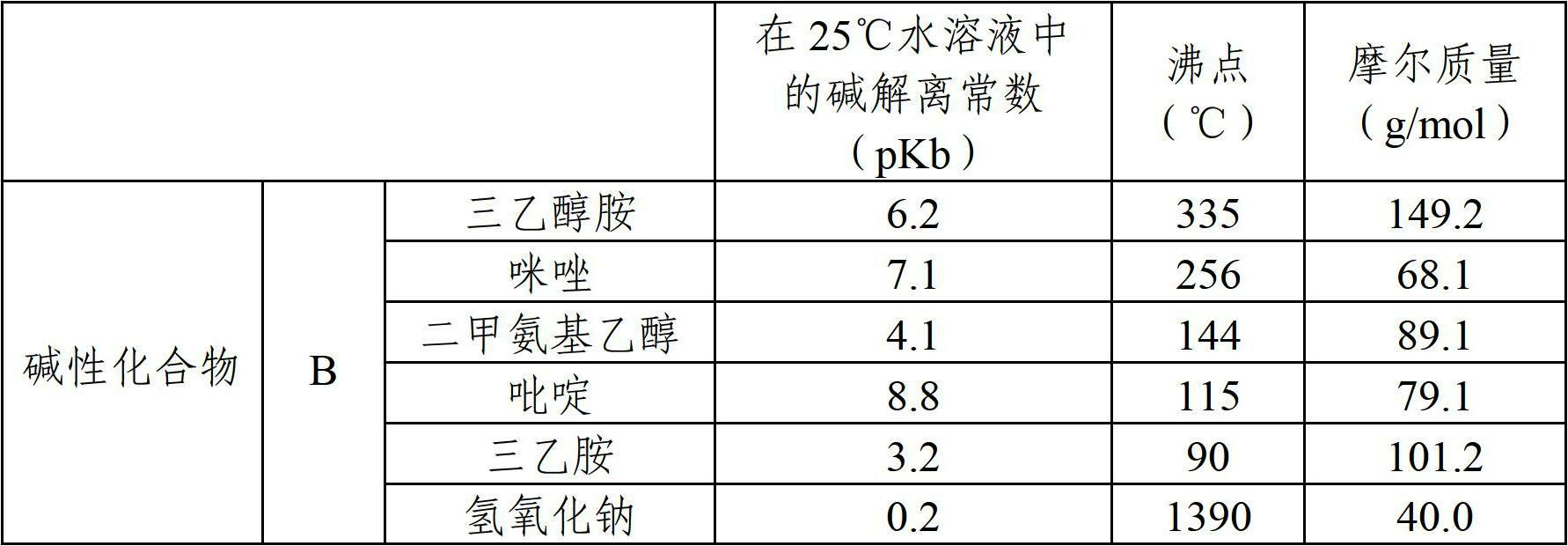
[0106] 5.04 g of triethanolamine (see Table 1, base dissociation constant pKb in aqueous solution at 25°C = 6.2, boiling point 335°C) as basic compound (B).
[0107] In addition, the amount of the basic compound (B) corresponds to 70 mol% of the sulfonic acid groups of AMPS as the ...
Embodiment 2~8
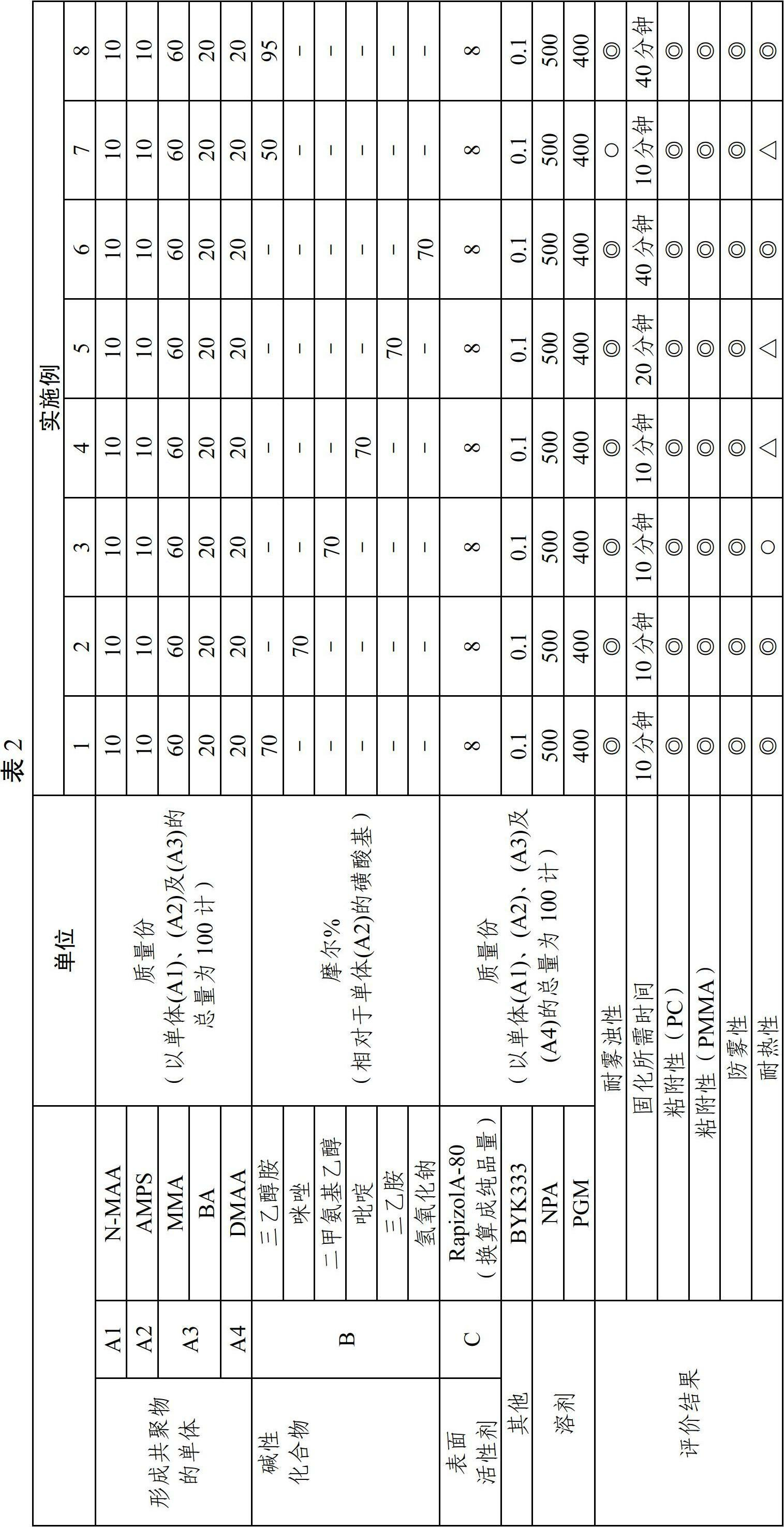
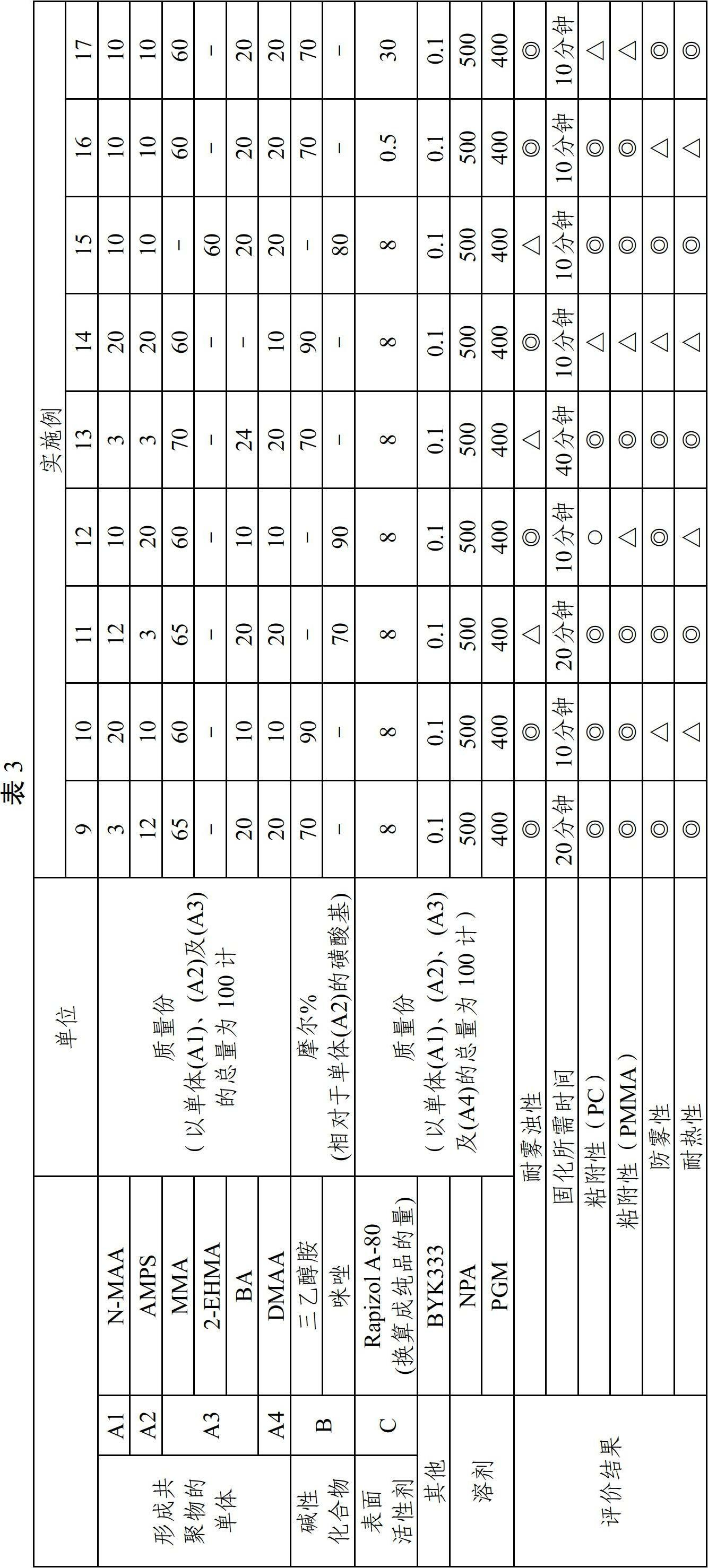
[0142]Except that the kind of the basic compound (B) and the addition amount of the sulfonic acid group relative to the monomer (A2) are changed as shown in Table 2, all the other prepare the copolymer solution according to the same method as in Example 1, and then The anti-fog coating compositions were prepared and evaluated respectively, and the results are shown in Table 2. In addition, the physical properties of the basic compound (B) used in each example are shown in Table 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| humidity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| humidity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com