Method for removing conductive layer from ti-made fuel battery separation plate
A fuel cell and conductive layer technology, which is applied to fuel cell parts, cleaning methods using liquids, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve problems such as declining yield and recycling efficiency, and achieve high effect of loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
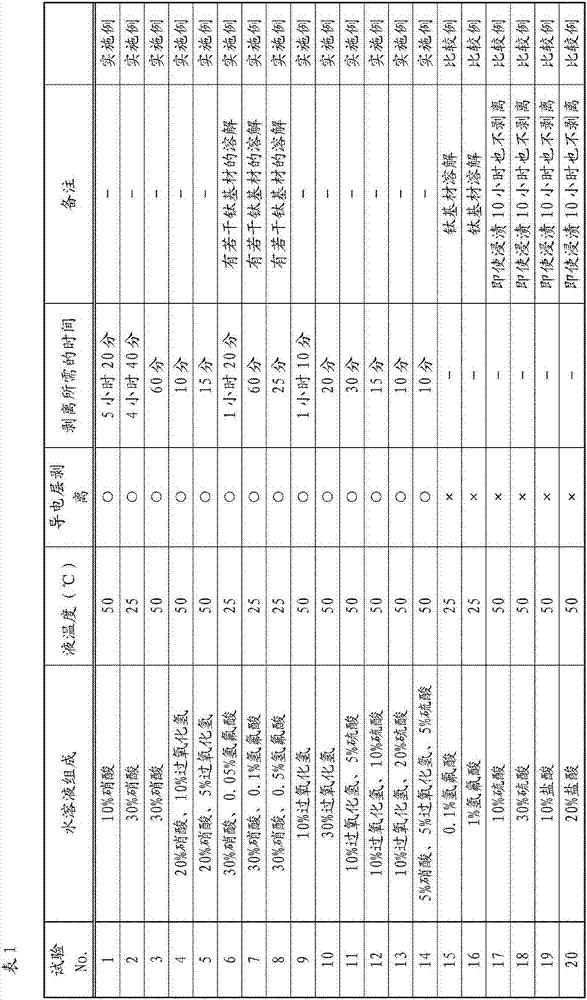
[0097] Next, with regard to the method for removing the conductive layer of the titanium fuel cell separator material of the present invention, Examples (Test Nos. 1 to 14) satisfying the requirements of the present invention and Comparative Examples (Test No. 15) not satisfying the requirements of the present invention are compared. ~20) to specify.
[0098] (Test material)
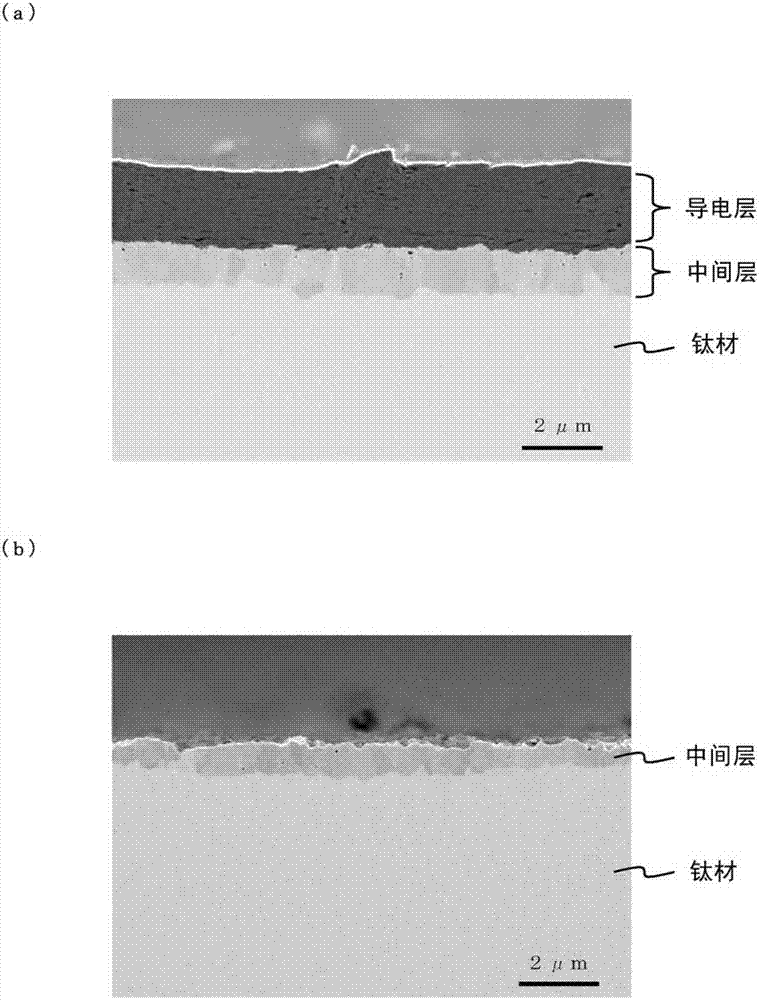
[0099] The substrate is made of pure titanium according to JIS Class 1. After coating the slurry containing expanded graphite powder on both sides of the substrate, the two-stage roller punching machine is used for crimping, and then in a vacuum environment (6.7×10 -3 Pa) at 700°C for 60 minutes, and then heat-treated under furnace cooling conditions. The above-mentioned treatment was used to manufacture a test material in which a carbon-based conductive material was covered (on both sides) on a base material formed of pure titanium as a conductive layer, and a titanium carbide-containing material was f...
Embodiment 2
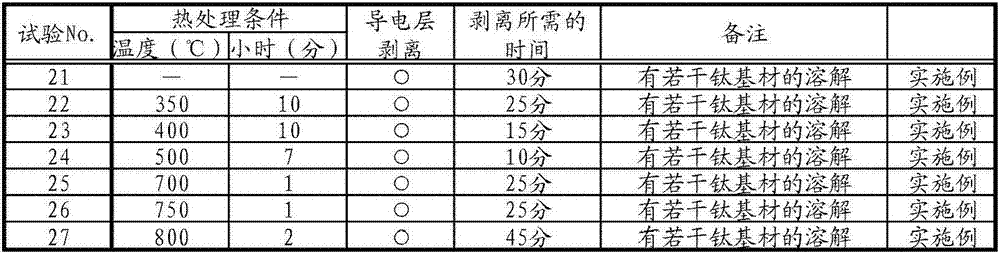
[0115] By the same process as in Example 1, a carbon-based conductive material covering (both sides) a base material made of pure titanium as a conductive layer was produced, and a middle layer containing titanium carbide was formed between the conductive layer and the base material. The material of the layer is cut and processed into a size of 20×30mm.
[0116] Then, a part was removed, and a heat treatment was performed at 350 to 750° C. for a predetermined time in an air atmosphere to prepare a test material.
[0117] (conductive layer removal test)
[0118] In the conductive layer removal test, 10 mass % nitric acid and 0.2 mass % hydrofluoric acid aqueous solution were used, 30 ml of the aqueous solution was put into a covered PP container (50 ml capacity), and the liquid temperature was adjusted to room temperature 50° C. for the test. In addition, the adjustment of the liquid temperature was performed using a constant temperature bath in the same manner as in Example 1...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com