High heat resisting phytase yeast engineering bacteria and constructing method thereof
A technology of yeast engineering and construction method, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of application, poor thermal stability, difficult pellets, etc., and achieve the effect of wide application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
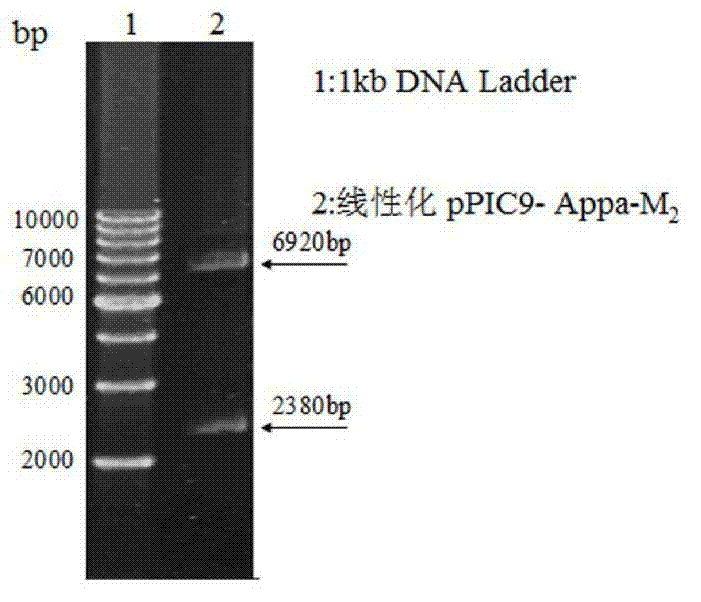
[0038] 1. Acquisition of phytase gene Appa
[0039] According to the AppA sequence (DQ513832) reported in GenBank, a biotechnology company was commissioned to synthesize the phytase gene Appa and clone it into the T-Easy vector to obtain the recombinant plasmid T-Easy-Appa.
[0040] 2. Analysis of Appa sequence glycosylation sites
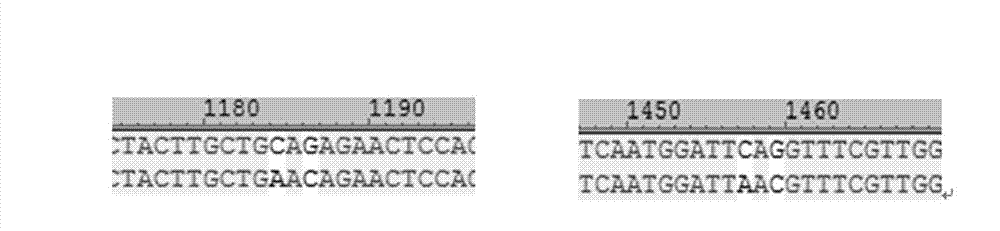
[0041] When the protein contains the consensus sequence Asn-X-Ser / Thr (N-X-S / T) (X represents any amino acid), Pichia pastoris can glycosylate the amide nitrogen on the aspartyl residue to produce N- Glycosylation. According to relevant literature reports, glycosylation has an important impact on the thermal stability of the enzyme. Sequence analysis shows that the phytase encoded by the Appa gene has three glycosylation sites, namely: N139, N204, and N317 sites. The analysis found that there are two potential sites for introducing glycosylation through modification of the gene, namely: Q259, Q350, asparagine N codons: AAT, AAC, and AAC is a pref...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com