Multidrug-resistant mycobacterium tuberculosis non-fluorescent DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) microarray detection method and kit
A Mycobacterium tuberculosis detection method technology, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problems that cannot meet the needs of clinical detection, slow growth of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and reduce the affinity of rifampicin, etc. It achieves the effects of convenient monitoring and quality control, clear and accurate test results, and reduced testing costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
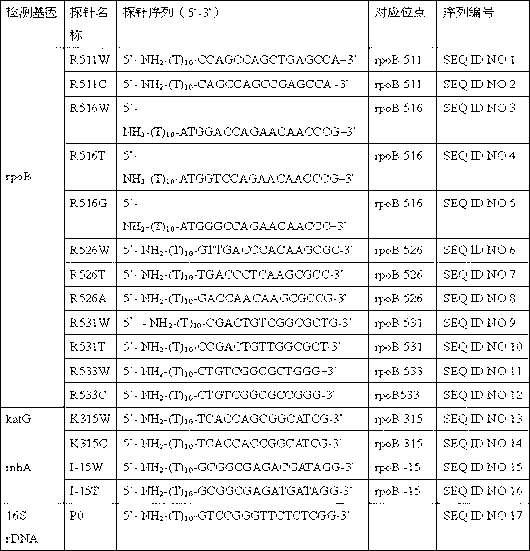
[0054] Example 1: Preparation of probe synthesis and gene chip
[0055] Purchase aldehyde-modified glass slides. Design 16 oligonucleotide probes, modify the 5' ends of the probes with amino groups, and commission related companies to synthesize the probes. The synthesized probe was diluted into an aqueous solution with a concentration of 100 μM, and mixed with 2× spotting buffer (product of Shanghai Bio-Technology Co., Ltd.) in equal proportions. Use the spotting instrument of Affymetrix Company to spot the chip array according to the method described in the manual, and place it at room temperature for 3 hours for later use. The probe information is shown in Table 4.
Embodiment 2
[0056] Example 2: Extraction of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Genomic DNA
[0057] (1) Take the isolates from clinical samples identified as positive for Mycobacterium tuberculosis after culture as samples, inactivate the bacteria at 80°C for 2 hours, and use a commercial bacterial genomic DNA extraction kit to extract the sample DNA. The obtained genomic DNA can be It can be directly used as a PCR reaction template, and can also be stored at -20°C for future use.
[0058] (2) Take 2 mL of clinically obtained sputum, add 2.5 times the volume of 4% NaOH, and incubate at 37°C for 30 minutes. The liquefied sputum was centrifuged to remove the supernatant. The obtained precipitate was extracted with a commercial bacterial genomic DNA extraction kit, and the obtained genomic DNA could be directly used as a PCR reaction template or stored at -20°C for future use.
Embodiment 3
[0059] Example 3: Primer synthesis, PCR reaction and product labeling
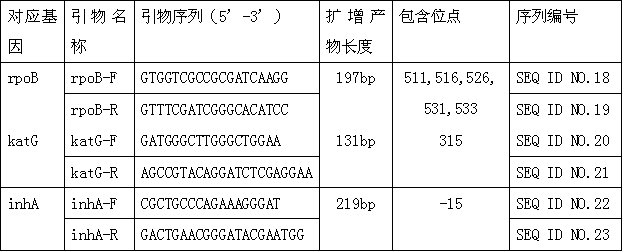
[0060] Download the promoter sequences of Mycobacterium tuberculosis rpoB gene, katG gene and inhA gene from the NCBI database, use Primer Primer 5 software to design forward and reverse primers and entrust Jerui Biotech to synthesize them (reverse primers rpoB-R, katG-R, inhA The 5' end of -R is labeled with biotin), and the primer information is shown in Table 1.
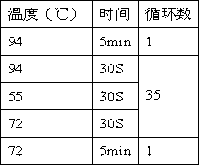
[0061] The synthesized primers were dissolved in water and diluted to 10 μM. Mix a pair of forward and reverse primers with Taq DNA polymerase, 10×PCR buffer, dNTP, UNG enzyme, dUTP, MgCl 2 The solution, pure water and the amplification template obtained in Example 2 were mixed to prepare a PCR amplification system for the target fragment of rpoB / katG / inhA gene. The PCR amplification system formula is as follows:
[0062] PCR system (rpoB / katG / inhA) Volume (μL) 10×PCR buffer 5 dNTPs (2 μM) 1 Forward primer (10 μ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com