Expression human seralbumin carrier and engineering bacterium
A technology for human serum albumin and yeast expression vectors, applied in the direction of using vectors to introduce foreign genetic material, fungi, and microbial-based methods, can solve the problem of low HSA production and achieve broad application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
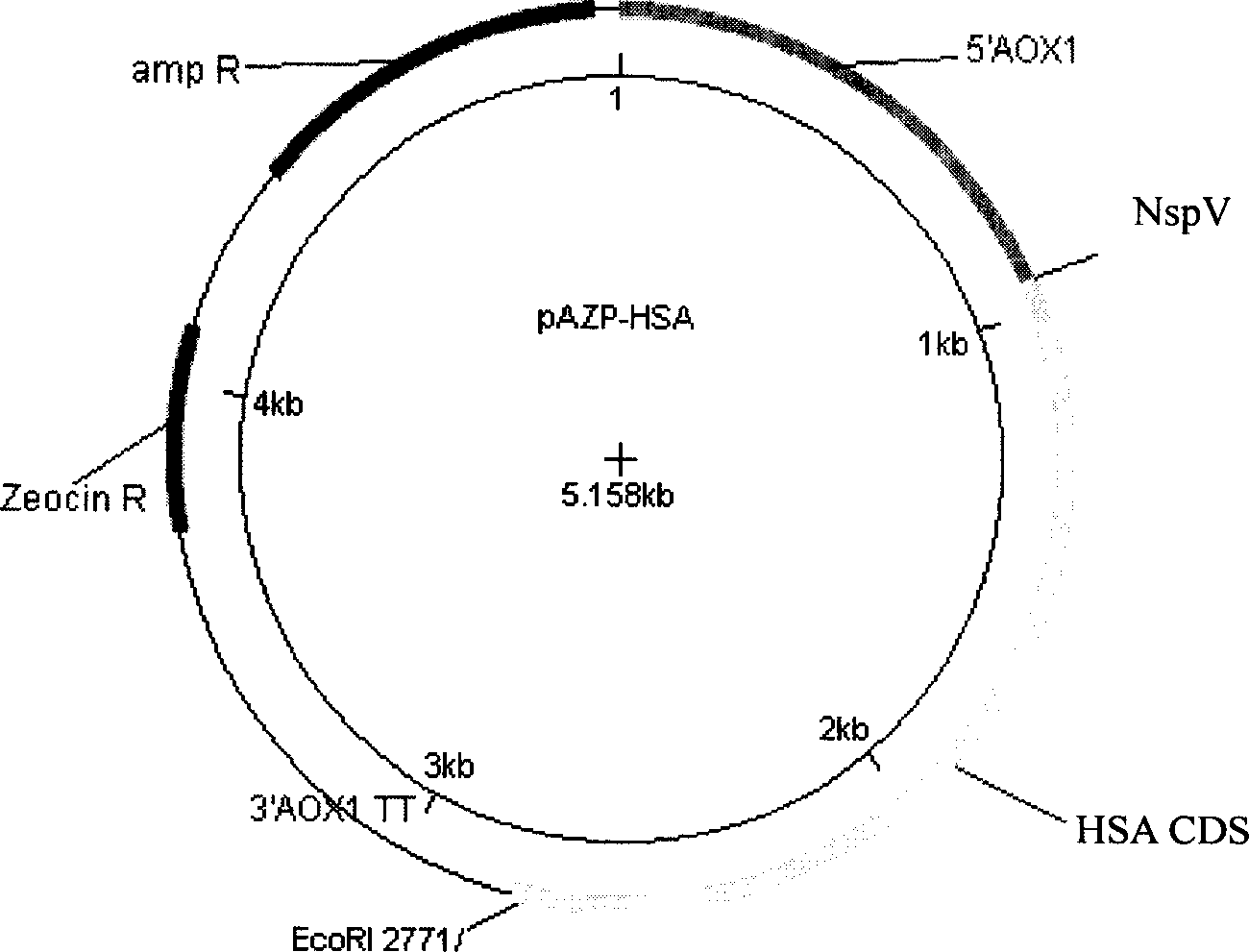
[0023] Embodiment 1, the construction of the vector pAZP-HSA expressing HSA and engineering bacteria Pichia pastoris (Pichia pastoris) HSA75-10 CGMCC No.1360
[0024] 1. Isolation of HSA mRNA from human liver tissue
[0025] Isolation of messenger RNA (mRNA) from livers of accident-dead children. The specific method is as follows:
[0026] Add 210 ml of lysate (4 mol / L thiocyanidine, 0.1 mol / L Tris-HCl, 0.1 mol / L 2-mercaptoethanol, pH 7.5) to 10.5 g of frozen human liver tissue to homogenate. Centrifuge at 10,000 rpm at 4°C for 10 minutes to pellet cell debris. Transfer the supernatant to a new centrifuge tube, add 1 mol / L phosphoric acid 0.04 times the volume of the supernatant and 95% acetic acid 0.5 times the volume of the supernatant, and place at -20°C for 2 hours. Then centrifuge at 7500 rpm at 4°C for 10 minutes. The precipitate was resuspended in 50ml washing solution (6mol / L guanidine hydrochloride, 10mmol / L Na 2 EDTA, 10mmol / L DTT, pH7.0), centrifuged at 5500rpm...
Embodiment 2
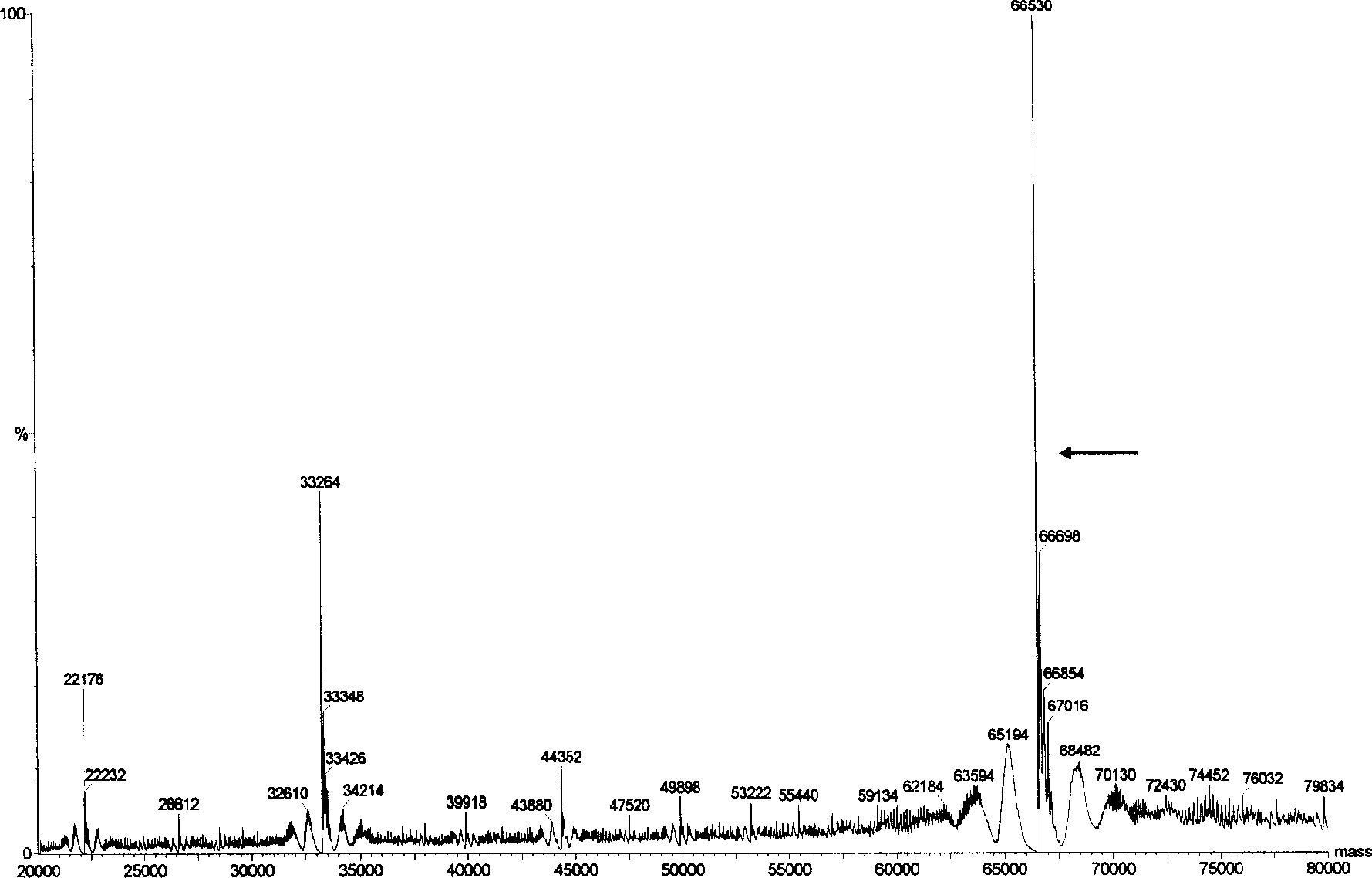
[0099] Embodiment 2, the molecular weight determination of the HSA expressed by Pichia pastoris (Pichia pastoris) HSA75-10 CGMCC No.1360
[0100] 1. Purification of HSA expressed by Pichia pastoris HSA75-10 CGMCC No.1360
[0101] Various buffers used in the purification process are shown in Table 2.
[0102] name
Buffer formulation
Solution A
25mmol / L sodium acetate at pH4.5
Solution B
50mmol / L sodium phosphate at pH7.0, 0.1mol / L sodium chloride, 10mmol / L sodium octanoate
Solution C
50mmol / L sodium phosphate at pH6.0, 0.1mol / L sodium chloride
Solution D
50mmol / L sodium phosphate at pH6.0, 0.2mol / L sodium chloride
[0103] (1) Heat treatment of fermentation broth
[0104] 7L of the fermentation supernatant of Pichia pastoris (Pichia pastoris) HSA75-10CGMCC No.1360 prepared according to the method of Example 1 step 7 was filtered with a 0.22um membrane (manufactured by MILLIPORE), and then 2% activated carb...
Embodiment 3
[0119] Example 3, C-terminal and N-terminal sequence determination of HSA expressed by Pichia pastoris (Pichia pastoris) HSA75-10 CGMCC No.1360
[0120] The HSA purified in step 1 in step 2 was submitted to the Shanghai Institute of Biochemistry and Cells, Chinese Academy of Sciences and the State Key Laboratory of Protein Engineering and Plant Genetic Engineering, Peking University for C-terminal and N-terminal sequencing. The C-terminal sequencing results showed that Pichia pastoris ( The C-terminal sequence of HSA expressed by Pichia pastoris) HSA75-10 CGMCC No.1360 is AALGL, and the N-terminal sequencing results show that the N-terminal sequence of HSA expressed by Pichia pastoris (Pichia pastoris) HSA75-10 CGMCC No.1360 is DAHKSEVAHRFKDLG, identical to the C-terminal and N-terminal sequences of HSA purified from human blood.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com