Blood purifying adsorbent used for removing blood toxin and preparation method
A blood purification and adsorbent technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve problems such as ligand shedding, high production costs, and risks to patient safety, and achieve high chemical and physical stability, stable physical and chemical properties, and good biocompatibility sexual effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
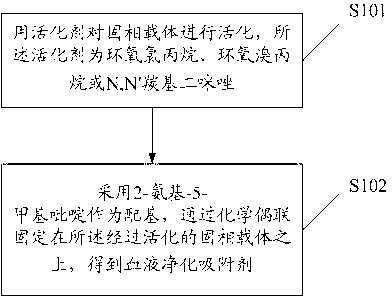
[0055] Such as figure 1 As shown, the embodiment of the present invention provides a method for preparing a blood purification adsorbent for removing blood toxins, including:
[0056] S101, activating the solid phase support with an activator, the activator being epichlorohydrin, epibromohydrin or N,N' carbonyldiimidazole.
[0057] Preferably, the activator is epichlorohydrin or N,N'carbonyldiimidazole.
[0058] Preferably, the solid phase carrier is cellulose, agarose or chitosan.
[0059] S102, using 2-amino-5-picoline as a ligand, and immobilizing it on the activated solid phase carrier through chemical coupling to obtain a blood purification adsorbent;
[0060] Wherein, the solid-phase carrier material is in the form of porous microspheres, and its gel pore permeability molecular weight is 11,000-5,100,000.
[0061] Preferably, the solid phase carrier material is in the form of porous microspheres, and its gel pore permeability molecular weight is 11,800-5,000,000.
[...
Embodiment 1
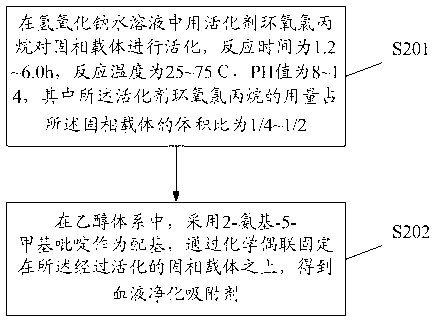
[0137] Add 10ml of cellulose spheres to the water until the total volume reaches 34ml, then add 10ml of 1mol / L sodium hydroxide solution and heat to 40°C. Then add 3ml of epichlorohydrin into the system, and stir at 65 degrees for two hours to carry out system reaction. After the reaction, the activated carrier was obtained by washing with a large amount of water. After measurement, the activated substitution degree is 1.6mmol / g.
[0138] Add 10ml of activated carrier to 150mg of 2-amino-5-picoline and 40ml of 75% ethanol solution. At a constant temperature of 45 degrees, the activated carrier and 2-amino-5-picoline were stirred and reacted in 75% ethanol solution for 6 days. After the reaction, it was washed with ethanol and water. The coupling density was measured to be 1.2 mmol / g.
Embodiment 2
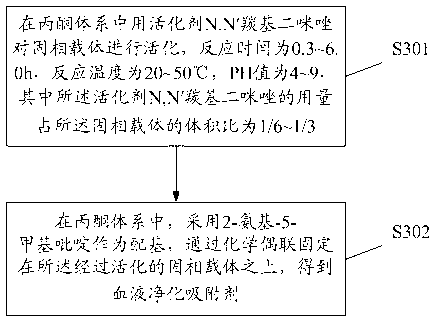
[0140] Take 10 mL of cellulose balls, wash them with acetone to remove the water in the gel, and then disperse them in 10 mL of acetone. Weigh 2g of N,N'carbonyldiimidazole and mix it with cellulose balls, place it in a shaking table at 30°C and 150rpm for 1 hour to react; after the reaction, wash with acetone to remove the unreacted N,N'carbonyldiimidazole to obtain Activated cellulose spheres. After measurement, the activated substitution degree is 2.0mmol / g.
[0141] Take 10mL of N,N'carbonyldiimidazole-activated cellulose spheres, and then disperse them in 10mL of acetone, add 2g of 2-amino-5-picoline to it, and place it in a shaker at 30°C and 150rpm for 3h. Wash with acetone and water for injection to remove unreacted substances to obtain cellulose spheres coupled with 2-amino-5-picoline. The coupling density was measured to be 1.4 mmol / g.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com