Patents
Literature
1953 results about "Anti-fog" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Anti-fog agents, also known as anti-fogging agents and treatments, are chemicals that prevent the condensation of water in the form of small droplets on a surface which resemble fog. Anti-fog treatments were first developed by NASA during Project Gemini, and are now often used on transparent glass or plastic surfaces used in optical applications, such as the lenses and mirrors found in glasses, goggles, camera lenses, and binoculars. The treatments work by minimizing surface tension, resulting in a non-scattering film of water instead of single droplets. This works by altering the degree of wetting. Anti-fog treatments usually work either by application of a surfactant film, or by creating a hydrophilic surface.
Coating composition for multiple hydrophilic applications
InactiveUS20030203991A1Tough and durable and printable surfaceImprove wettabilityOther chemical processesSynthetic resin layered productsColloidWear resistance
A coating composition is disclosed which comprises an aqueous polymeric matrix, a hydrophilic polymer, a colloidal metal oxide and a crosslinker. The coating composition when applied on medical devices is hydrophilic, shows improved lubricity, abrasion resistance and substrate adhesion on metallic or plastic substrates. The coating also shows improved water sheeting thus providing the coated substrates with anti-fog properties. The coating absorbs aqueous dye or stain solutions making the substrate suitable for printing.
Owner:HYDROMER INC
Coating composition for multiple hydrophilic applications
InactiveUS7008979B2Improve adhesionImprove the lubrication effectSurgerySynthetic resin layered productsColloidWear resistance
Owner:HYDROMER INC
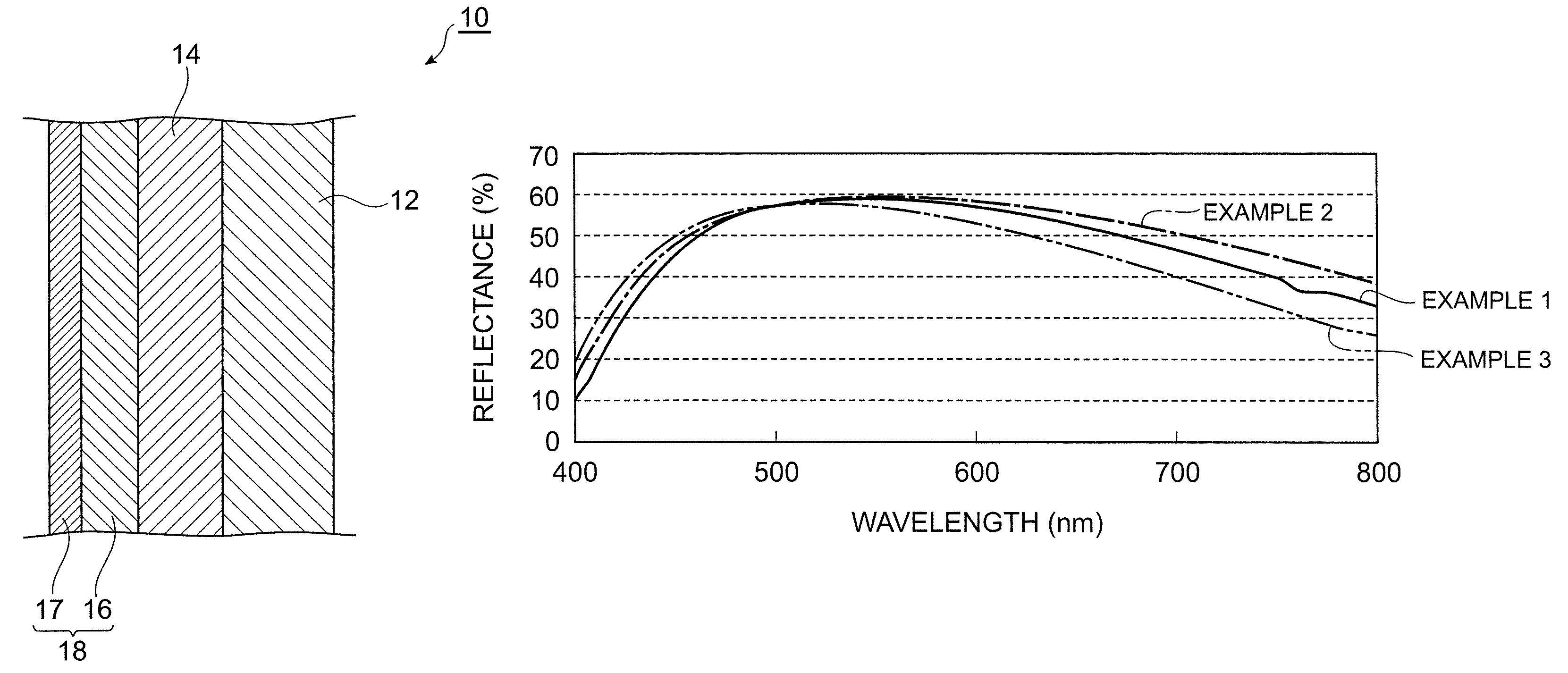
Colored anti-fog mirror
A colored anti-fog mirror that emits reflected light in response to incident light, the colored anti-fog mirror comprising a substrate, a hydrophilic functional layer containing a photocatalytic substance, and a metallic reflecting film provided between the substrate and the hydrophilic functional layer, wherein a material of the metallic reflecting film and a thickness of the hydrophilic functional layer are set such that the reflected light has a spectral reflection spectrum having a maximum reflectance in the visible region over 510 nm and not more than 600 nm.
Owner:MURAKAMI CORP
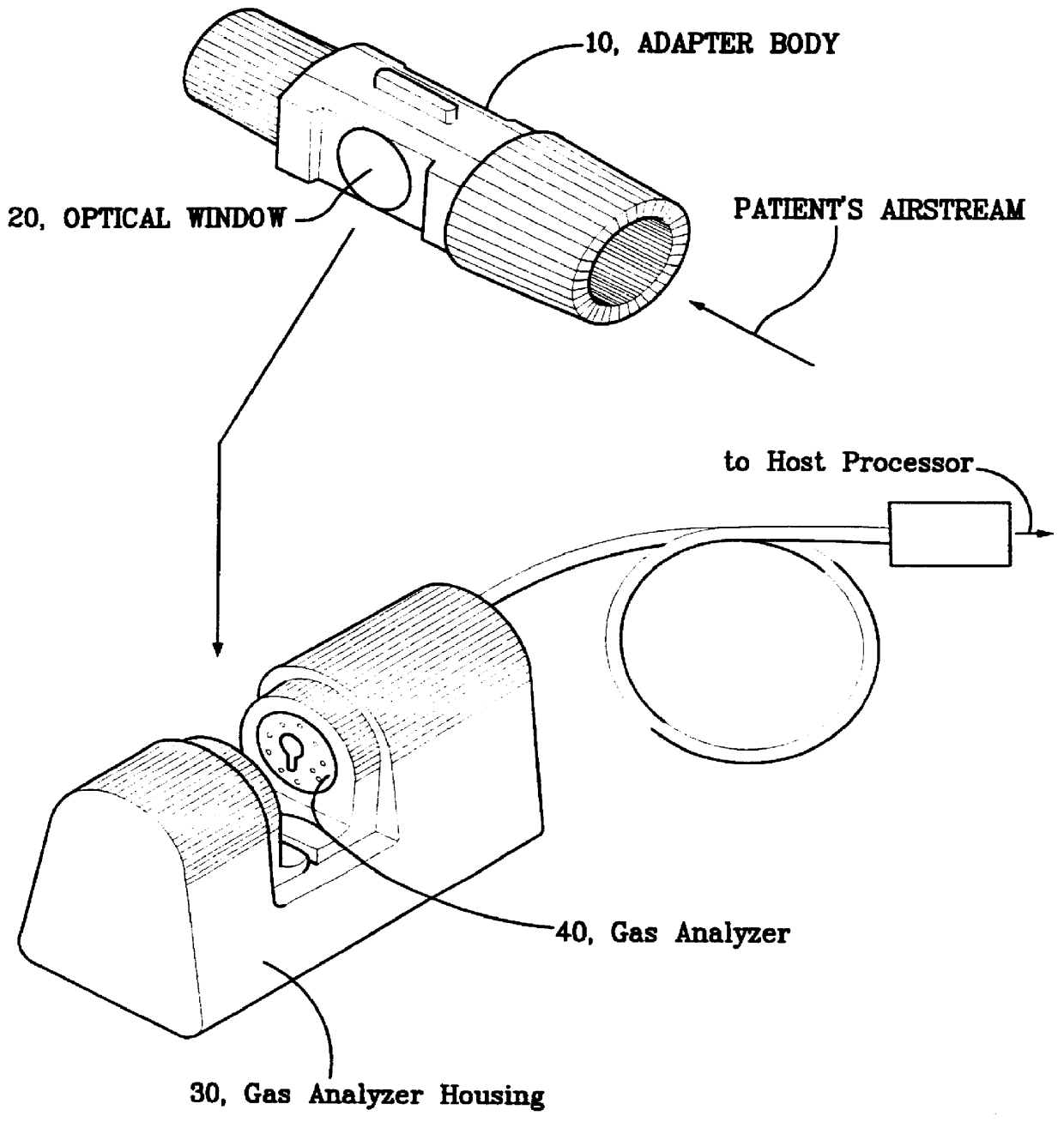
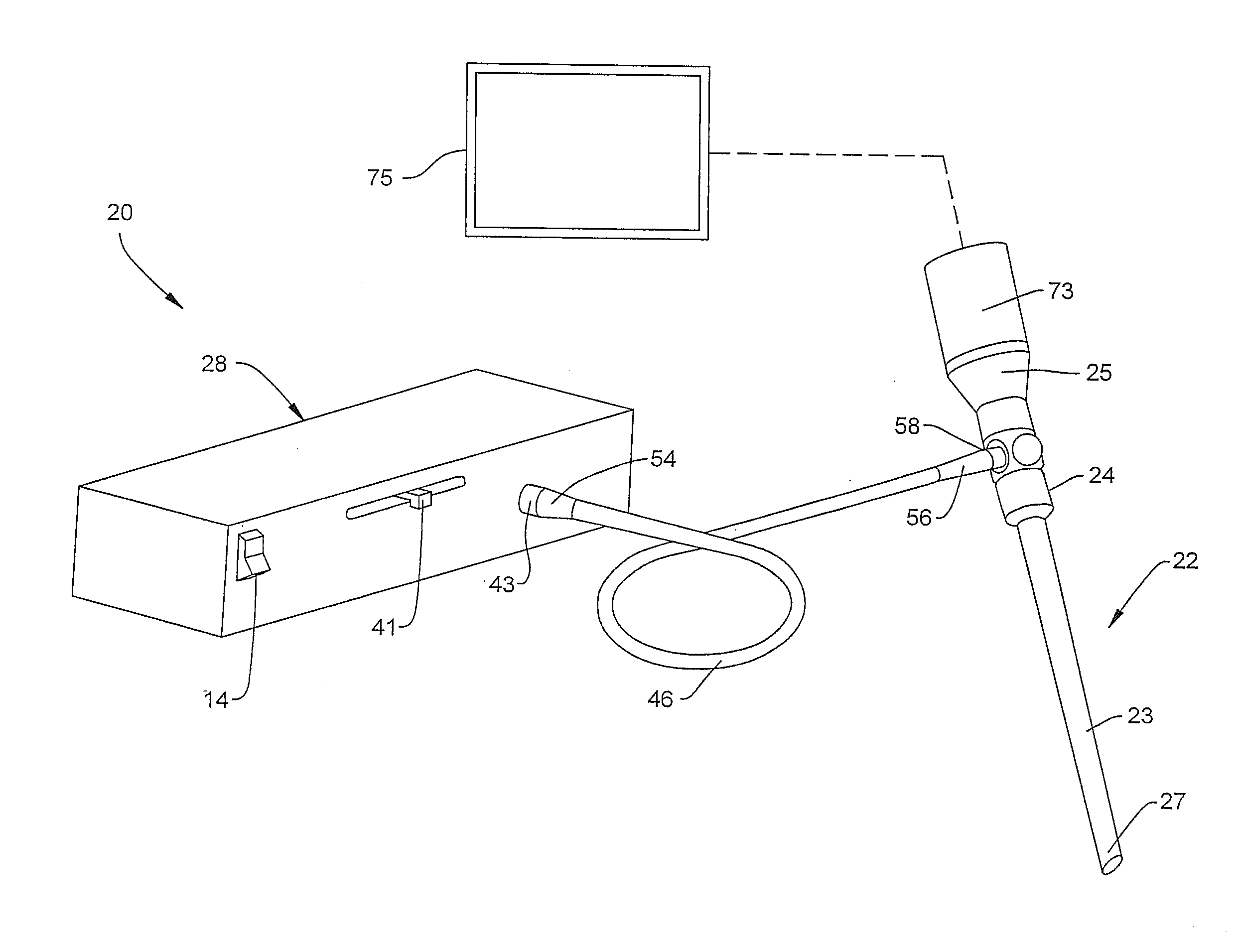
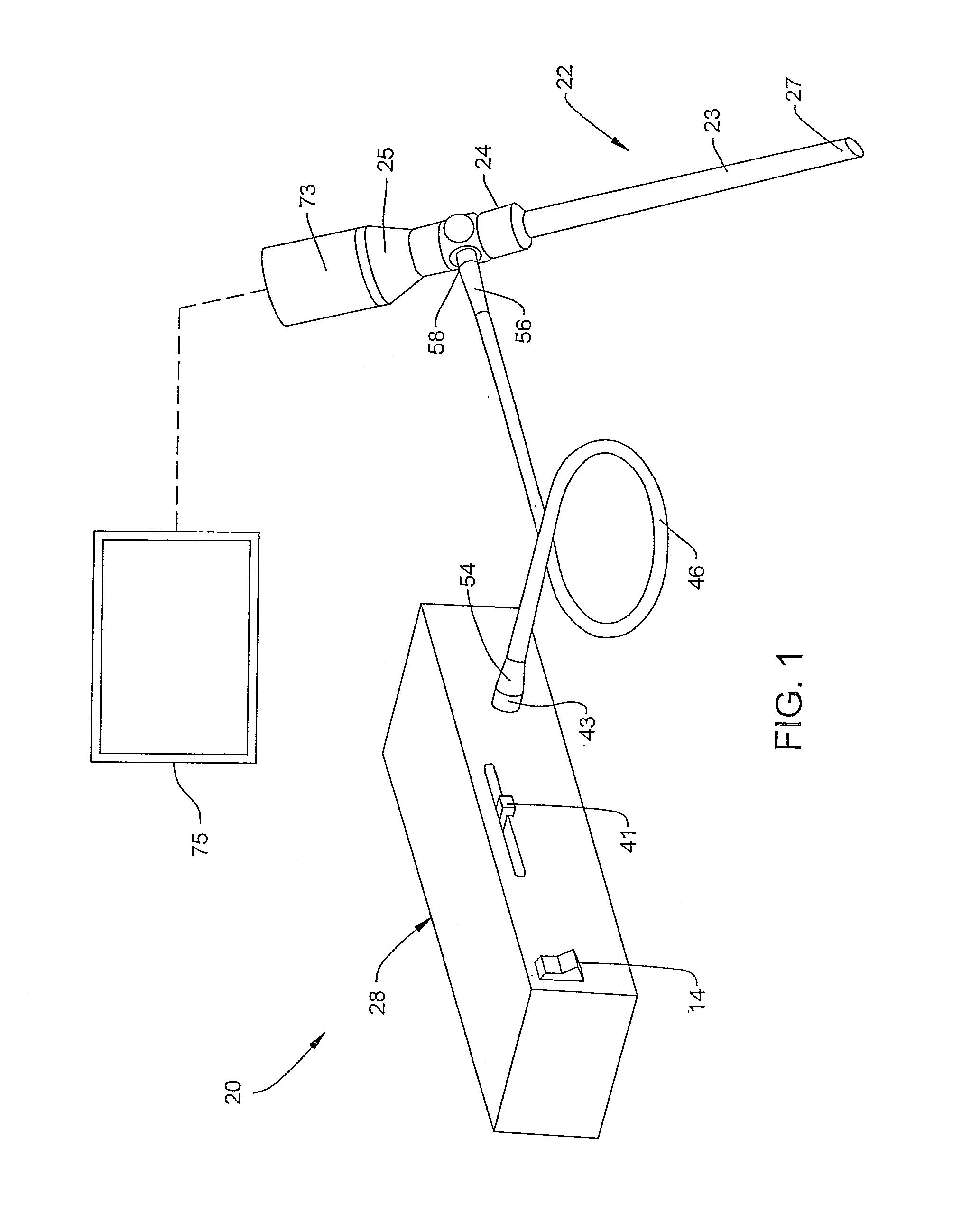
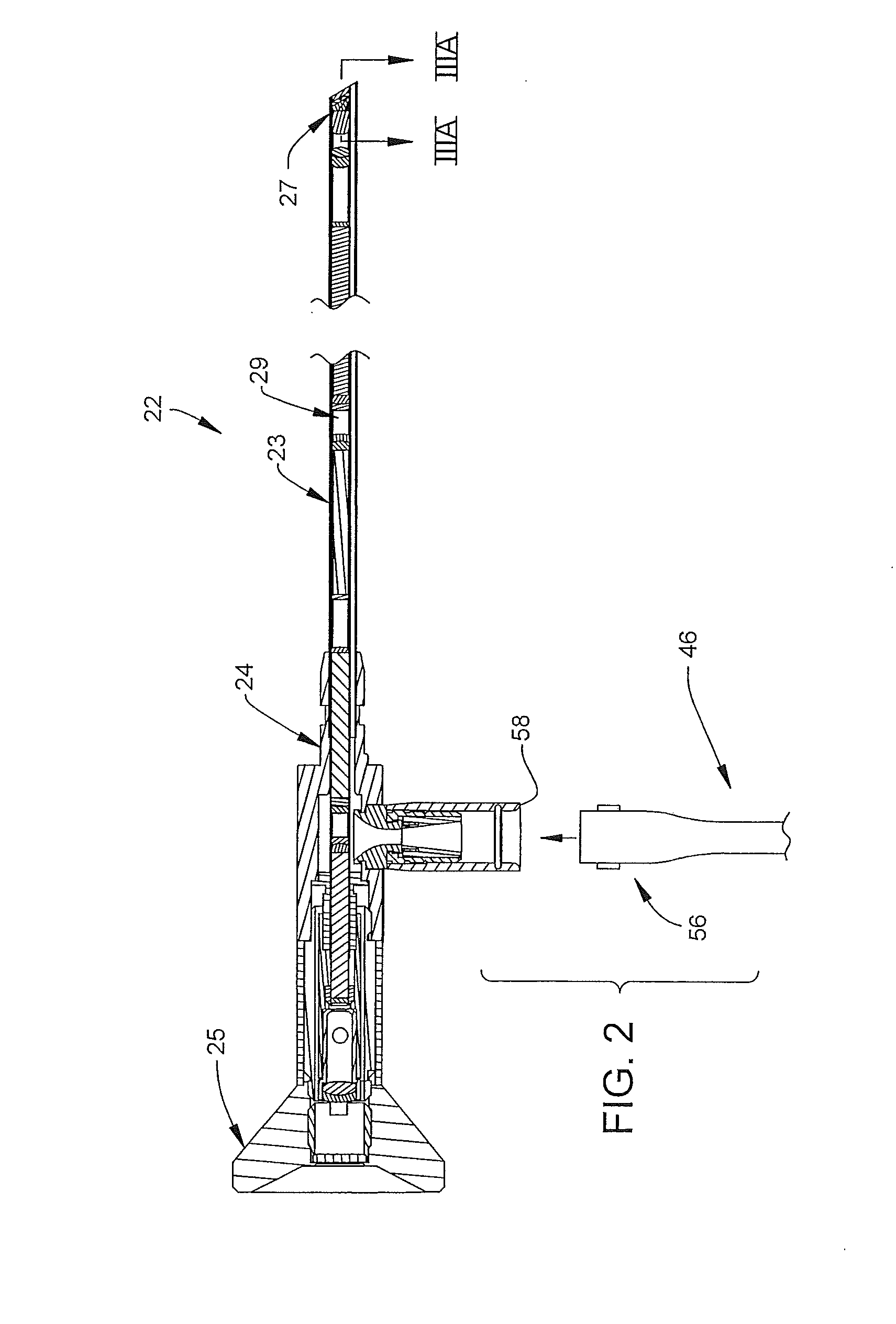
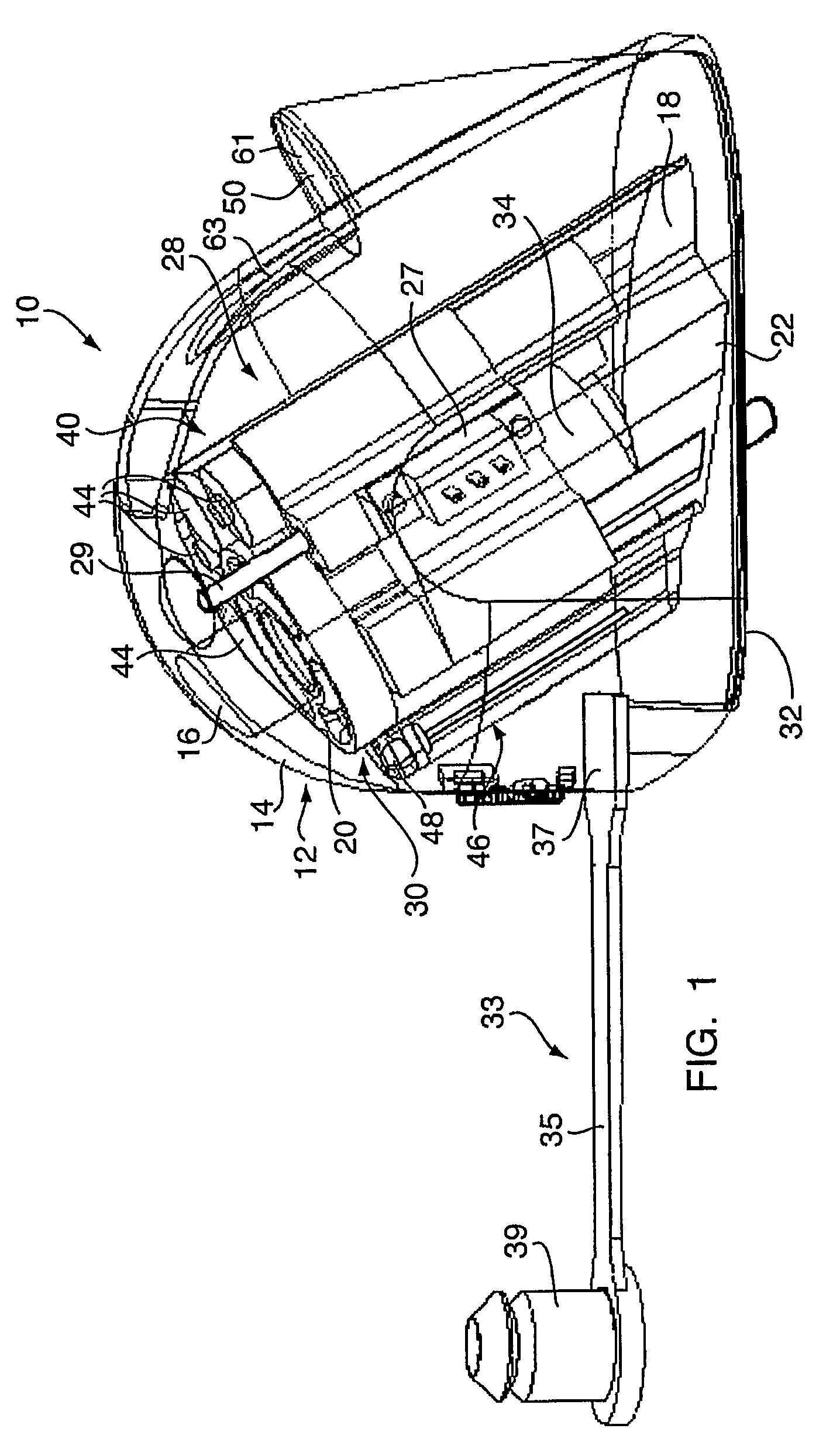
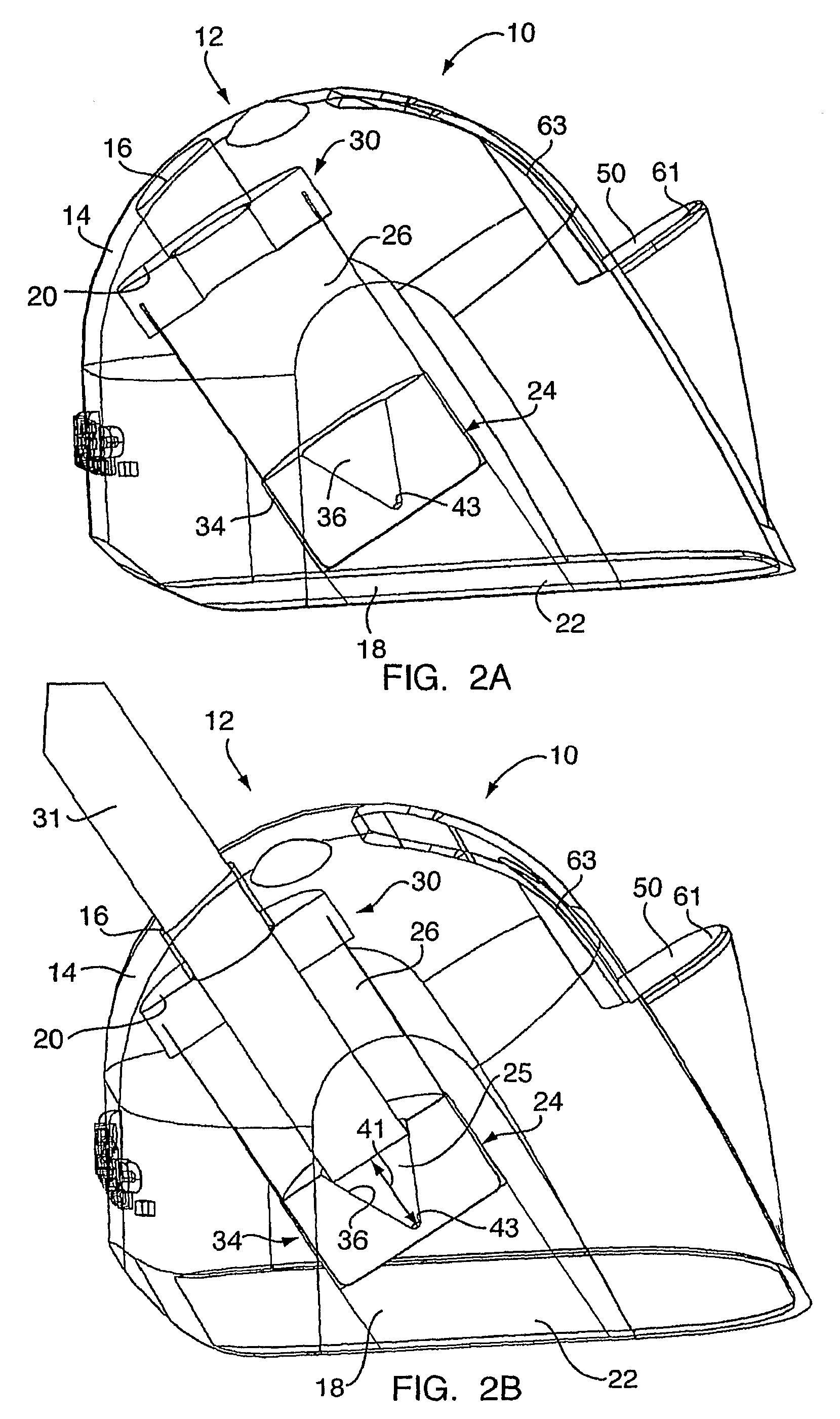
Device For White Balancing And Appying An Anti-Fog Agent To Medical Videoscopes Prior To Medical Procedures
ActiveUS20080161646A1Improve visualizationPrevent foggingBronchoscopesColor signal processing circuitsLens plateEndoscope
A device is configured for white balancing a medical videoscopic camera system prior to videoscopic medical procedures, as well as optionally simultaneously or non-simultaneously applying a fog-prohibiting agent to the distal lens of a medical videoscope such as an endoscope or laparoscope. The device combines a white balancing mechanism, protective mechanism, and defogging mechanism in one simple easy to use device.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
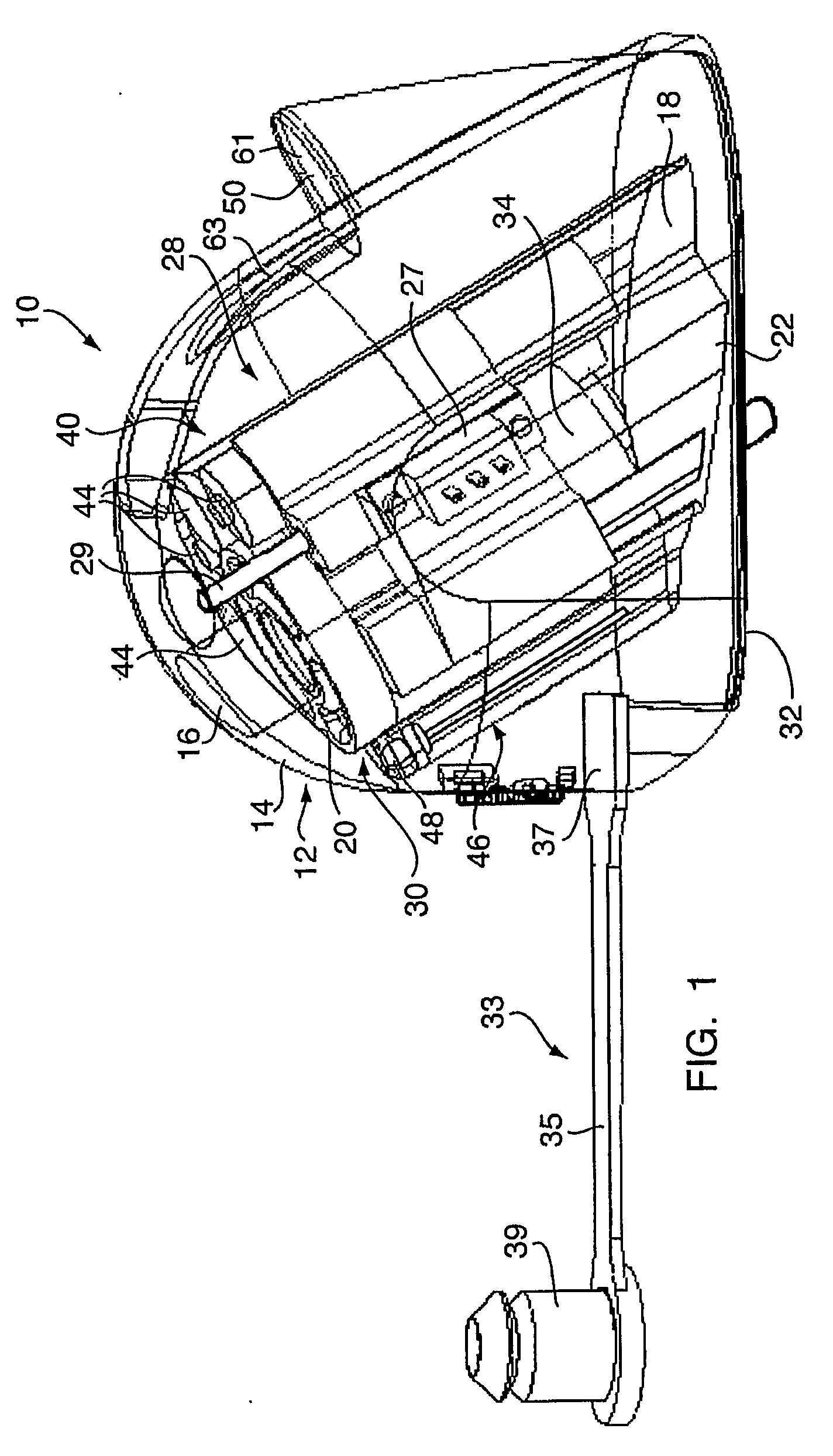
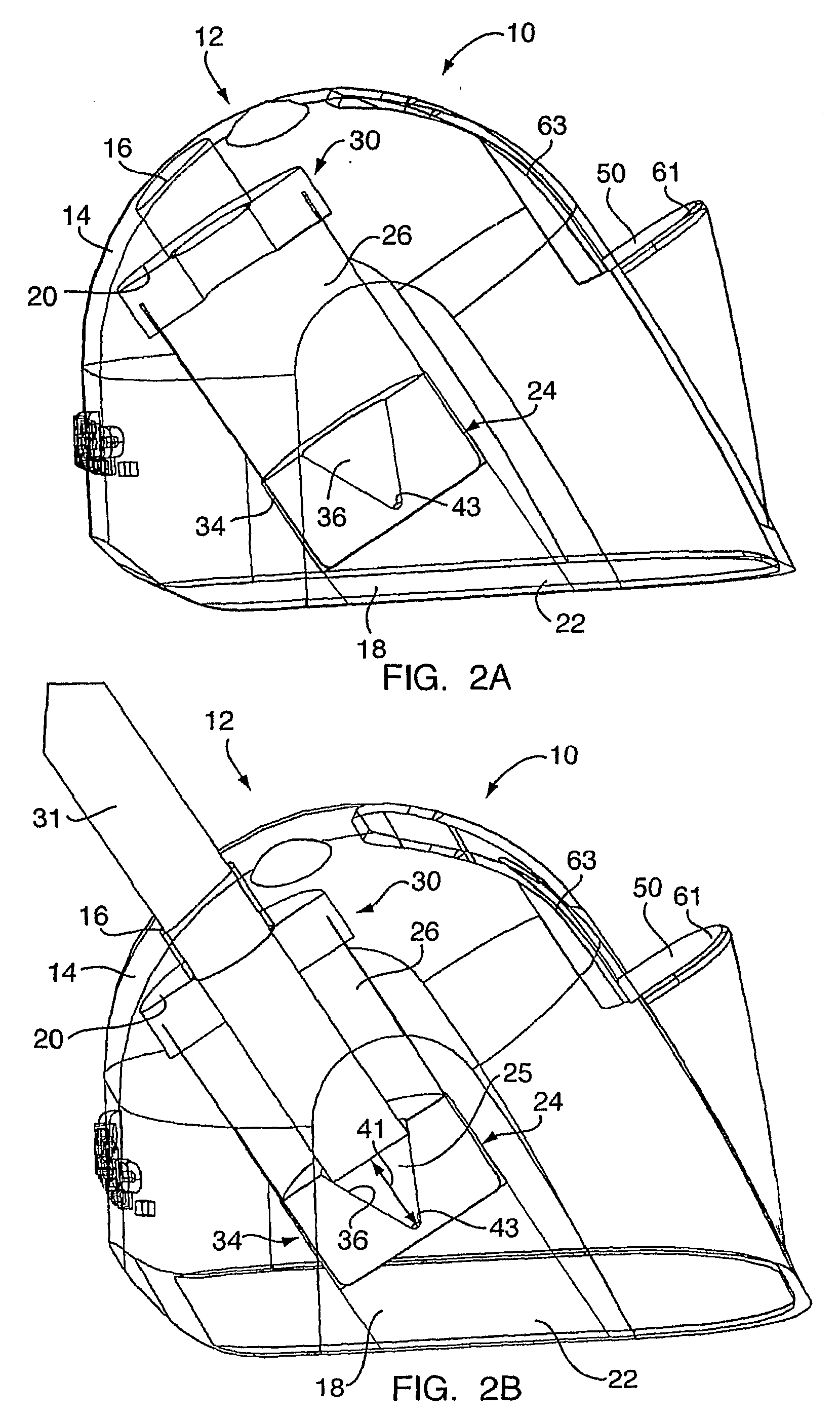
Disposable anti-fog airway adapter
InactiveUS6095986AImprove abilitiesOvercome problemsRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAirway adaptorHeat capacity
A disposable anti-fog airway adapter for use with a mainstream respiratory gas analyzer which provides a measurement of a patient's inhaled and exhaled gases. The airway adapter includes windows that are constructed of a thin, low heat capacity plastic that rapidly equilibrates to the temperature of the warm moist gases in the patient breathing circuit. In addition, the inside of the windows is also coated with an anti-fog surfactant either by laminating an anti-fog film with the window plastic prior to attaching the window to the airway adapter body or by first attaching the window to the airway adapter body and then applying the surfactant to the airway adapter after the window film is bonded in place so that the surfactant coats the entire inside of the adapter. The surfactant functions to increase the critical wetting tension of the surface it covers so that water on the window spreads into a uniform thin layer which does not absorb very much infrared energy and thus does not significantly reduce the signal strength. "Instant on" operation is accomplished because no heater and the like is necessary to warm up the windows to maintain them at an elevated temperature to prevent fogging. Numerous techniques are also provided for adhering the windows to the airway adapter body so that a substantially airtight seal may be obtained.
Owner:OSI OPTOELECTRONICS
Method of making an antifogging window plate of synthetic resins
InactiveUS6024904AReduce the number of stepsFlat surfaceMouldsSynthetic resin layered productsConductive pasteEngineering
An antifogging window plate has a transparent film and a base both made of thermoplastic resins. Conductive lines and electrodes are printed using a conductive paste on one side of the film, which is then bonded to the base. One portion of each electrode is exposed as a terminal portion to be connected to an electric contact member. The window plate is made by injection molding with the surface of the film opposite from the printed surface being in contact with the cavity wall of the mold, so that the integration of the film with the base is effected simultaneously with the forming of base. Each contact member is subsequently fitted in an injection-molded void facing the terminal portion, or is secured in place at the same time as the injection molding.
Owner:TSUTSUNAKA PLASTIC IND
Anti-fogging device for endoscope
Anti-fogging system for an endoscope including an endoscope having an outer housing, an imaging arrangement, and a distal window. A filter lens is located at the distal window, with the filter lens allowing a first portion of electromagnetic light to pass therethrough while absorbing a second portion of electromagnetic light in order to heat the filter lens.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
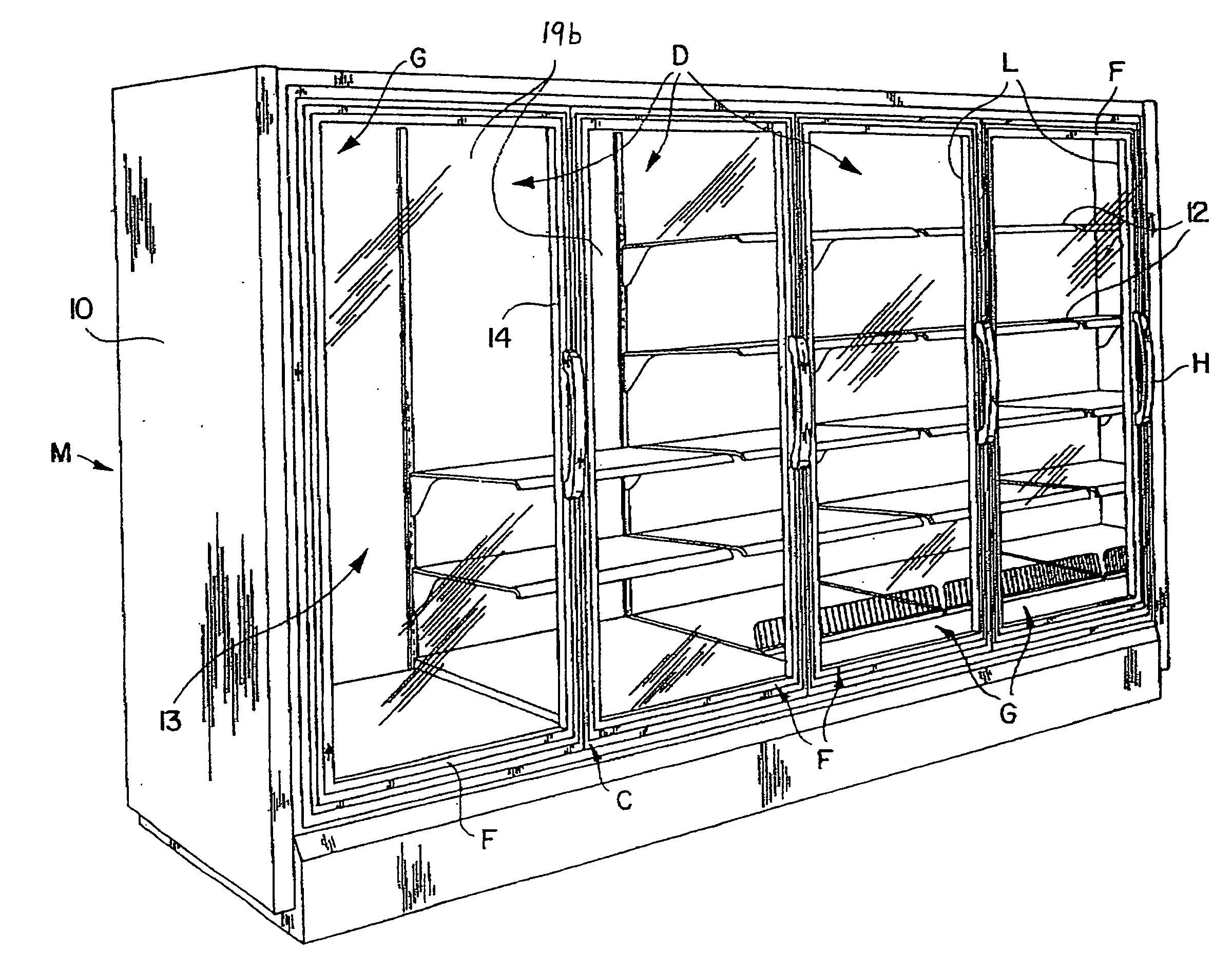
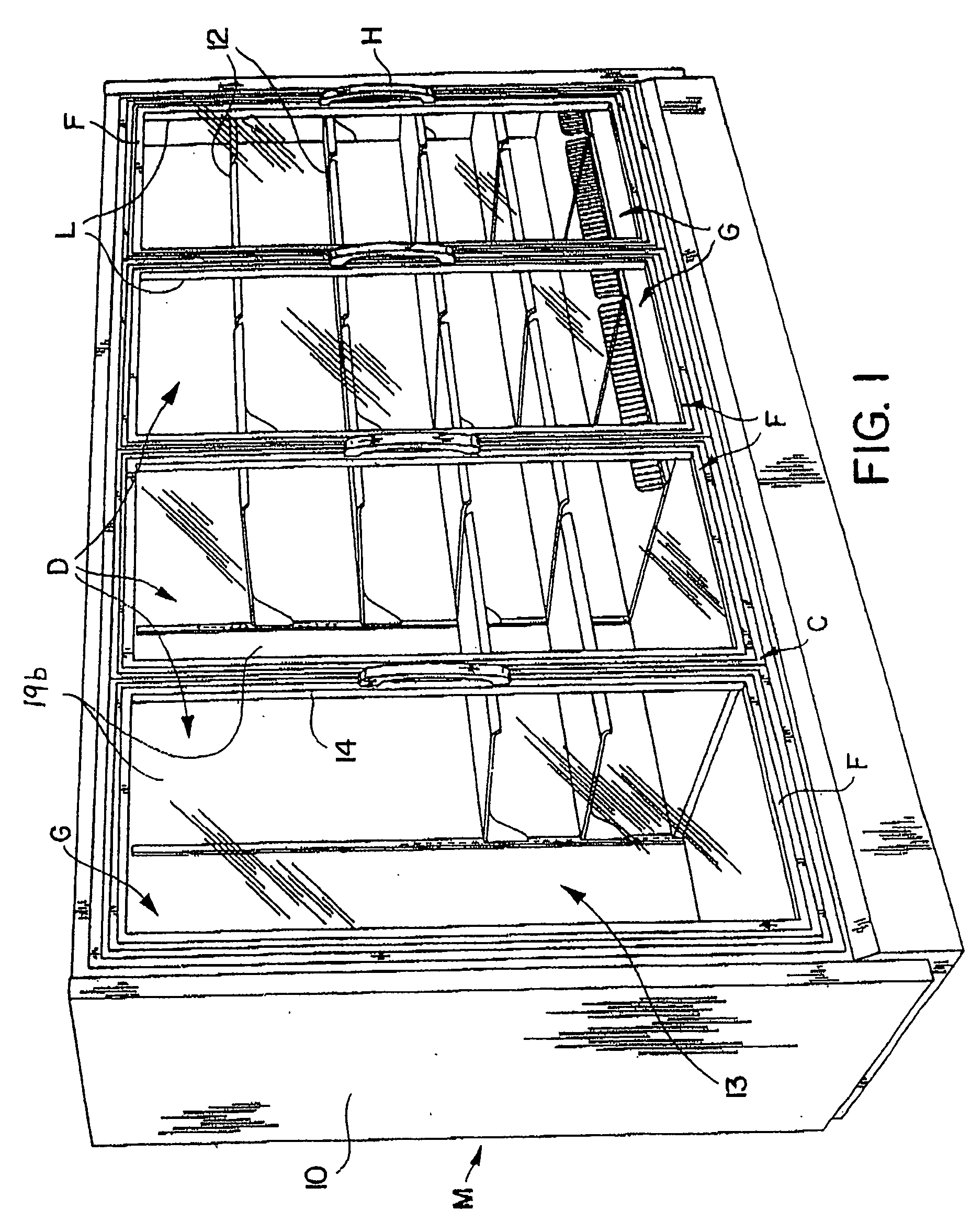
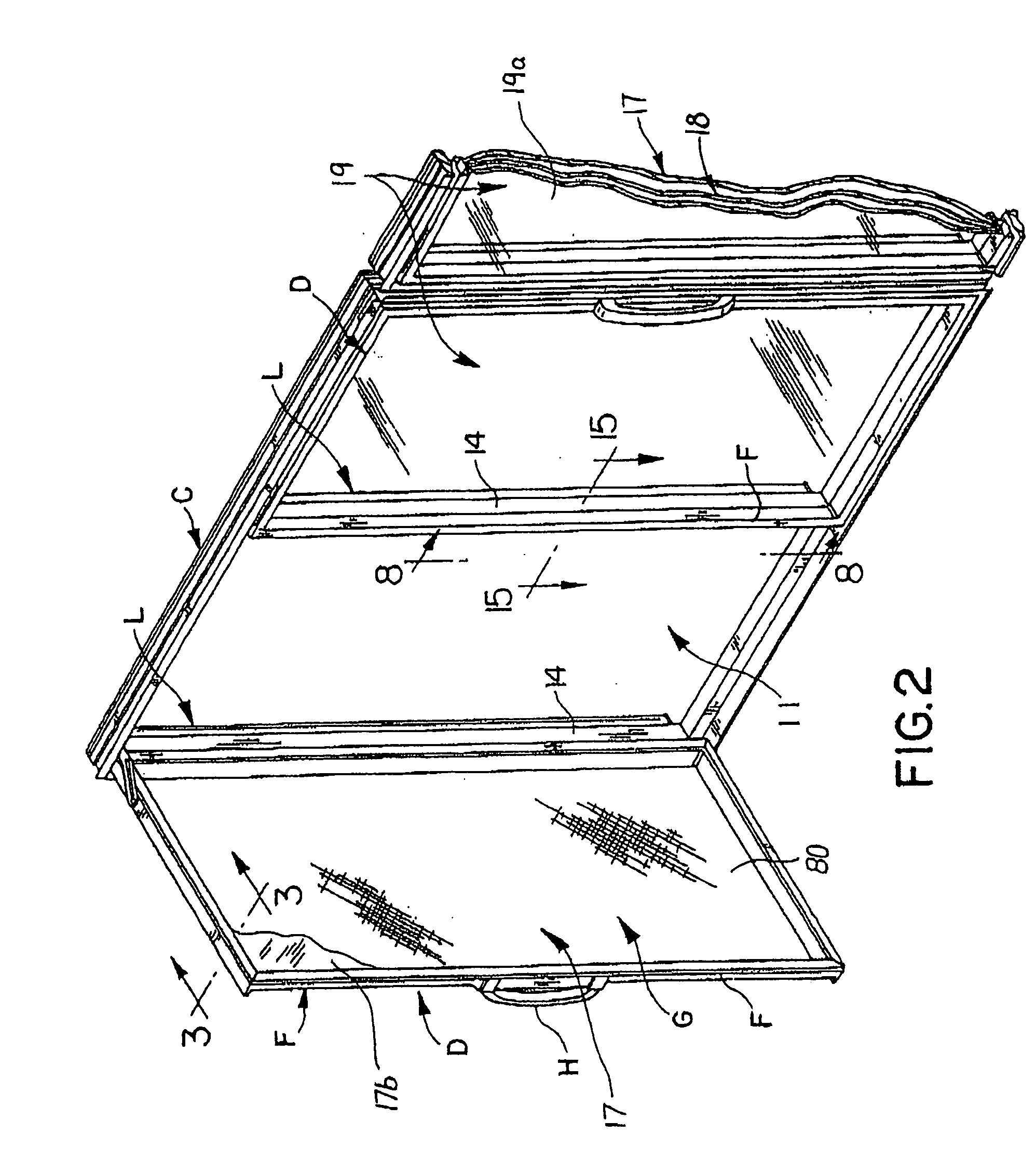
Anti-fog refrigeration door and method of making the same
InactiveUS20060265979A1BurdeningIncreased energy costShow cabinetsRailway roofsThermal insulationLow emissivity
The energy-free refrigeration door of the present application provides a way to control condensation when the door of a refrigeration unit is opened by providing thermal insulation to the door with glass panels which have a low emissivity coating. The door includes a door frame housing and an insulating glass unit comprising inner, middle and outer sheets of glass. A first sealant assembly disposed around the periphery of the inner and middle sheets of glass forms a first chamber between the inner and middle sheets of glass. A second sealant assembly disposed around the periphery of the middle and outer sheets of glass forms a second chamber between the middle and outer sheets of glass. A gas, such as krypton, air, or argon is held in the first and second chambers. The outer sheet of glass and inner sheet of glass each have an unexposed surface that faces the middle sheet of glass. A low emissivity coating is disposed on the unexposed surfaces of the inner and outer sheets of glass so that the glass door as a whole avoids formation of condensation on the outer surface of the outer sheet of the glass door, without the application of electricity to heat the door, while also providing the desired evaporation rate of condensation from the inner side of the inner sheet of the glass door. An anti-fog or anti-frost coating is included on a surface of one of the sheets of glass.
Owner:AGC FLAT GLASS NORTH AMERICA INC
Injection molding of lens
InactiveUS7077985B2Good photochromic efficiency and durabilityGood effectSpectales/gogglesSynthetic resin layered productsPhotochromic lensInjection molding machine
A flat or curved photochromic laminate structure and a plastic photochromic lens blank can be produced in a simple and efficient manner from relatively low-cost polymeric sheet materials. These laminates can be used to provide goggles, face shields, windows, window coverings, skylights, and optical lenses having efficient, uniform and high quality photochromic properties. The use of a polyesterurethane as the binder for the photochromic material has been found to improve the performance of the photochromic material. There may be a desire to have a protective exterior layer (e.g., an abrasion resistant layer) in combination with the lens system, but that may be provided in various methods. In the case of using the laminate in a goggle application, the laminate may be hard coated on one or both outer surfaces with an abrasion resistant coating, antireflective coating, and / or an anti-fog hard coating.
Owner:HOYA OPTICAL LABS OF AMERICA INC
Merchandisers having anti-fog coatings and methods for making the same
A variety of refrigerators and merchandisers having glass or plastic substrates that are substantially fog-resistant are provided. For example, refrigerator doors having a substantially transparent substrate including an anti-fog coating on at least a portion thereof are provided. Many of the coatings exhibit color stable properties.
Owner:HUSSMANN CORP
Method and apparatus for heating and applying warm antifog solution to endoscopes as well as a distal lens protector
InactiveUS7311660B2Avoid condensationImprove protectionExothermal chemical reaction heat productionOther heat production devicesCombined useTemperature difference
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
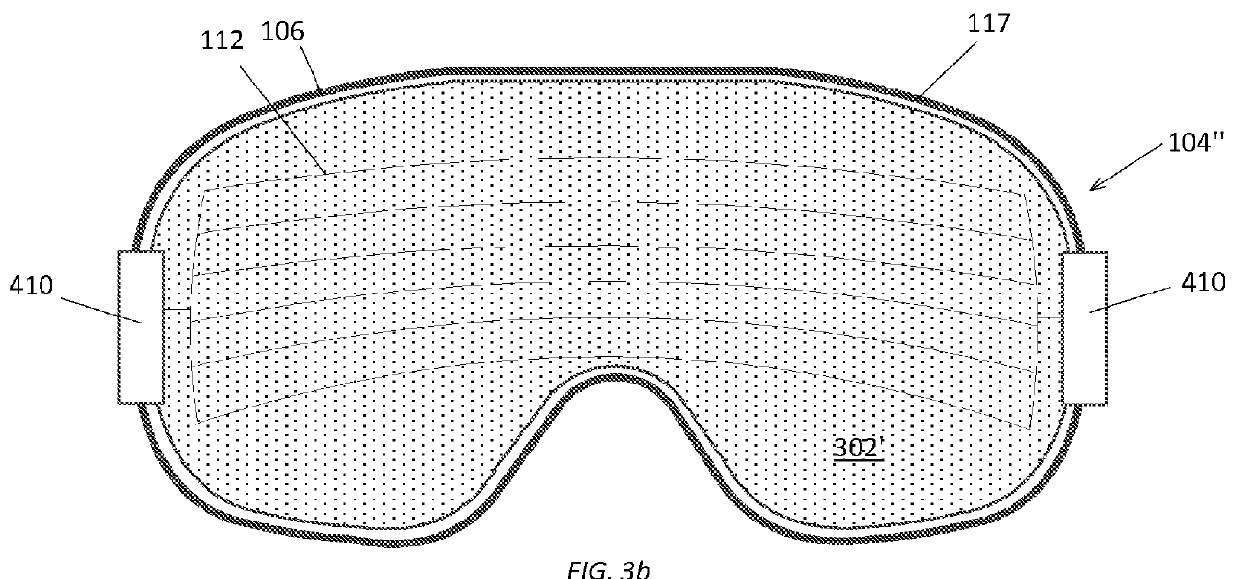
Goggle with easily interchangeable lens that is adaptable for heating to prevent fogging
ActiveUS20130091623A1Easy to adaptEasy interchangeGogglesNon-optical adjunctsElectrical resistance and conductanceInterconnection
Anti-fog, interchangeable-lens goggle adapted for use with a battery comprising: a body with a flexible posterior portion for engaging a user's face and an anterior portion; a lens having a resistive anti-fog element thereon, the lens adapted for engaging the anterior portion of the body; an engagement mechanism for releasably interconnecting the lens and the body; an interconnection mechanism depending from the body adapted for detachably interconnecting the heating element of the lens and the battery, the interconnection means operable or integral with the engagement mechanism such that interconnecting the heating element of the lens with the battery also reinforces interconnecting of the lens with the semi-rigid anterior portion of the body; and a strap adapted for holding the goggle on one of a user's head and helmet.
Owner:ABOMINABLE LABS LLC +1
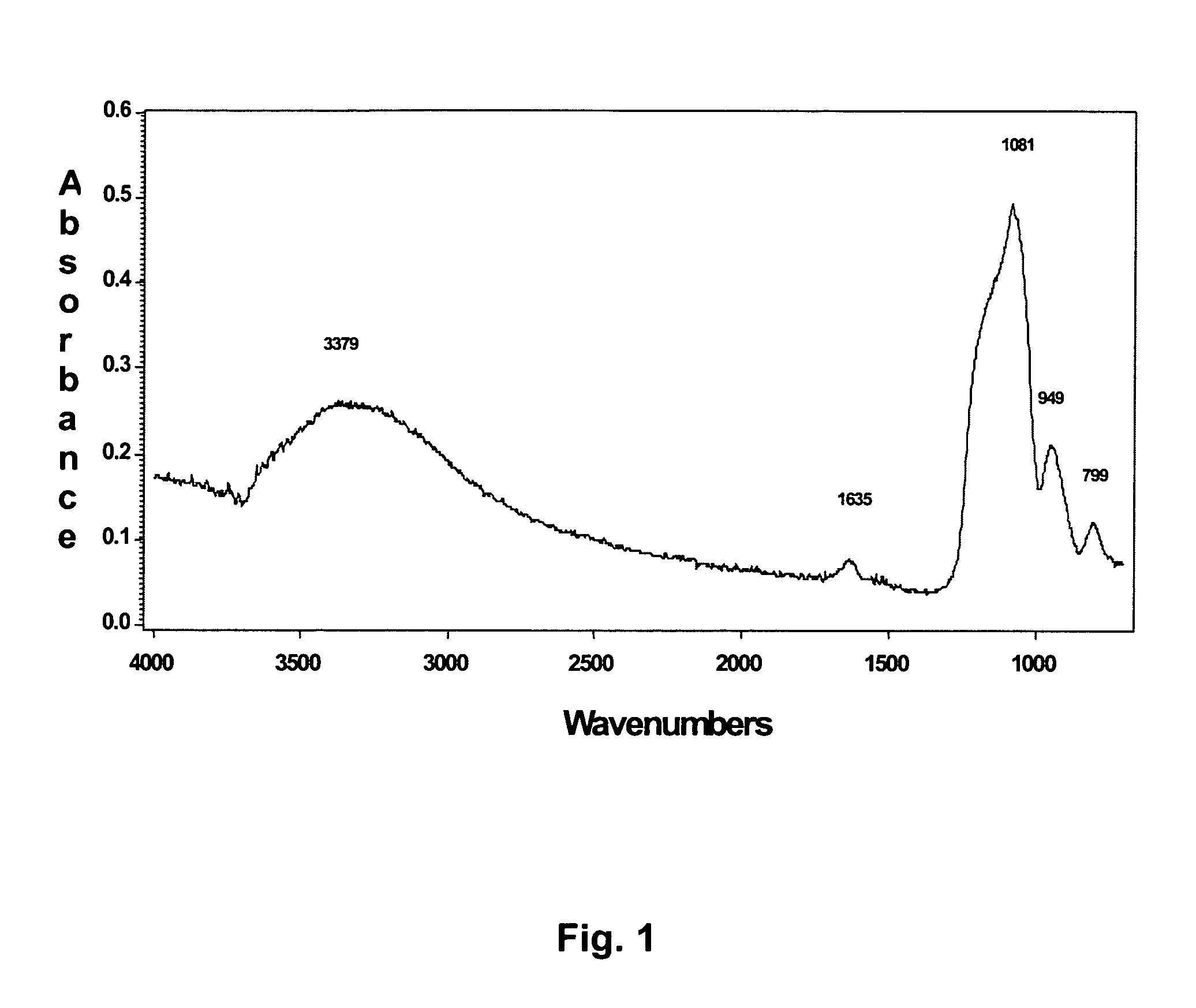
Anti-fog coating composition, anti-fog thin film and product
The invention provides an anti-fog coating composition which comprises at least one hydrophilic polymer; at least one anionic surfactant which accounts for 0.5% by weight-25% by weight calculated by taking the weight of the polymer as 100% by weight; inorganic oxide particles which account for 0% by weight-60% by weight calculated by taking the weight of the polymer as 100% by weight; and a solvent, wherein the polymer is at least one selected from cellulose, polyvinylpyrrolidone, polyacrylic acid, polypropylene amide and polyvinyl alcohol. The invention further provides an anti-fog thin film, which comprises a substrate and a coating which is positioned on one part of the surface of at least one surface of the substrate and produced by the composition. The invention also provides a product comprising the anti-fog thin film, such as masks and glasses for medical operations, mine masks, food packaging boxes, food packaging bags and the like.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Multi-layer coatings with an inorganic oxide network containing layer and methods for their application
InactiveUS7354650B2Good antifoulingImprove self-cleaningAlkali metal silicate coatingsPretreated surfacesAnti-fogInorganic oxide
Multi-layer coatings are disclosed that include (1) a first layer comprising an inorganic oxide network, and (2) a second layer applied over at least a portion of the first layer, wherein the second layer is deposited from at least one liquid composition that is hydrophilic and includes an essentially completely hydrolyzed organosilicate. Also disclosed are substrates coated with such multi-layer coatings, methods of applying such multi-layer coatings to a substrate and methods for improving the anti-fouling, self-cleaning, easy-to-clean, and / or anti-fogging properties of an article.
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
Injection molding of lens
InactiveUS20030214080A1Reduce distortionReduce strainSpectales/gogglesSynthetic resin layered productsPhotochromic lensInjection molding machine
A flat or curved photochromic laminate structure and a plastic photochromic lens blank can be produced in a simple and efficient manner from relatively low-cost polymeric sheet materials. These laminates can be used to provide goggles, face shields, windows, window coverings, skylights, and optical lenses having efficient, uniform and high quality photochromic properties. The use of a polyesterurethane as the binder for the photochromic material has been found to improve the performance of the photochromic material. There may be a desire to have a protective exterior layer (e.g., an abrasion resistant layer) in combination with the lens system, but that may be provided in various methods. In the case of using the laminate in a goggle application, the laminate may be hard coated on one or both outer surfaces with an abrasion resistant coating, antireflective coating, and / or an anti-fog hard coating.
Owner:HOYA OPTICAL LABS OF AMERICA INC
Merchandisers having anti-fog coatings and methods for making the same
Owner:HUSSMANN CORP
Facemasks containing an anti-fog / anti-glare composition
A coating composition that is incorporated into a facemask to reduce fogging and glare is provided. For example, in one embodiment, the facemask contains a shield or visor formed from a transparent substrate having at least one surface applied with the coating composition of the present invention. The present inventors have unexpectedly discovered that one or more water-soluble organic polymers, such as ethyl hydroxyethylcellulose, may be utilized as a principal component of the coating composition to reduce fogging and glare in a simple, yet effective manner.
Owner:O&M HALYARD INC
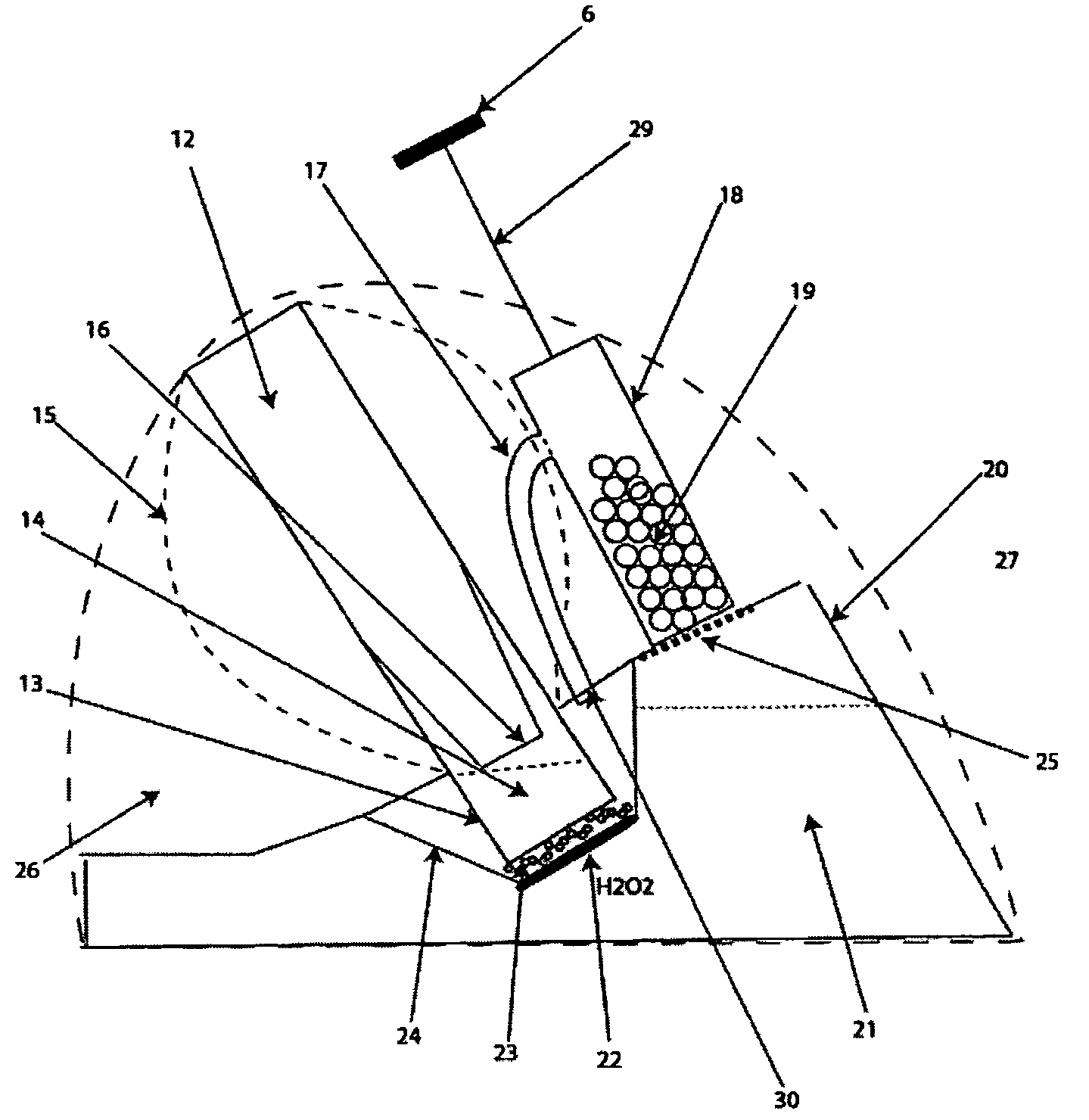
Method and device for evaluating inhibiting ability of drilling fluid on formation and decomposition of hydrate
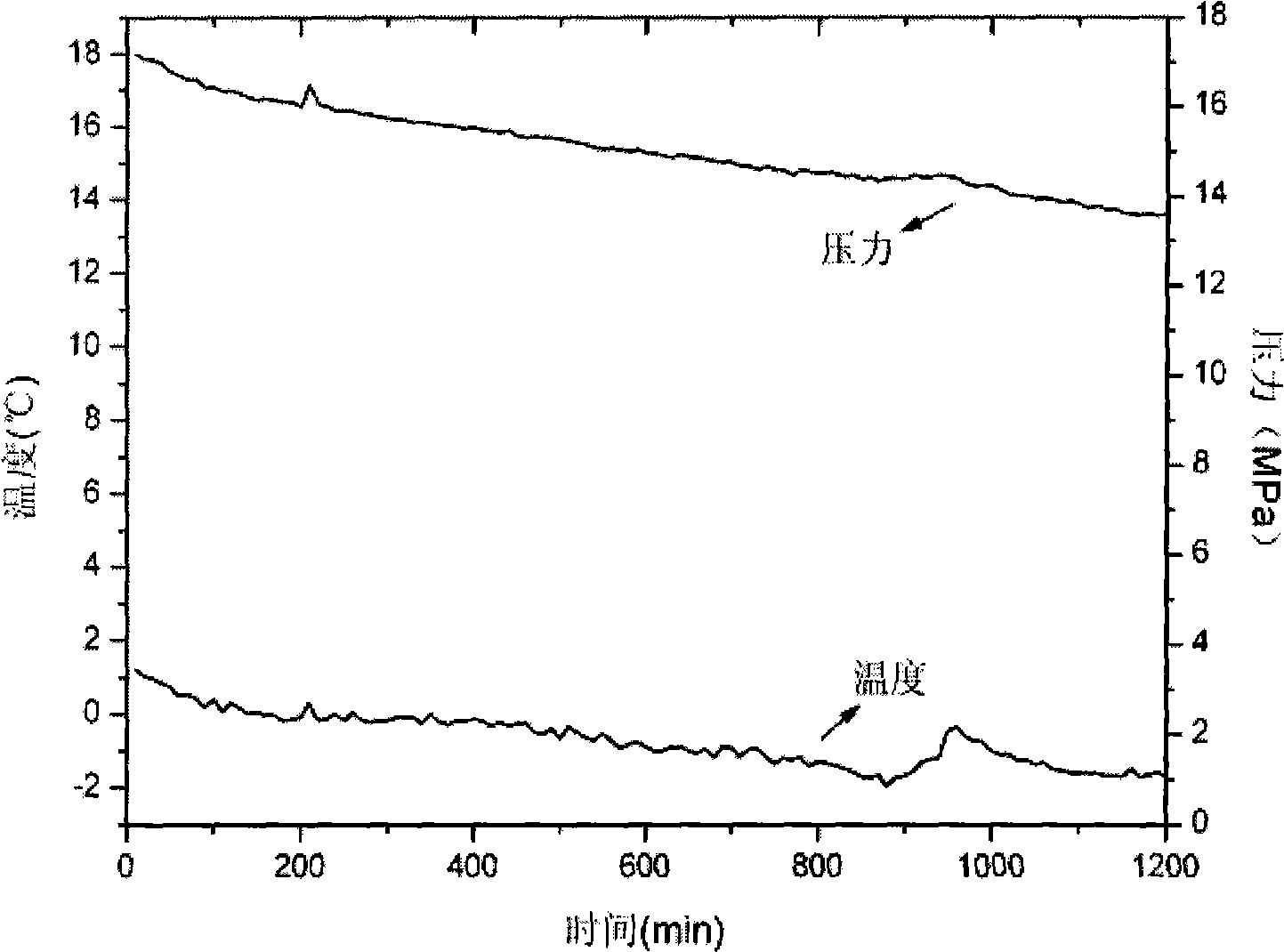
InactiveCN101532936AGood reproducibilityLarge test volumeGaseous fuelsFlushingDecompositionControl system
The invention relates to a method and a device for evaluating inhibiting ability of drilling fluid on formation and decomposition of hydrate. The device comprises a high and low temperature experimental box (1), a high-pressure reaction kettle (2) in the high and low temperature experimental box, a pressure controlling system, a microvideo camera and a data acquisition and control system (12). The reaction kettle is connected with the pressure controlling system through high-pressure pipelines on the upper and lower parts of the kettle; data acquisition and control system is connected with sensors arrange at the bottom of the reaction kettle and a high-pressure control platform (13) through data acquisition signal wires, wherein drilling fluid (4) to be tested is put on the high-pressure control platform; the microvideo camera is arranged in an observation cylinder (21) extended into a working chamber outside the high and low temperature experimental box and approaches front end of the observation cylinder (21) having anti-fog transparent glass so as to observe. The invention provides the device to evaluate inhibiting experiments of drilling fluid in underground bored wells and frozen earth and marine bored wells on formation and decomposition of hydrate under different temperature and pressure.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
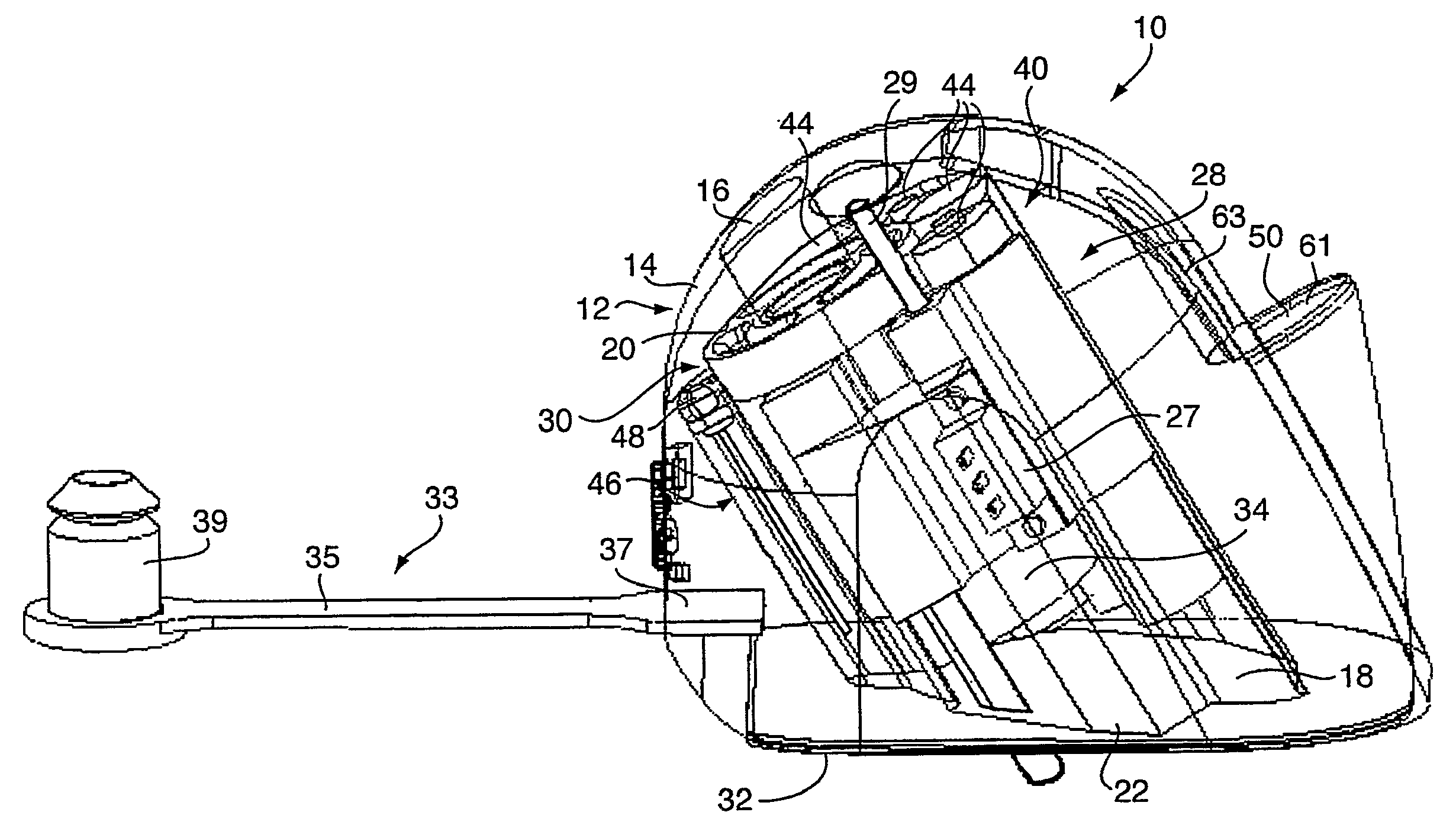
Anti-Fogging Device and Anti-Fogging Viewing Member
ActiveUS20080290081A1Reduce thicknessReduce capacityLighting and heating apparatusTransparent/reflecting heating arrangementsMetallic foilRespirator
An anti-fogging device has a substantially transparent or optically clear plastic layer with a heater element formed of etched metallic foil bonded to it. The device has an adhesive element disposed at the periphery of the device for sticking to a viewing member such as a motorcycle helmet visor, surgical mask or rear windscreen for a convertible car, to leave a gap between the heater element and the viewing member.
Owner:MAN INNOVATIONS LTD
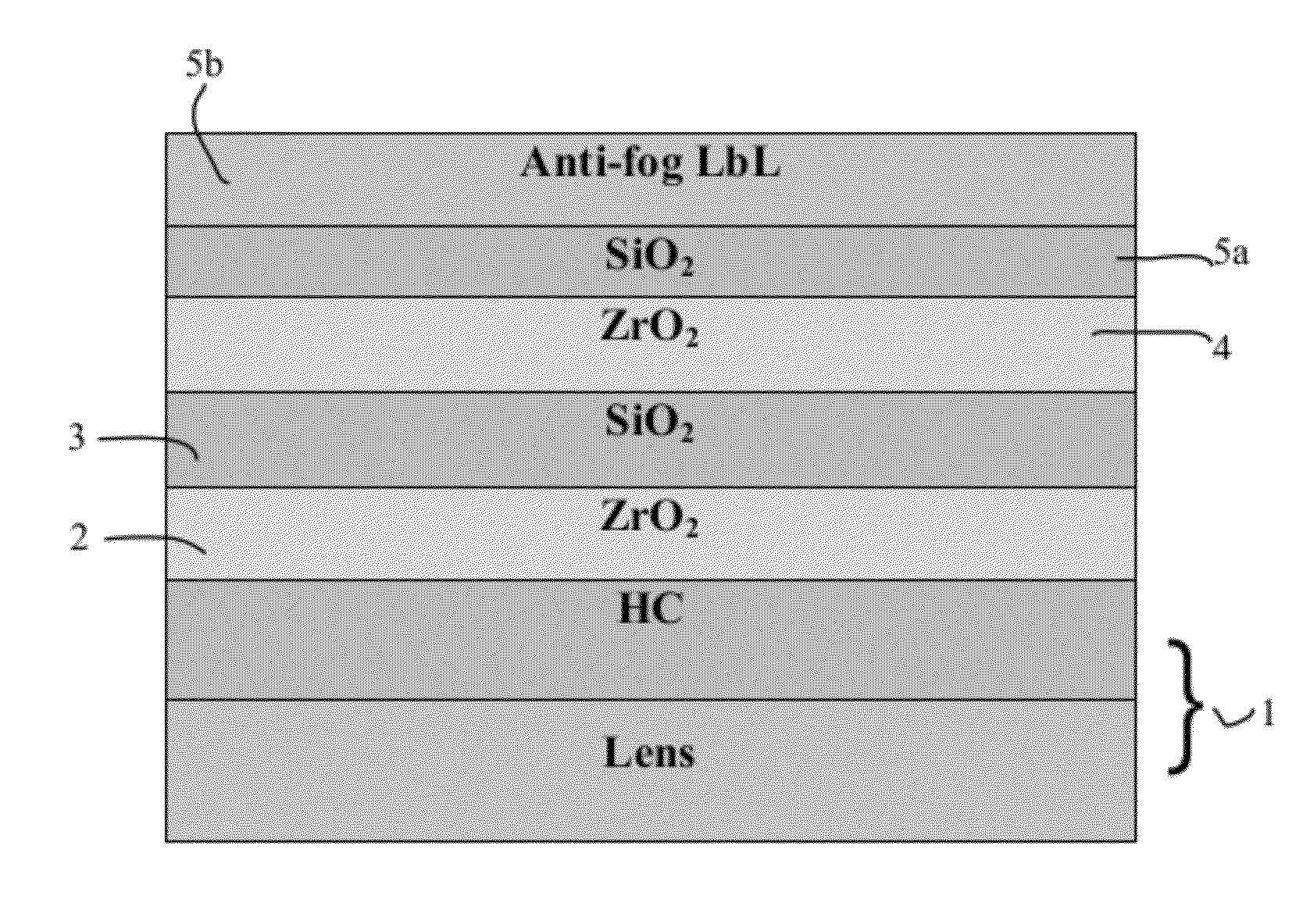
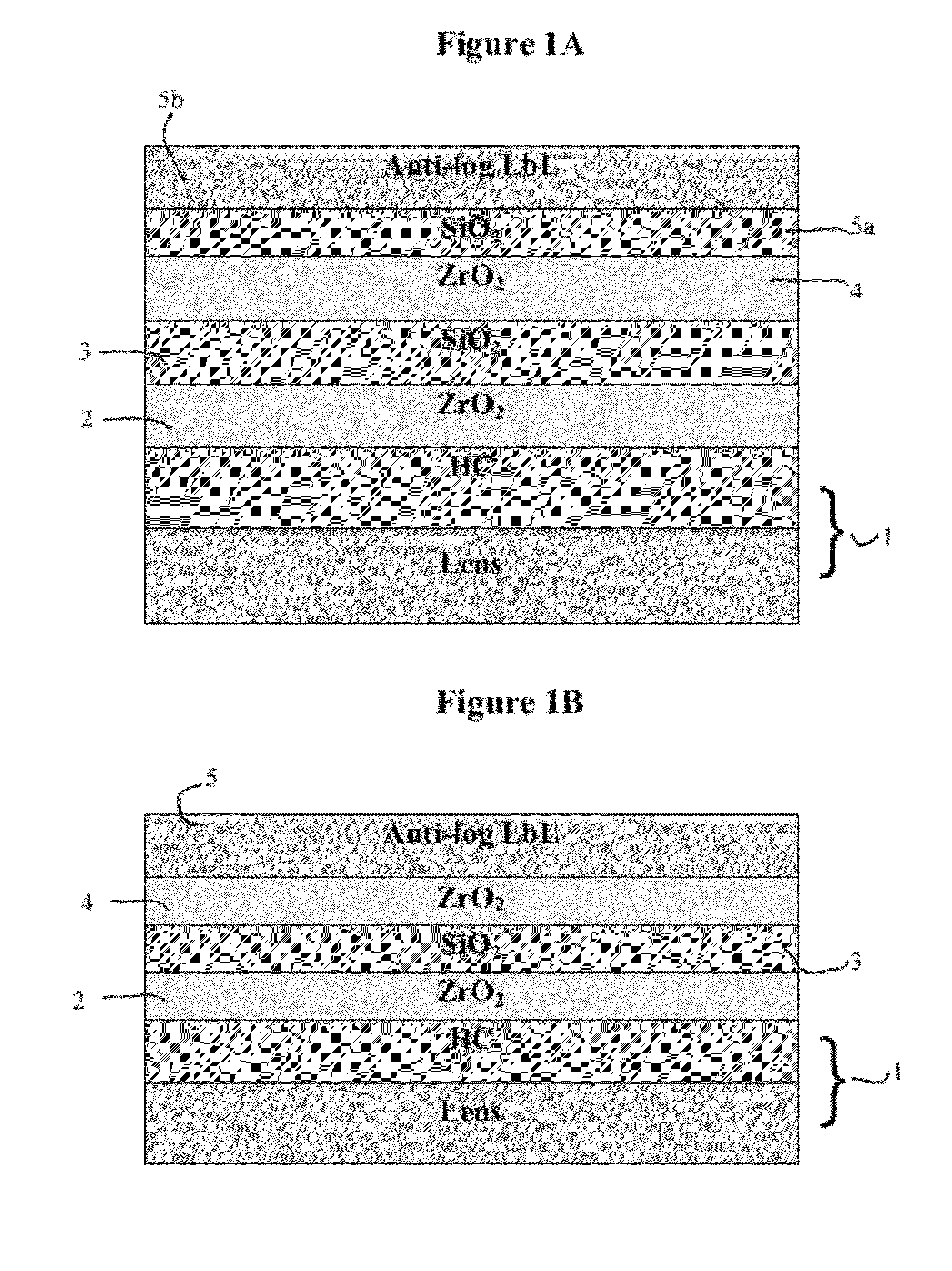
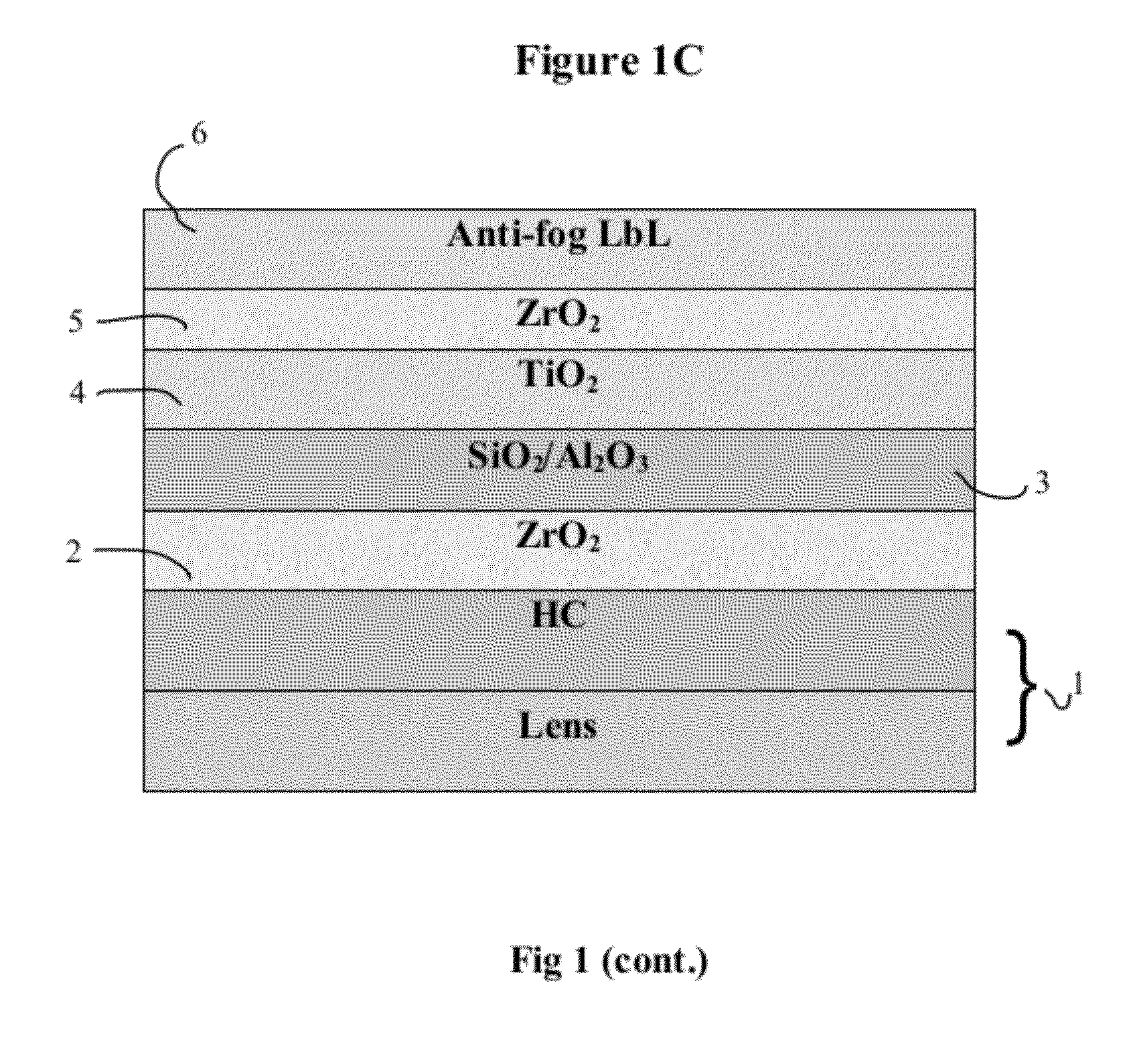
Optical Article Including an Antireflecting Coating Having Antifog Properties and Process for Making Same
ActiveUS20120028005A1Improve mechanical propertiesReduce reflectivityLayered productsVacuum evaporation coatingAnti-reflective coatingRefractive index
An optical article comprising a substrate and on at least one face of the substrate a multilayered antireflecting coating functioning in an interferential manner having antifog properties, said antireflecting coating including a last layer with a refractive index n≦1.55 and a physical thickness of 120 nm or less directly deposited on a high refractive index layer (HI layer) having a refractive index n>1.55, and a thickness of less than 500 nm.
Owner:ESSILOR INT CIE GEN DOPTIQUE
Device for white balancing and appying an anti-fog agent to medical videoscopes prior to medical procedures
ActiveUS8152717B2Prevent foggingFacilitates easy and accurate white balancingBronchoscopesColor signal processing circuitsEndoscopeBiomedical engineering
A device is configured for white balancing a medical videoscopic camera system prior to videoscopic medical procedures, as well as optionally simultaneously or non-simultaneously applying a fog-prohibiting agent to the distal lens of a medical videoscope such as an endoscope or laparoscope. The device combines a white balancing mechanism, protective mechanism, and defogging mechanism in one simple easy to use device.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Multi-layer coatings with an inorganic oxide network containing layer and methods for their application
InactiveUS20050266235A1Good antifoulingImprove self-cleaningAlkali metal silicate coatingsPretreated surfacesAnti-fogInorganic oxide
Multi-layer coatings are disclosed that include (1) a first layer comprising an inorganic oxide network, and (2) a second layer applied over at least a portion of the first layer, wherein the second layer is deposited from at least one liquid composition that is hydrophilic and includes an essentially completely hydrolyzed organosilicate. Also disclosed are substrates coated with such multi-layer coatings, methods of applying such multi-layer coatings to a substrate and methods for improving the anti-fouling, self-cleaning, easy-to-clean, and / or anti-fogging properties of an article.
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
Merchandisers having Anti-fog coatings and methods for making the same
A variety of refrigerators and merchandisers having glass or plastic substrates that are substantially fog-resistant are provided. For example, refrigerator doors having a substantially transparent substrate including an anti-fog coating on at least a portion thereof are provided. Many of the coatings exhibit color stable properties.
Owner:HUSSMANN CORP
Self-cleaning, antibacterial and anti-fog film
InactiveCN103396634AAntistaticWith anti-electromagnetic radiation performanceUltraviolet lightsHeat sensitive
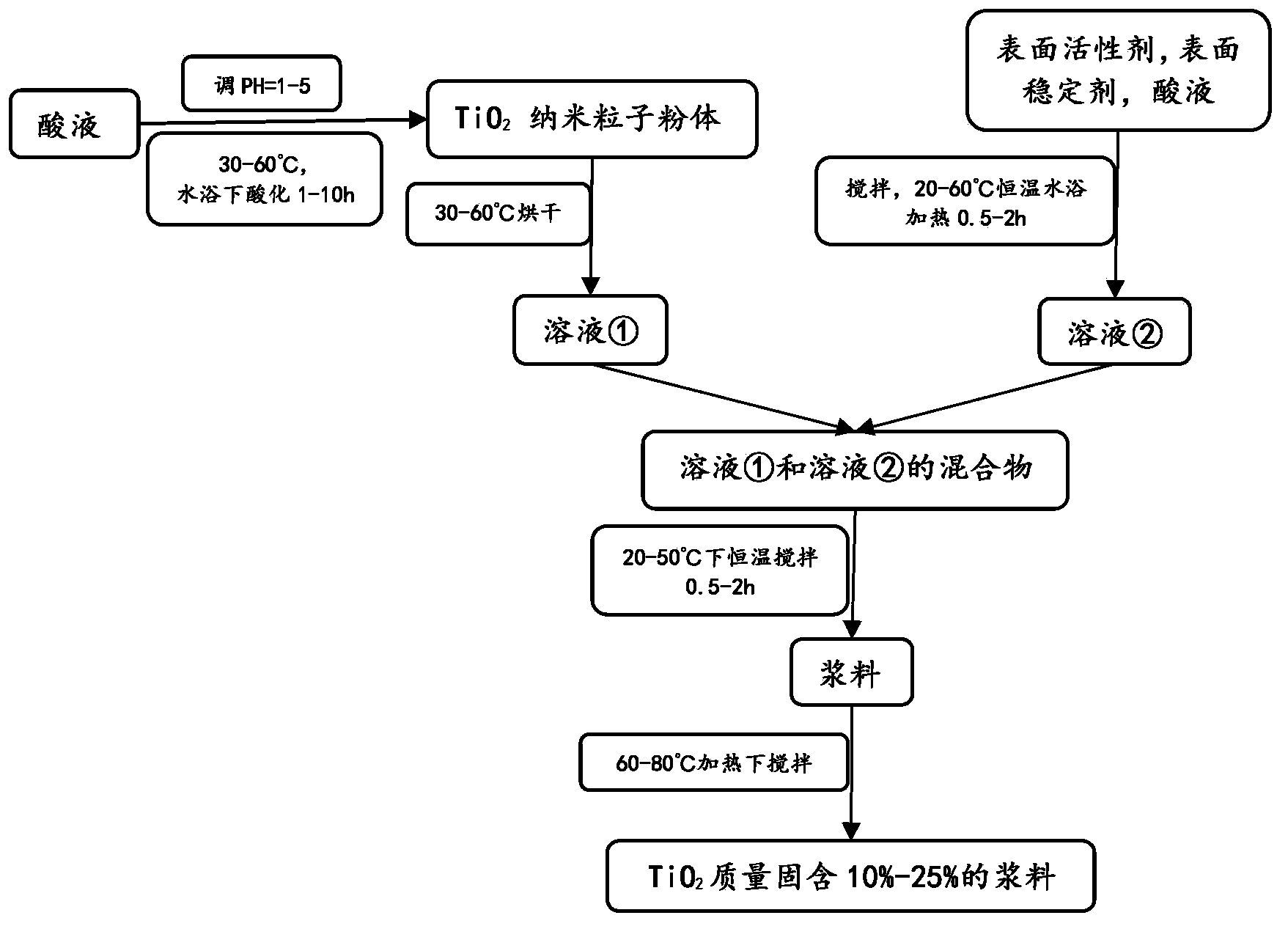
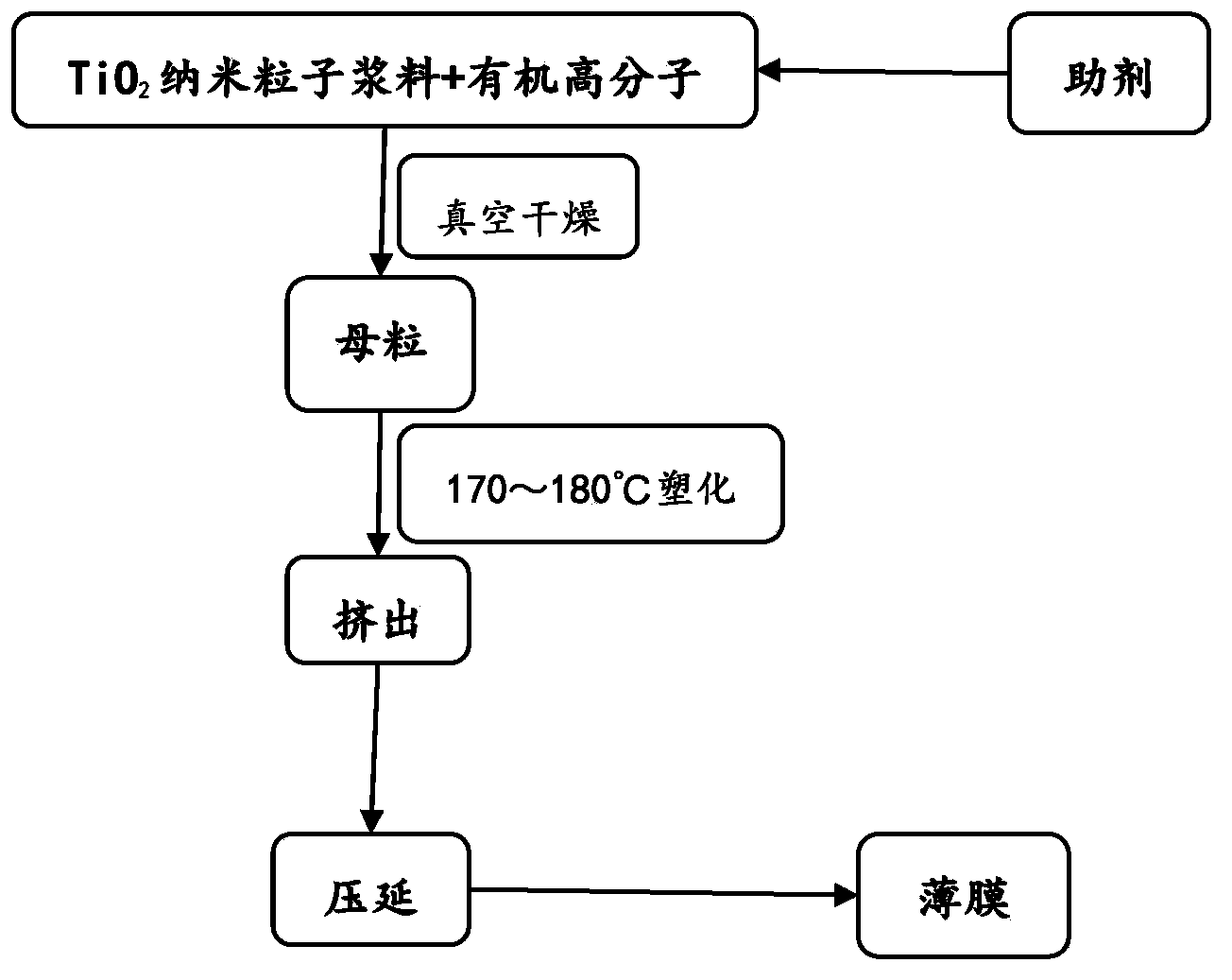
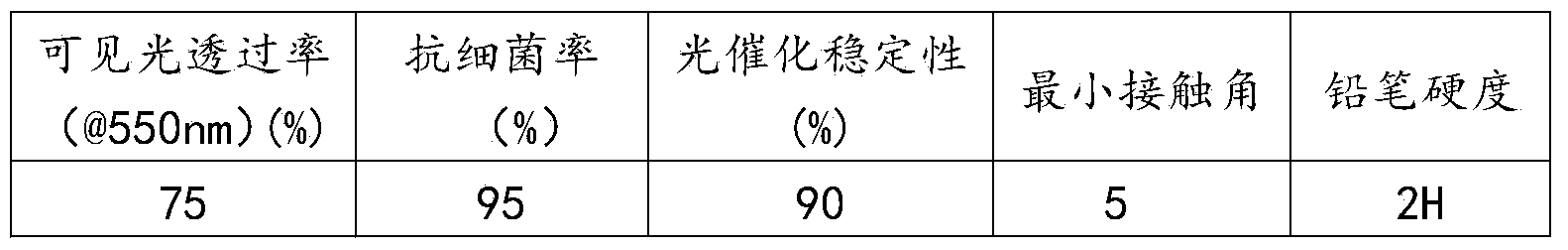
The invention relates to a self-cleaning, antibacterial and anti-fog film. The self-cleaning, antibacterial and anti-fog film is prepared by acidizing TiO2 nano-particle powder, adding a surfactant, a stabilizer, an acid and the like, preparing, and concentrating to obtain TiO2 nano-particle slurry, adequately mixing the slurry with an organic high-molecular polymer and auxiliaries, and drying to obtain master batches; and commonly plasticizing, extruding and calendaring the master batches to prepare the self-cleaning, antibacterial and anti-fog film, wherein the constituents of the film comprise 72.89-92.34 wt% of the organic high-molecular polymer, 0.5-22.63 wt% of TiO2 nano particles and 3.36-23.45 wt% of auxiliaries. The film has a high visible light transmittance, self-cleaning, antibacterial and anti-fog functions, reflection and control effects on ultraviolet light rays and far-infrared light rays, antistatic property and anti-electromagnetic radiation property; the film is prepared with no need of high vacuum and high-temperature heating, simple and practicable equipment, and low cost; the film can be compounded with pressure-sensitive adhesive and heat-sensitive adhesive, used as the films of building glass, and the windows of vehicles and ships for improving the self-cleaning, antibacterial and anti-fog functions of the building glass and the windows, and used for performing transformation and large-area field construction on the installed glass and windows.
Owner:武汉羿阳科技有限公司
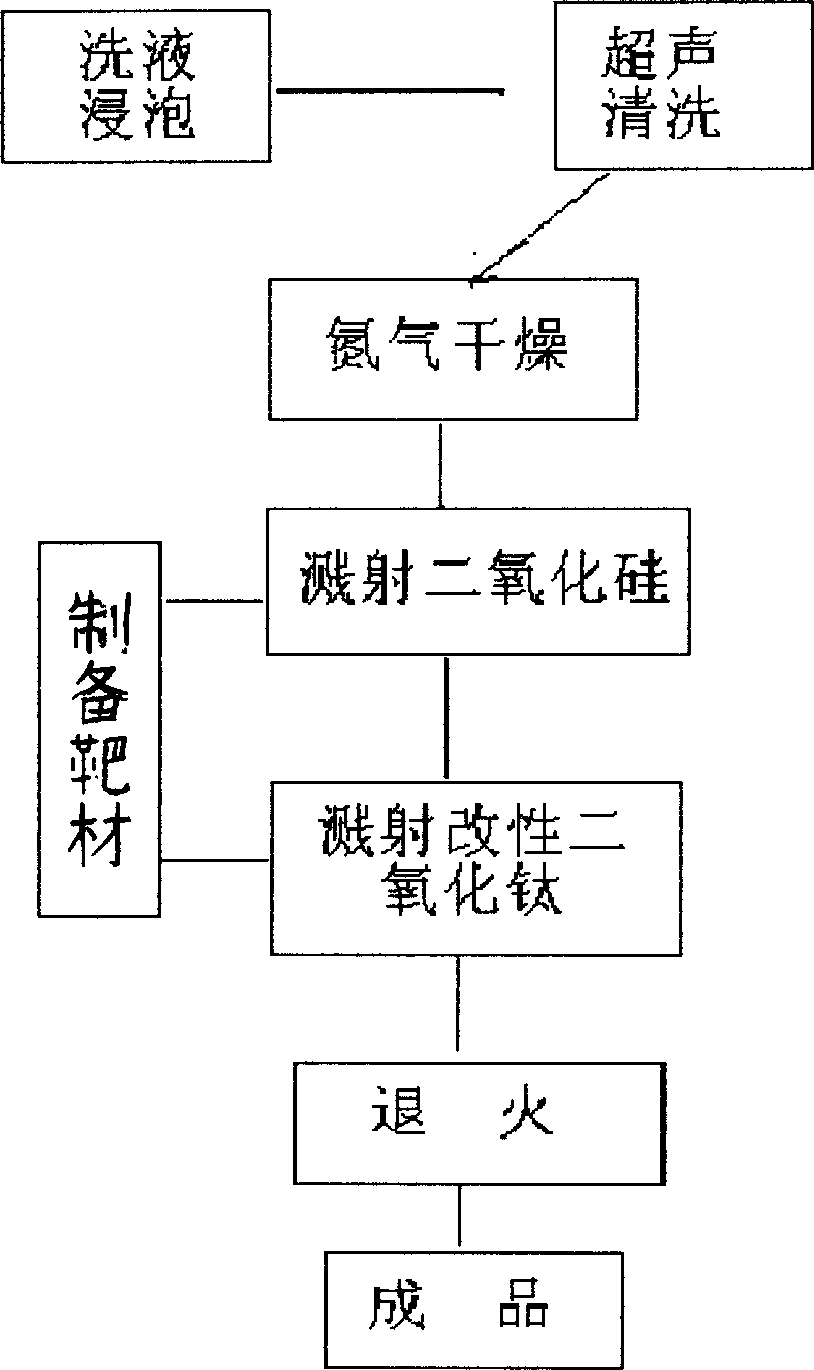
Permanent self-cleaning glass with visible light responsibility and preparation method thereof
The invention belongs to functional material technology and glass processing field, concretely discloses a permanent self-cleaning glass with visible light response and method for making it. Firstly, sputtering silica dioxide film on the surface of glass, sputtering a layer of titanium oxide film with anion and cation codoping on the surface of silica dioxide film, annealing the glass with twin layer films at 500-600 DEG C, cooling by radiation in sintering stove, to get the product. The self-cleaning glass has good photocatalysis property and photo-induced hydrophilicity, stable performance, almost perpetual availability, high light transmittance ratio and transparency. It is widly used in glass curtain wall of skyscrapers, automobile glass, road lamp shade, kitchen galss and antifog glass, avoiding artificial cleaning indoor and outdoor glass of skyscrapers, saving manual power and material, reducing corrosion destruction of cleaning agent to glass and building machinery, embodying environment protection notion.
Owner:JIEYANG HONGGUANG COATED GLASS
Method and apparatus for heating and applying warm antifog solution to endoscopes as well as a distal lens protector
InactiveUS20050234301A1Superior anti-fogging protectionAvoid condensationSurgeryEndoscopesElectricityEngineering
A sterile, self-contained, disposable apparatus used for heating and applying solution to the distal end of endoscopes as well as an endoscopic lens protector. The heating mechanism is chemical, electrical or a combination of both. Further the apparatus serves as a self sealing container for the storage and application of anti-fog solution. By placing the apparatus over the distal scope prior to surgery, the scope is protected from damage from other instruments or trays. At the same time the distal lens is submerged in the warm anti-fog solution and it is uniformly and completely coated. Heat is transferred to the instrument from the solution in one example to act as an important and additional measure to prevent fogging of the lens. By heating the solution and the instrument, the drastic temperature difference between the interior of the body (98.6) and the instrument is eliminated. This inhibits the condensation of moisture, which always occurs upon inserting the cool scope inside the warm body. The apparatus combines the use of an anti-fog solution as well, which helps prevent fogging during the procedure when smoke and heat is generated within the body during the procedure. Lastly, the apparatus is designed to be used as a holder of the scope while protecting it from impact with a shock absorbent outer shell prior to, during, and after the medical procedure. A new method for defogging endoscopes by which a sterile protective device is combined with a defogging mechanism and placed over the distal lens of endoscopes prior to the medical procedure, used intermittently during the procedure, then placed over the lens at the end of the procedure. The apparatus is not removed until scope reaches the cleaning facility. This apparatus is ideal for sterile operations where the instrument is used intermittently and repeatedly.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Facemasks containing an anti-fog / anti-glare composition
A coating composition that is incorporated into a facemask to reduce fogging and glare is provided. For example, in one embodiment, the facemask contains a shield or visor formed from a transparent substrate having at least one surface applied with the coating composition of the present invention. The present inventors have unexpectedly discovered that one or more water-soluble organic polymers, such as ethyl hydroxyethylcellulose, may be utilized as a principal component of the coating composition to reduce fogging and glare in a simple, yet effective manner.
Owner:O&M HALYARD INC
Exterior coating antifogging film and preparation method
InactiveCN1687199ACoating method is simple and easyCuring method is simpleCoatingsLight irradiationDouble coating
The present invention provides a new externally-coated fog-resisting film and its preparation method. It is characterized by that said invention adopts inorganic-organic coating process on the plastic film surface to prepare fog-resisting film. The described fog-resisting film has a double-coating structure, first coating layer is coated on the base film, it is a mixture obtained by using silane coupling agent and one or two kinds of ethyl orthosilicate and butyl titanate through hydrolysis reaction, after the first coating layer is solidified by means of heating or UV-light irradiation, on said layer of solidified film a second coating layer is coated, and said second coating layer also is a mixture formed from silane coupling agent and one or two kinds of ethyl orthosilicate and butyl titanate through hydrolysis reaction, and also is solidified by means of heating or UV-light irradiation.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Anti-fogging mirrors and methods
InactiveUS20150060431A1Picture framesTransparent/reflecting heating arrangementsProcess engineeringEngineering
A mirror assembly can include a mirror secured to a housing portion. In some embodiments, the mirror assembly can include a heating element disposed between the housing portion and the mirror. The heating element can heat a surface of the mirror to a pre-determined temperature, preferably above the dew point.
Owner:SIMPLEHUMAN
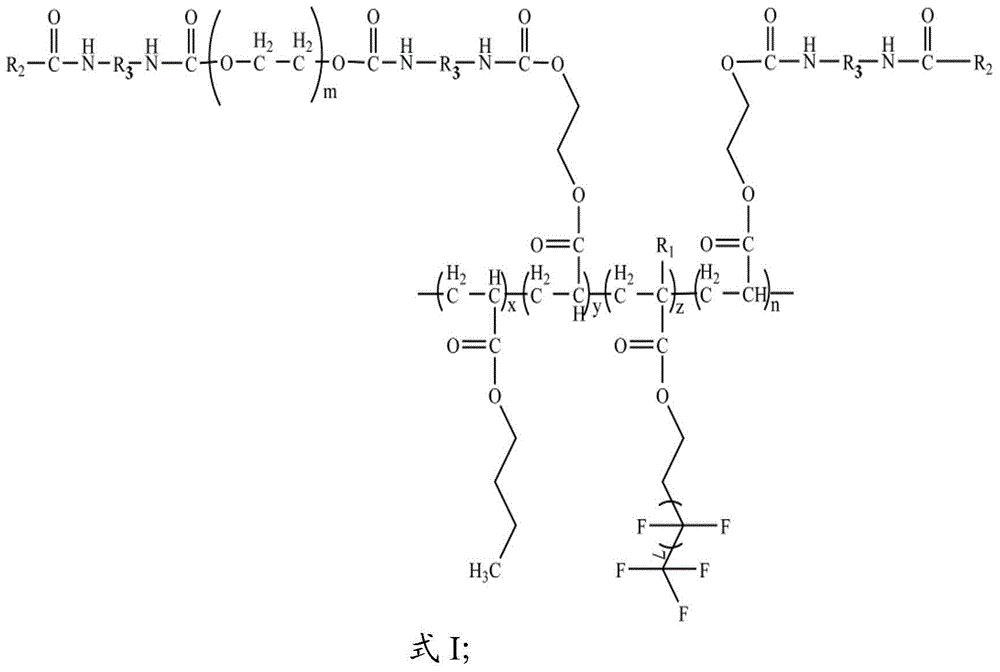
Urethane acrylate oligomer, and preparation method and ultraviolet-curing antifogging coating thereof
The invention provides a urethane acrylate oligomer, which has a structure shown in a formula I. The urethane acrylate oligomer with the structure shown in the formula I is taken as matrix resin, and the ultraviolet-curing antifogging coating is provided, and comprises the urethane acrylate oligomer, a flatting agent, a defoamer, a photoinitiator and a silane coupling agent. The urethane acrylate oligomer provided by the invention comprises an ethoxy group and a fluoride group; the urethane acrylate oligomer has hydrophily by the ethoxy group; the urethane acrylate oligomer has low surface energy by the fluoride group, so that the ultraviolet-curing antifogging coating has lasting anti-fog performance. The experiment result shows that the primary anti-fog performance of the film cured by the ultraviolet-curing antifogging coating provided by the invention can be up to 10 levels, and the anti-fog persistence can be up to 8-10 levels.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com