Recovery and utilization method for dyeing residual liquid of reactive dye
A technology of dyeing residual liquid and reactive dyes, which is applied in the textile field, can solve the problems of expensive treatment costs, inability to remove salt, and high equipment requirements, and achieve the effects of reducing sewage treatment costs, reducing dyeing salinity costs, and reducing COD values
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Example 1 (Adsorption Rate of Dye Capture Agent Color Clean)
[0027] Reactive black KN-B: 1.5%
[0028] Yuan Mingfen: 60 g / L
[0029] Sodium carbonate: 18g / L
[0030] Sodium bicarbonate: 2 g / L
[0031] Liquor ratio 1:13, dyeing cotton knitted fabric at 60℃×60min.
[0032] After dyeing, the residual liquid was collected and treated with the dye catching agent Color Clean, and the absorbance of the test solution was calculated according to formula 1:
[0033] Adsorption rate = A1 / A0 × 100% (Equation 1)
[0034] Wherein, A1 is the absorbance of the solution after being treated with the dye catching agent Color Clean, and A0 is the absorbance of the solution before being treated with the dye catching agent Color Clean.
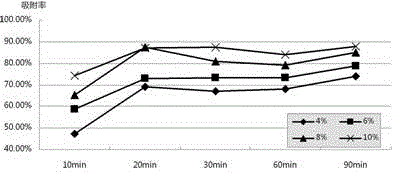
[0035] The effect of treatment time on the adsorption rate can be seen in figure 1 . Referring to Figure 1, from figure 1 According to the results, the removal rate of dye in the residual l...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Embodiment 2 (dyeing test)
[0037] The fabric used in this example is a 32s pure cotton double-sided semi-bleached fabric, and the dyeing process is a liquor ratio of 1:13, dyeing at 60° C. for 60 minutes.
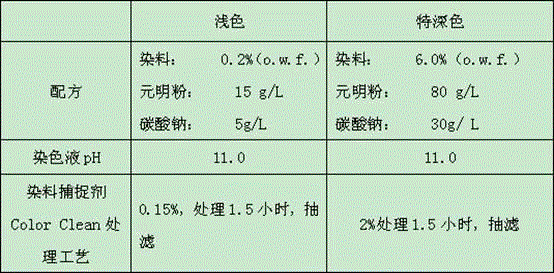
[0038] The dyeing recipe process is as shown in Table 1 in the present embodiment.
[0039] Table 1
[0040]
[0041] The above o.w.f = On weight the fabric, the concentration in the dyeing and finishing process is based on the weight of the fabric, relative to the percentage of the fabric, for example: under certain conditions, dyeing 100 kg of fabric, the amount of dye is 4% (o.w.f.) means dyeing these fabrics Required: 100 x 0.04 = 4 kg of dye.
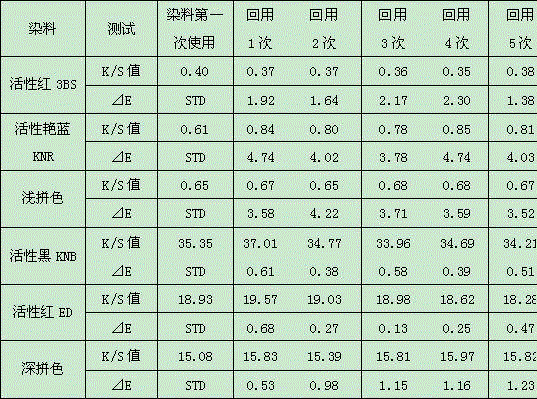
[0042] Table 2 shows the test results of dyeing depth (K / S value) and color difference (⊿E) in this example.
[0043] Table 2
[0044]
[0045] In Table 2, STD (standard) refers to the color difference of fabrics dyed with recycled water, using the tap water dyed sample as the standard, and the color differenc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com