High-pressure formed substrate film assisted laser desorption dissociation mass spectrum quantitative analysis method
A technology of laser analysis and high-pressure forming, which is applied in the direction of analyzing materials, conducting material analysis by electromagnetic means, measuring devices, etc. Uniformity and other issues, to achieve the effect of convenient quality control and industrialization, good reproducibility, and easy control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0060] The preparation steps of the high-pressure forming matrix film are as follows:
[0061] 1) Use an analytical balance to weigh a certain amount of matrix, such as 50mg CHCA (α-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid) and 12mg DHB (2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid), the type and amount of matrix can be determined according to different samples ;
[0062] 2). Grind the substrate obtained in step 1) with an agate mortar to make its particle size less than 2μm;
[0063] 3) Put the matrix powder obtained in step 2) into the abrasive tool of the tablet press, and then put it in the tablet press, apply a pressure of 4800kg, and keep it under this pressure for 1 minute;
[0064] 4). Take out the matrix film (CMTF) compressed in step 3) and store it at room temperature.
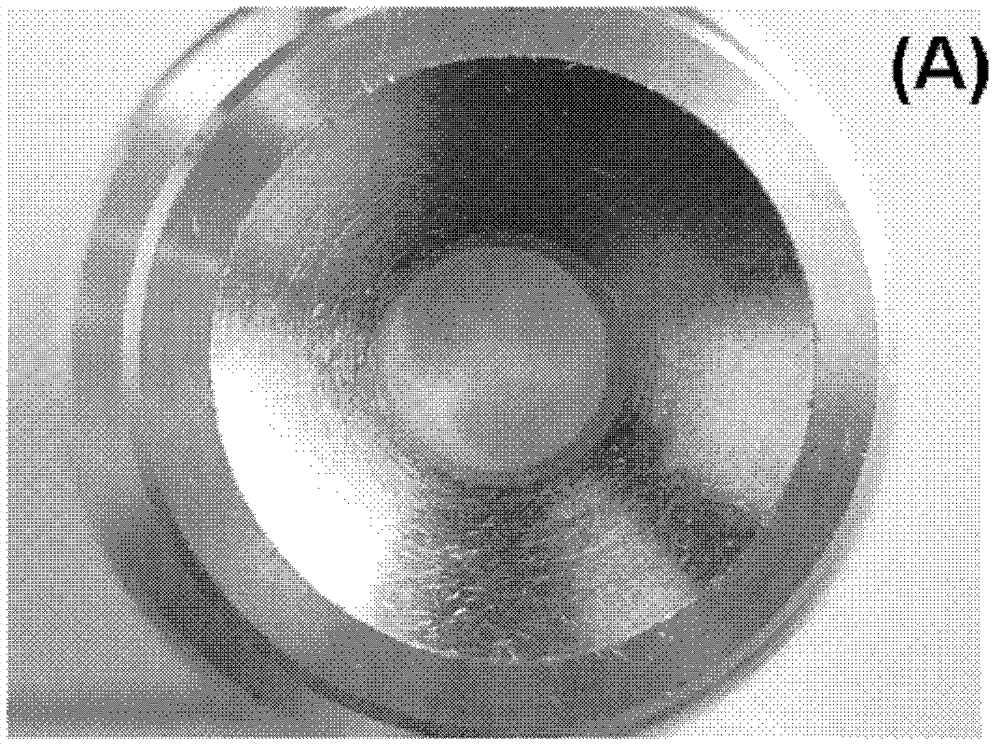
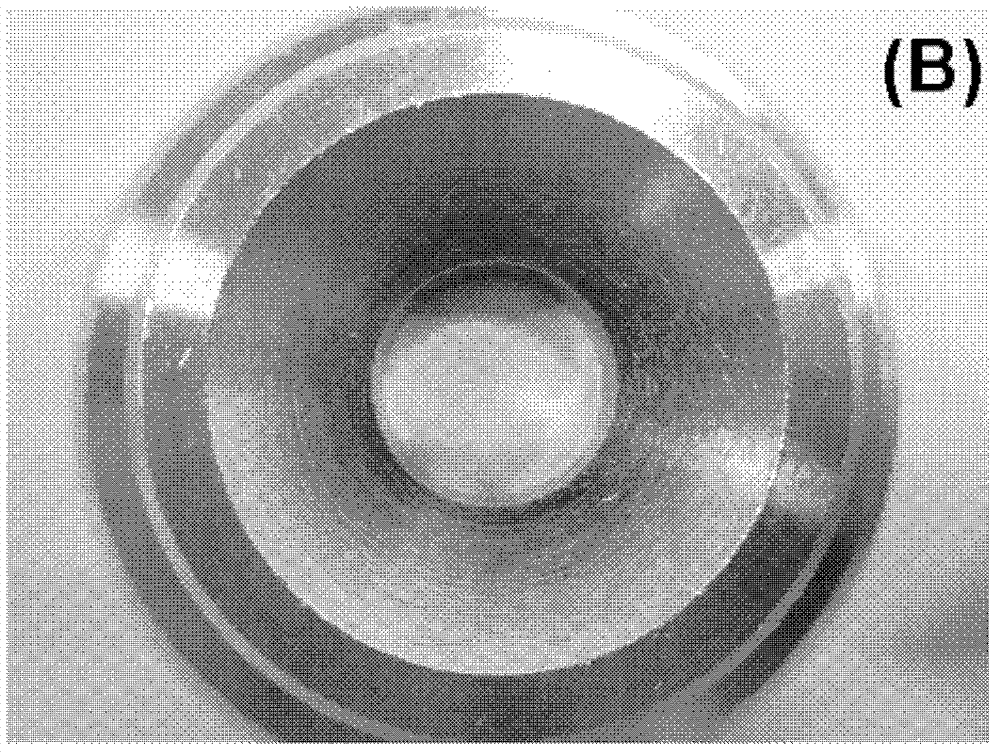
[0065] Among them, the picture of the CHCA film obtained in step 4) is as Figure 1-A As shown, the picture of the obtained DHB film is as Figure 1-B As shown, the figure shows that the obtained substrate film has a smooth surface and a u...
Embodiment 2
[0067] The high-pressure forming matrix film prepared in Example 1 is used for sample analysis signal intensity stability
[0068] 1) Stick the high-pressure forming matrix film prepared in Example 1 on the sample target;
[0069] 2) Adjust the α-casein hydrolysate sample to pH 1-2, use a pipette to spot 1μl sample on different sample spots on the film, and let it dry naturally;
[0070] 3) Take 10μl of 0.1wt% TFA aqueous solution to cover the sample point, hold for 2 seconds, absorb the water droplets with dust-free paper, and repeat 3 times;
[0071] 4) Put the sample target into the mass spectrometer;
[0072] 5) Use a laser with a certain frequency to bombard the sample to vaporize and ionize the sample to be tested, and detect its signal intensity;
[0073] Among them, step 5) obtained DHB high pressure forming matrix film total ion current diagram as image 3 As shown, the total ion current diagram of CHCA high pressure forming matrix film is as Figure 5 As shown, the total ion cu...
Embodiment 3
[0077] The in-situ desalination effect of the high-pressure forming matrix film prepared in Example 1
[0078] 1) Stand the high-pressure forming substrate film prepared in Example 1 on the sample target;
[0079] 2) Adjust the α-casein hydrolysate sample to pH 1-2, use a pipette to spot 1μl of the sample on different sample spots on the film, and let it dry naturally;
[0080] 3) Take 10μl of 0.1wt% TFA aqueous solution to cover the sample point, hold for 2 seconds, absorb the water droplets with dust-free paper, and repeat 3 times;
[0081] 4) Put the sample target into the mass spectrometer;
[0082] 5) Use a laser with a certain frequency to bombard the sample to vaporize and ionize the sample to be tested, and detect its signal intensity.
[0083] Among them, the mass spectrum of the α-casein hydrolysate obtained in step 5) after in situ desalination on the DHB matrix is Figure 7 As shown, the mass spectrum of α-casein hydrolysate after in situ desalination on the CHCA matrix is ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com