Magnesium hydride (MgH2) and ferrum-containing sulfide composite hydrogen storage material and preparation method thereof
A hydrogen storage material and sulfide technology, applied in the production of hydrogen and other directions, can solve the problems of high price, limitation, and insignificant improvement of dehydrogenation temperature, and achieve the effects of low cost, low energy consumption, and easy industrialization and promotion.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
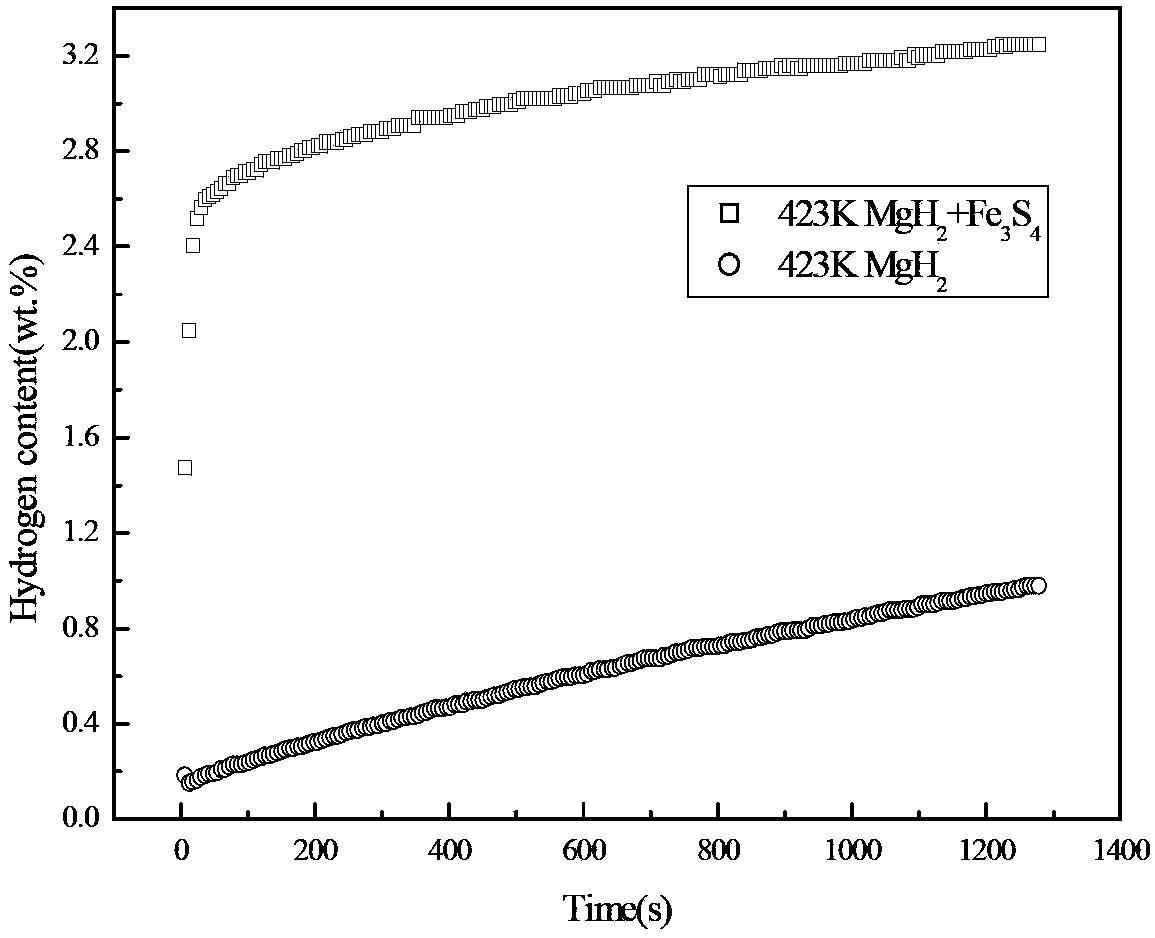
[0023] In an argon-protected glove box, the MgH 2 Powder and Fe 3 S 4 The powder is mixed according to the mass ratio of 4:1 and placed in a ball mill tank. The ball quality is stainless steel. The ball mill is a Pulverisette6 planetary ball mill. The time is 2 hours, and then filled with 0.1MPa high-purity argon gas, adopts high-energy ball milling method, after the ball milling is completed, it is naturally cooled to room temperature, and packaged under an argon-protected glove box. MgH prepared by ball milling 2 Composite hydrogen storage materials were tested for hydrogen absorption rate, and the results were as follows: figure 1 shown. It can be seen from the hydrogen absorption rate curve at 423K in the figure that the MgH 2 Fe 3 S 4 The composite hydrogen storage material prepared after ball milling can reach 80% of the maximum hydrogen absorption capacity in 30s, and in about 25 minutes, the hydrogen absorption capacity is 3.5 times that of the alloy without add...
Embodiment 2
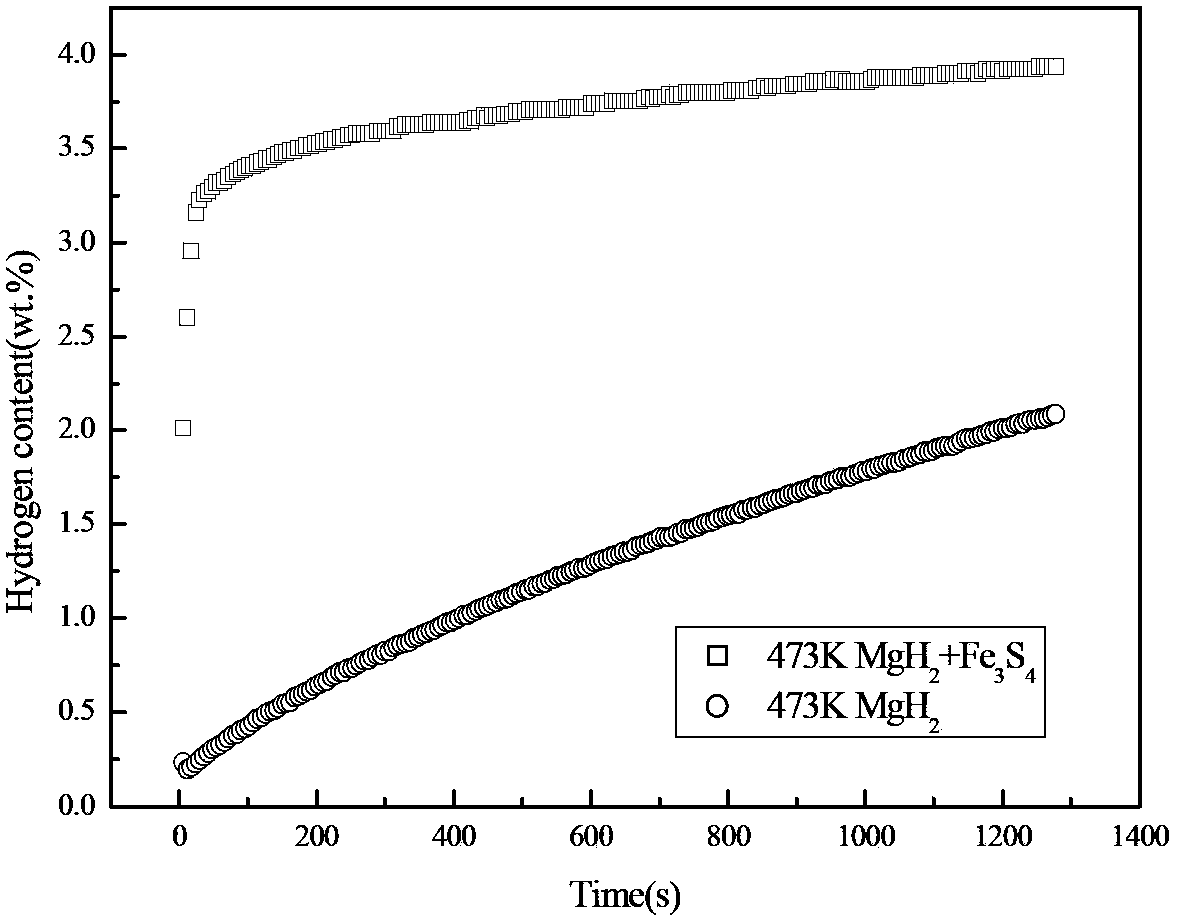
[0025] In an argon-protected glove box, the MgH 2 Powder and Fe 3 S 4 The powder is mixed according to the mass ratio of 9:1 and placed in a ball mill tank. The ball quality is stainless steel. The ball mill is a Pulverisette6 planetary ball mill. The time is 3 hours, and then filled with 0.5MPa high-purity argon gas, using high-energy ball milling method, after the ball milling is completed, it is naturally cooled to room temperature, and packaged under an argon-protected glove box. MgH prepared by ball milling 2 Composite hydrogen storage materials were tested for hydrogen absorption rate, and the results were as follows: figure 2 shown. It can be seen from the hydrogen absorption rate curve at 473K in the figure that the MgH 2 Fe 3 S 4 The composite hydrogen storage material prepared after ball milling can reach 80% of the maximum hydrogen absorption capacity in 30s, without adding Fe 3 S 4 MgH 2 It takes 900 seconds for the sample to reach 80% of the maximum hyd...
Embodiment 3
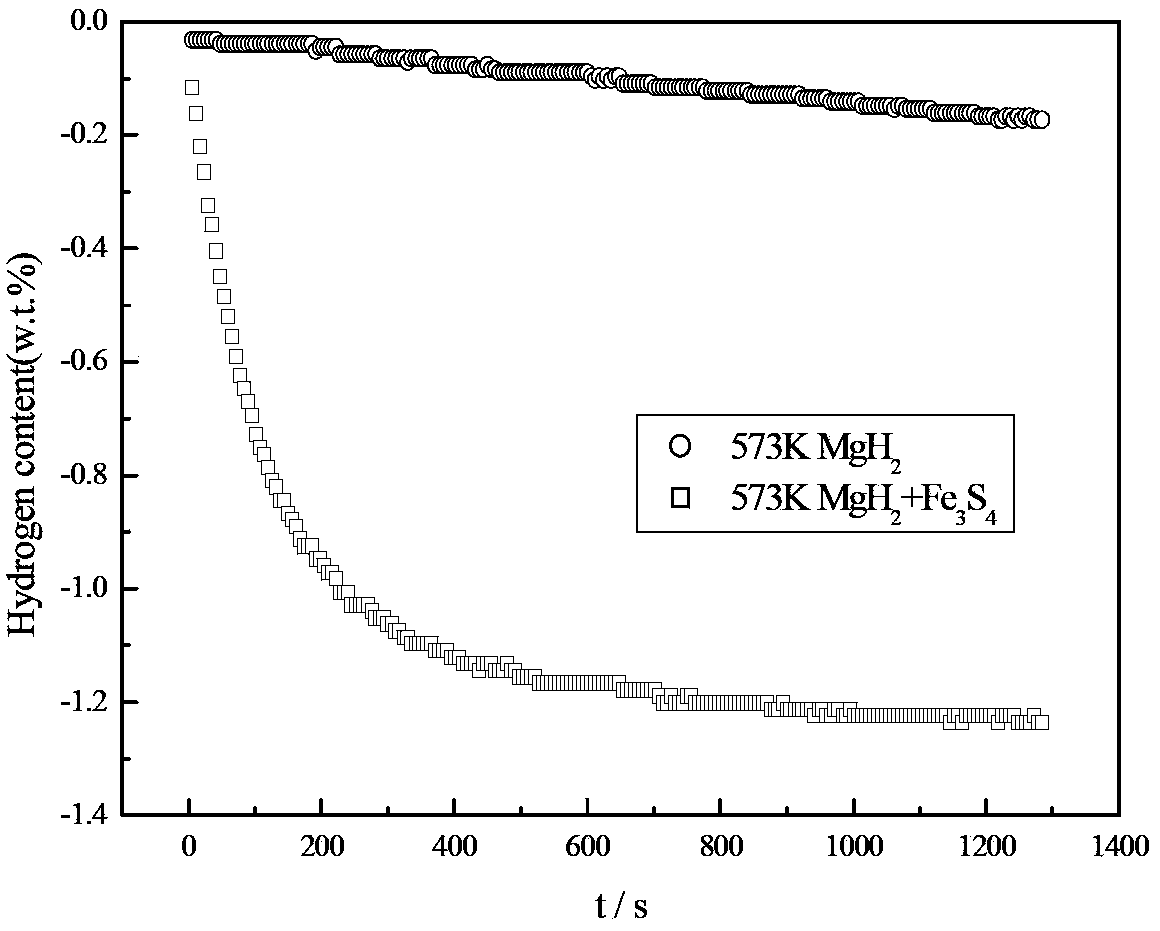
[0027] In an argon-protected glove box, the MgH 2 Powder and Fe 3 S 4 The powder is mixed and placed in a ball mill tank with a mass ratio of 7:3. The ball quality is stainless steel. The ball mill is a Pulverisette6 planetary ball mill. The time is 3 hours, and then filled with 0.1MPa high-purity argon gas, using high-energy ball milling method, after the ball milling is completed, it is naturally cooled to room temperature, and packaged under an argon-protected glove box. MgH prepared by ball milling 2 Composite hydrogen storage materials were tested for hydrogen desorption rate, and the results were as follows: image 3shown. It can be seen from the hydrogen desorption rate curve at 573K in the figure that the MgH 2 Fe 3 S 4 The composite hydrogen storage material prepared after ball milling can reach 80% of the maximum hydrogen release capacity in 200s, without adding Fe 3 S 4 MgH 2 It takes 1000s to reach 80% of the maximum hydrogen release. It can be seen that...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com