Method for preparing porous tantalum medical implant material through selective laser sintering forming
A technology of laser selective sintering and implantation of materials, applied in the fields of additive manufacturing, additive processing, medical science, etc., can solve the problems of complex shapes of biological materials, inability to meet requirements, and high requirements for small details, and achieve complete three-dimensional connectivity distribution, Excellent biosafety, non-toxic dust effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] A method for preparing a porous tantalum medical implant material. The pure tantalum powder with a particle size of 5 μm is delivered to a three-dimensional printing platform, rolled and laminated, and the sample size to be prepared is designed to be φ10×100mm, and its UG file Input into the molding equipment, and carry out laser selective sintering molding. The computer controls the two-dimensional scanning trajectory of the laser beam according to the slicing model of the prototype, and selectively sinters the delivered pure tantalum powder to form a layer of the part. After a layer of powder is completed, the working piston is lowered by 50 μm, and the powder spreading system is covered with new tantalum. Powder, the thickness of each layer of powder coating is 80 μm, control the laser beam and then scan and sinter the new layer, repeat this cycle, layer by layer, until the three-dimensional sample is formed. Then take out the molded sample, put it into a vacuum furn...
Embodiment 2
[0026] A preparation method of porous tantalum medical implant material, transporting pure tantalum powder with a particle size of 10 μm to a three-dimensional printing platform, rolling and laminating, designing the sample size to be prepared as φ10×100mm, and uploading its UG file Input into the molding equipment, and carry out laser selective sintering molding. The computer controls the two-dimensional scanning trajectory of the laser beam according to the slicing model of the prototype, and selectively sinters the delivered pure tantalum powder to form a layer of the part. After a layer of powder is completed, the working piston is lowered by 50 μm, and the powder spreading system is covered with new tantalum. powder, control the laser beam and then scan and sinter the new layer, and so on, and the layers are superimposed until the three-dimensional sample is formed; during the laser selective sintering process, the laser power is 65W, the scanning speed is 15mm / s, and the ...
Embodiment 3~7
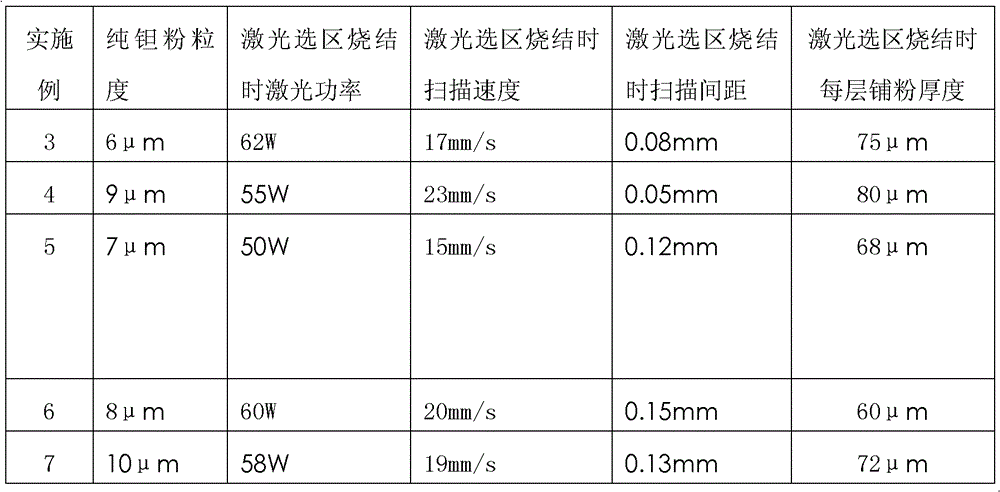
[0027] Embodiment 3~7: carry out according to following steps and process parameter, all the other are the same as embodiment 1.
[0028]
[0029]
[0030]
[0031]
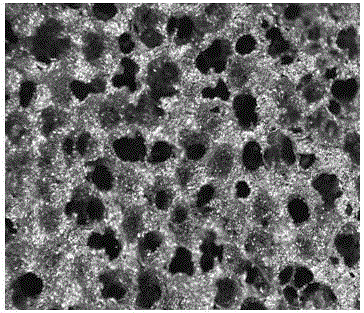
[0032] The obtained porous tantalum finished product is three-dimensionally completely connected, the pores are evenly distributed, and the biocompatibility is good. The test results according to the aforementioned method are as follows:
[0033] Example
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com