Medium-high temperature thermal expansibility microsphere and method for reducing residual monomers therein
A technology of heat-expandable microspheres and residual monomers is applied in the field of medium-high temperature heat-expandable microspheres and the reduction of residual monomers therein, and can solve the problems of pollution, low production efficiency and high cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
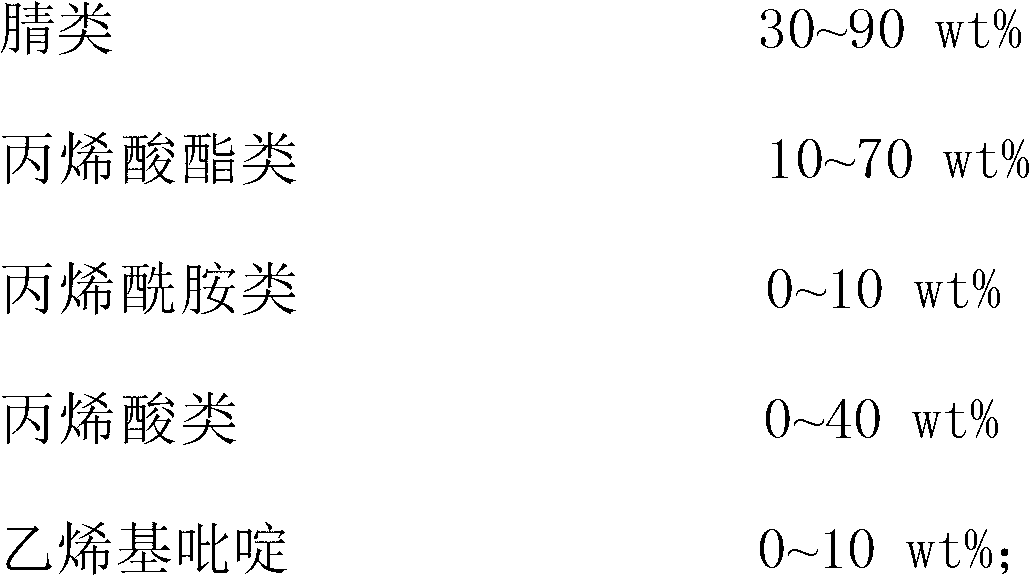
[0059] Obtained by mixing 160 g of acrylonitrile, 15 g of methyl acrylate, 5 g of methyl methacrylate, 20 g of vinylidene chloride, 1 g of ethylene glycol dimethacrylate, 0.4 g of dilauroyl peroxide and 70 g of hexane Suspension polymerized oil phase.
[0060] Add 200 grams of deionized water, 20 grams of sodium hydroxide, 30 grams of sodium chloride and 0.15 grams of sodium lauryl sulfate into beaker No. 1 to fully dissolve; add 200 grams of deionized water, 60 grams of six Magnesium chloride hydrate, 20 grams of sodium chloride, and 0.01 grams of sodium nitrite are fully dissolved; the solution in the No. 1 beaker is first poured into a 1-liter three-necked flask with a stirring paddle, and then stirred at a speed of 1200 rpm, and then poured into the three-necked flask Slowly add the solution in the No. 2 beaker to the flask. After the addition was complete, the mixture was fully stirred for 15 minutes to obtain a suspension-polymerized aqueous phase.
[0061] The oil pha...
Embodiment 2
[0065] By mixing 130 g of acrylonitrile, 40 g of methacrylonitrile, 20 g of methyl methacrylate, 10 g of methacrylic acid, 0.4 g of trimethylolpropane trimethacrylate, 1 g of azobisisobutyronitrile, 60 g of isooctane resulted in a suspension polymerized oil phase.
[0066] In 400 grams of ion-exchanged water, add 45 grams of sodium chloride, 20 grams (active ingredient amount: 20% by weight) of colloidal silicon dioxide, 0.2 grams of polyvinylpyrrolidone and 0.02 grams of sodium nitrite, then adjust the pH to 2.4, uniform mixed as an aqueous dispersion medium.
[0067] The oil phase and the water phase were dispersed by stirring at 6000 rpm for 3 minutes with a homomixer to prepare a suspension solution. Immediately inject the suspension solution into a 1-liter high-pressure reactor, replace the air with nitrogen, and pressurize the reactor to reach an initial pressure of 0.3 MPa. Then, after the polymerization reaction was carried out at 60-61°C for 15 hours, 1 g of hydroge...
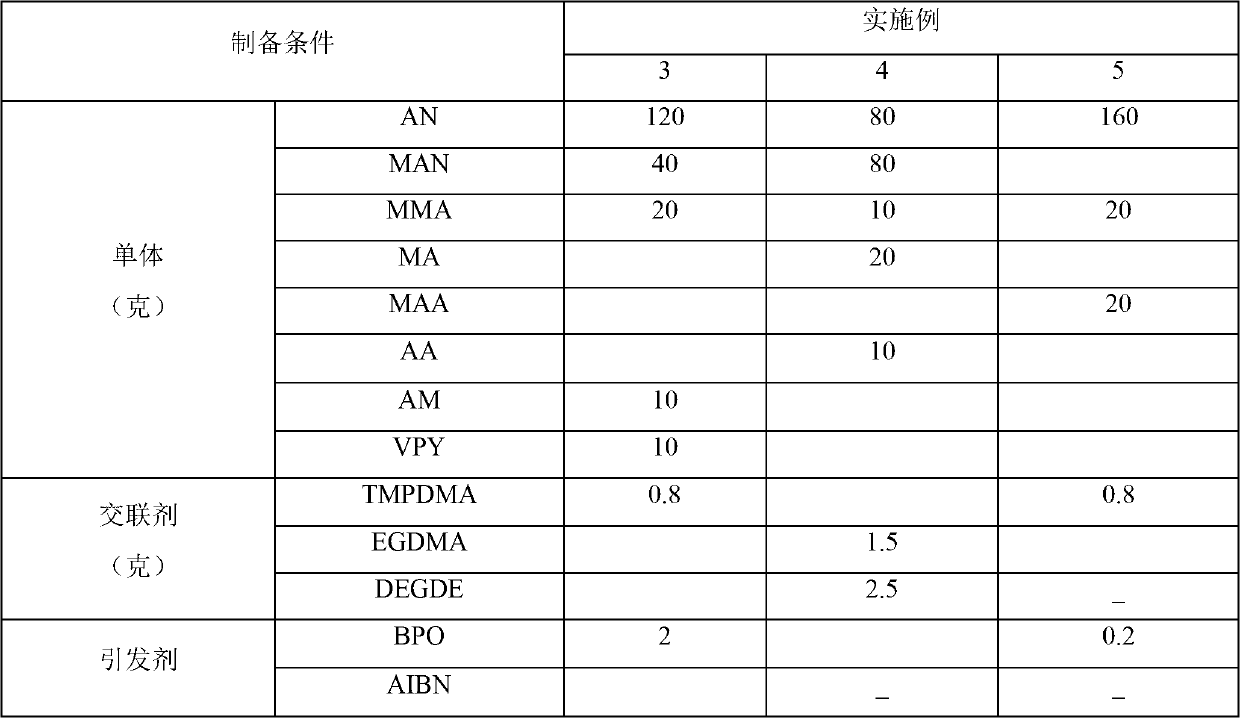
Embodiment 3-4
[0071] Except for changing the types and amounts of monomers, cross-linking agents, initiators and foaming agents used, and the polymer temperature (see Table 1 for details), other conditions are the same as in Example 1, and different medium- and high-temperature thermal expansion micro The properties of the ball are listed in Table 2.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com