Method for immobilizing VEGF-carried heparin/polylysine nanoparticles on Ti surface
A technology of polylysine and nanoparticles, which is applied in the field of nanoparticle preparation technology and surface modification of inorganic materials, can solve the problems of non-inhibition, Hep/PLL nanoparticle immobilization, poor hemocompatibility of titanium materials, etc., and achieve extended The half-life, preparation process and fixation method are simple and easy to operate, and the effect of reducing drug loss rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
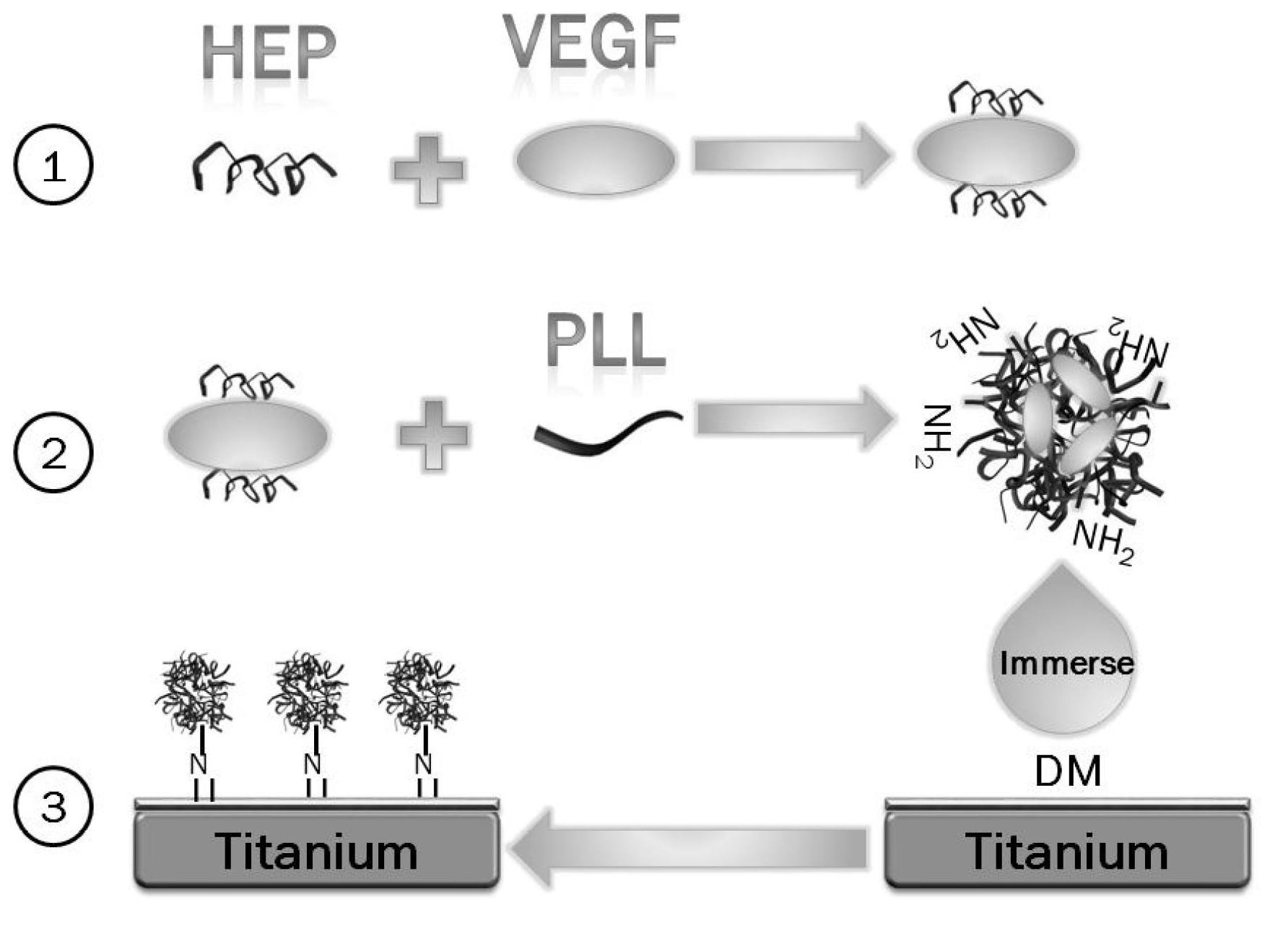
[0023] see figure 1 , the first embodiment of the present invention is a method for immobilizing VEGF-loaded heparin / polylysine nanoparticles on the Ti surface, the steps of which are:
[0024] A. Sample preparation. Deposit a polydopamine coating on the polished pure Ti surface for use;
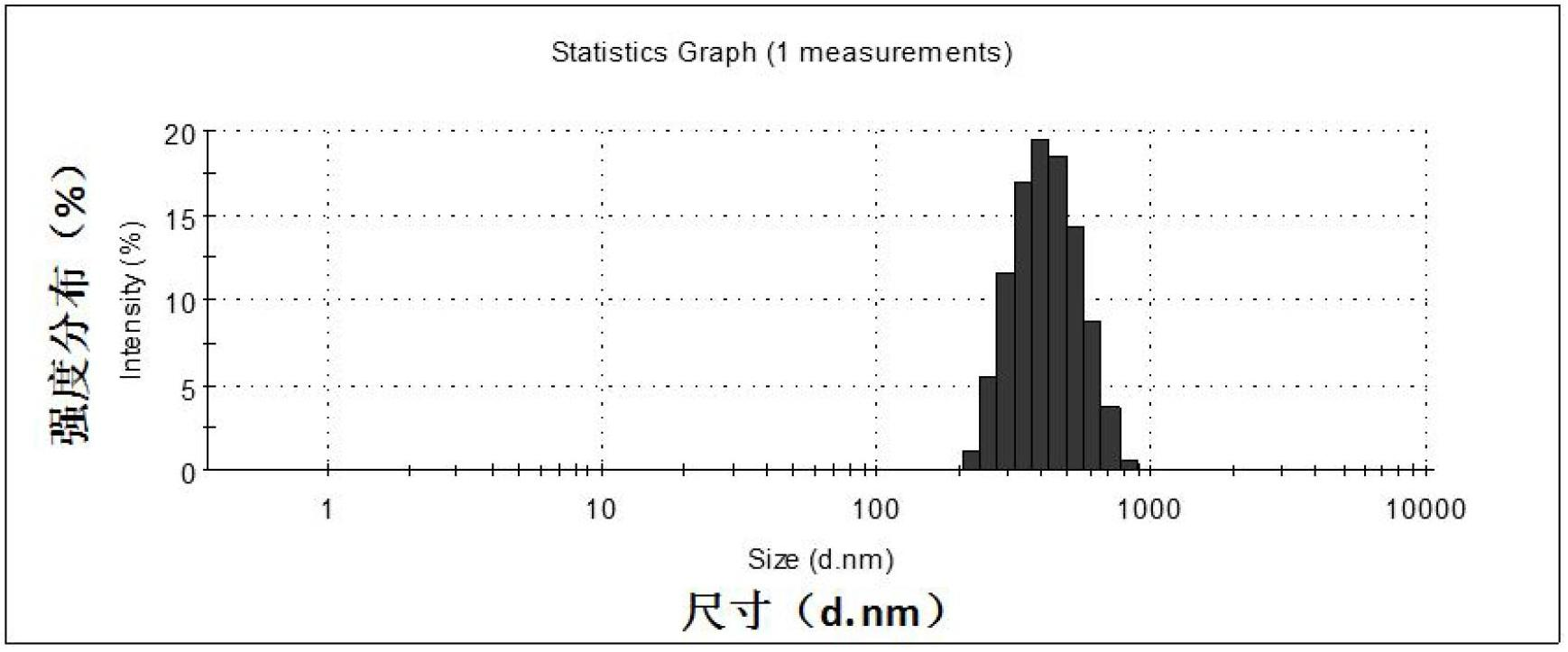
[0025] B. Preparation of Hep / PLL nanoparticles loaded with VEGF. An equal volume of VEGF solution (PBS, pH 7.4) with a concentration of 500 ng / ml was added dropwise to a heparin solution (PBS, pH 7.4) with a concentration of 20 mg / ml, and allowed to stand at 37° C. for 1 h. Then, under room temperature and magnetic stirring conditions, an equal volume of Hep and VEGF mixture was added dropwise to a PLL (MW 150,000-300,000) solution (PBS, pH 7.4) with a concentration of 1 mg / ml;
[0026] C. Nanoparticle immobilization. Soak the Ti sheet deposited with DM in step A in the nanoparticle suspension obtained in step B, react under shaking conditions at 15-50°C for 24 hours, rinse with PBS and ...
Embodiment 2
[0028] A method for immobilizing VEGF-loaded heparin / polylysine nanoparticles on the Ti surface, the steps of which are:
[0029] A. Sample preparation. Deposit a polydopamine coating on the polished pure Ti surface for use;
[0030] B. Preparation of Hep / PLL nanoparticles loaded with VEGF. An equal volume of VEGF solution (PBS, pH 7.4) with a concentration of 50 ng / ml was added dropwise to a heparin solution (PBS, pH 7.4) with a concentration of 5 mg / ml, and allowed to stand at 37° C. for 2 hours. Then, at room temperature and under magnetic stirring conditions, an equal volume of Hep and VEGF mixture was added dropwise to a PLL (MW 150,000-300,000) solution (PBS, pH 7.4) with a concentration of 0.2 mg / ml;
[0031] C. Nanoparticle immobilization. The Ti sheet deposited with DM in step A was soaked in the nanoparticle suspension obtained in step B, reacted at 50°C under shaking conditions for 6 hours, rinsed with PBS and double distilled water, and dried to obtain the targe...
Embodiment 3
[0033] A method for immobilizing VEGF-loaded heparin / polylysine nanoparticles on the Ti surface, the steps of which are:
[0034] A. Sample preparation. Deposit a polydopamine coating on the polished pure Ti surface for use;
[0035] B. Preparation of Hep / PLL nanoparticles loaded with VEGF. An equal volume of VEGF solution (PBS, pH 7.4) with a concentration of 200 ng / ml was added dropwise to a heparin solution (PBS, pH 7.4) with a concentration of 10 mg / ml, and stood at 37° C. for 3 h. Then, at room temperature and under magnetic stirring conditions, an equal volume of Hep and VEGF mixture was added dropwise to a PLL (MW 150,000-300,000) solution (PBS, pH 7.4) with a concentration of 0.5 mg / ml;
[0036] C. Nanoparticle immobilization. The Ti sheet deposited with DM in step A was soaked in the nanoparticle suspension obtained in step B, reacted at 37 °C under shaking conditions for 12 h, rinsed with PBS and double distilled water, and dried to obtain the target product.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com