Cooling, heating and power integrated system based on fuel cell and hydrogen storage device of fuel cell for extravehicular spacesuit
A fuel cell and hydrogen storage device technology, which is applied in the field of outboard activities, can solve the problems of difficulty in meeting the power supply requirements of extravehicular space suits, few charging/discharging cycles, and no integrated cooling, heating and power design, etc. Memory effect, short filling time, reduced mass loss effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
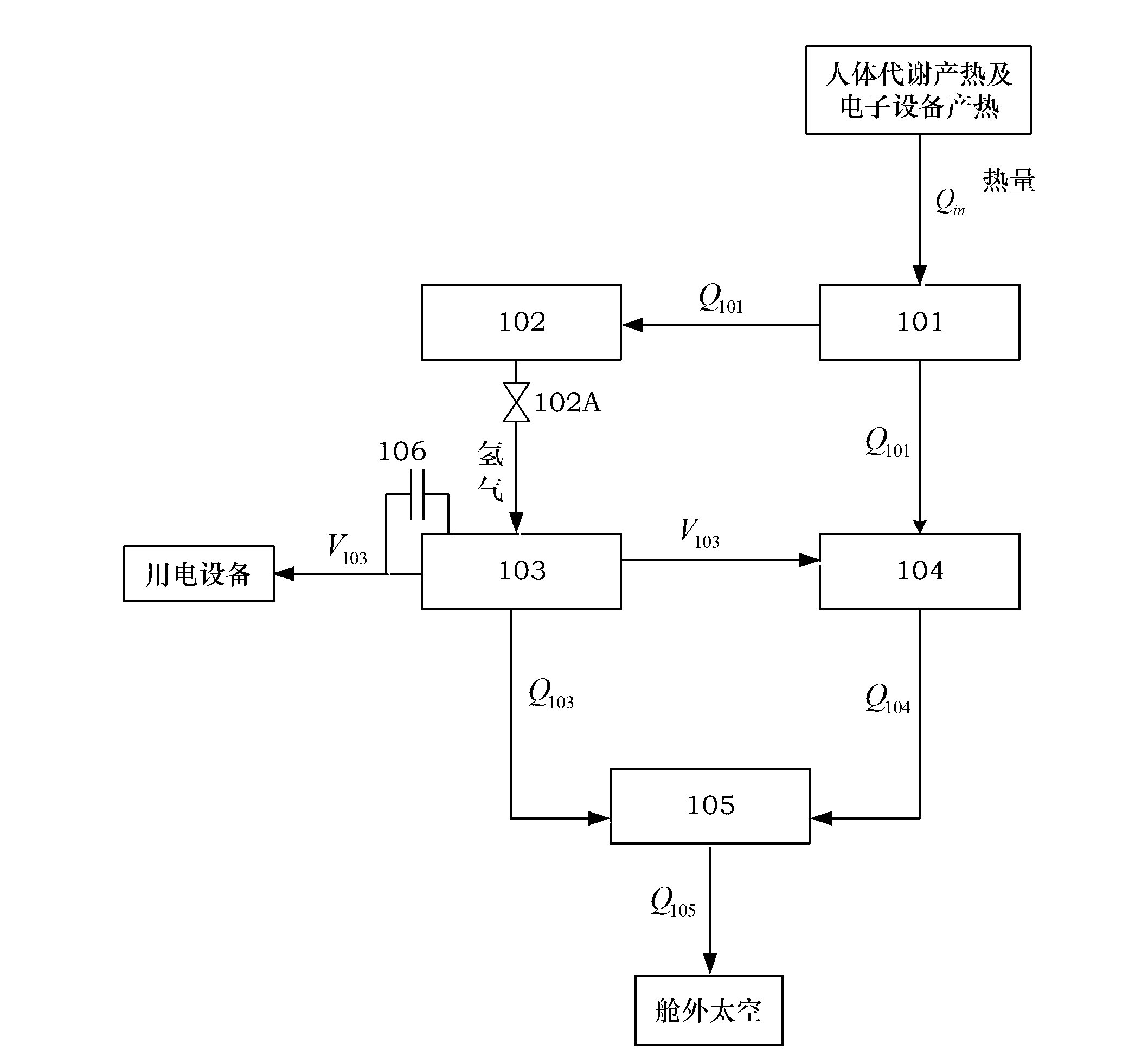
[0040] like figure 1 The connection of each device shown in the figure constitutes an extravehicular space suit cooling, heating and power integration system with the metal hydride fuel cell hydrogen storage device as the cold source. The system includes the following components: liquid cooling suit 101, metal hydride fuel cell A hydrogen storage device 102 , a proton exchange membrane fuel cell 103 , a thermoelectric cooling assembly 104 , a radiator 105 and a supercapacitor 106 .
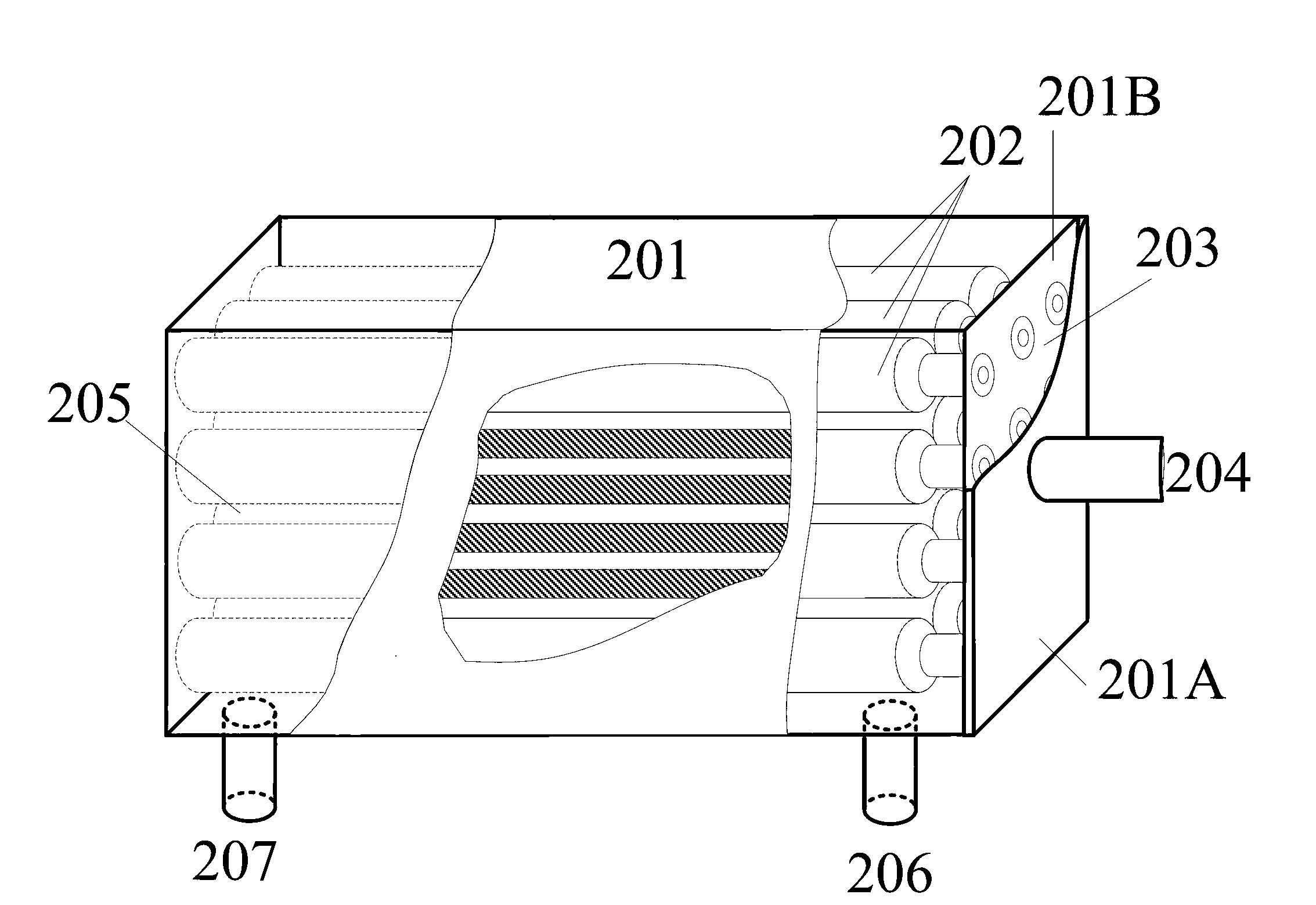
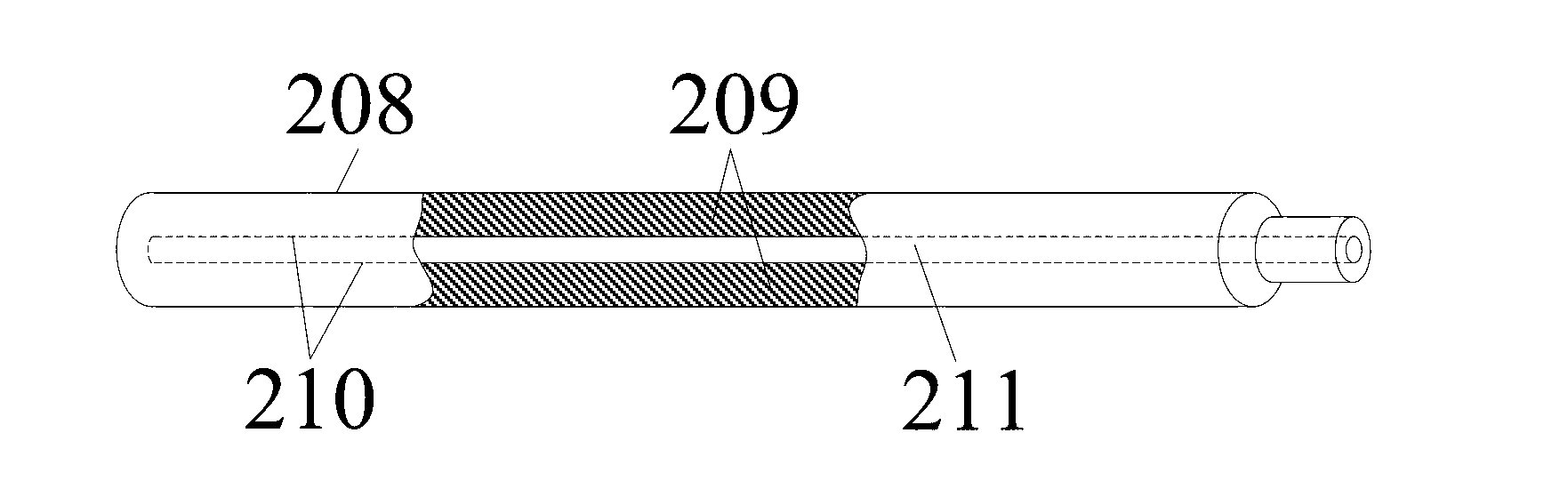
[0041] The structure of the metal hydride fuel cell hydrogen storage device 102 in Embodiment 1 is as follows figure 2 , Figure 2A As shown, there is a hydrogen chamber 203 between the side plate 201A of the reaction bed shell 201 and the partition plate 201B, and the hydrogen chamber 203 is used to store hydrogen; the reaction bed shell 201 is provided with a hydrogen storage unit 202 and a liquid chamber 205, so One end of the hydrogen storage unit 202 is connected to the hydrogen chamber 20...
Embodiment 2
[0049] The only difference between embodiment 2 and embodiment 1 is the fuel cell hydrogen storage device used. The fuel cell hydrogen storage device 102 used in embodiment 2 is a liquid hydrogen storage device, so here only the liquid hydrogen storage device is described, and the rest No longer.
[0050] The structural schematic diagram of the liquid hydrogen storage device of this embodiment is as follows image 3 As shown, it mainly includes: shell 301, support 302, interlayer 303, liner 304, safety valve 305, pump 306, heat exchanger 307, high pressure cylinder 308, pressure regulating valve 309, pressure regulating valve 310, stop valve 311 and other sections. The liquid hydrogen storage tank is divided into inner and outer layers. The shell 301 is generally made of low-carbon steel, stainless steel and other materials, and aluminum alloy materials can also be used to reduce the quality of the container; Thermal insulation performance, used to fix the liner 304 to the c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com