Method for continuous hydrogenation of dinitrobenzene and recycling of reaction heat thereof
A dinitrobenzene hydrogenation reaction technology, applied in chemical recovery, chemical instruments and methods, preparation of amino compounds, etc., can solve the problems of increased circulating water consumption, reduced reaction heat efficiency, and large mass transfer resistance, etc., to achieve reaction Improve the rate and device production efficiency, improve the selectivity and conversion rate, and ensure the effect of quality and yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Specific steps are as follows:
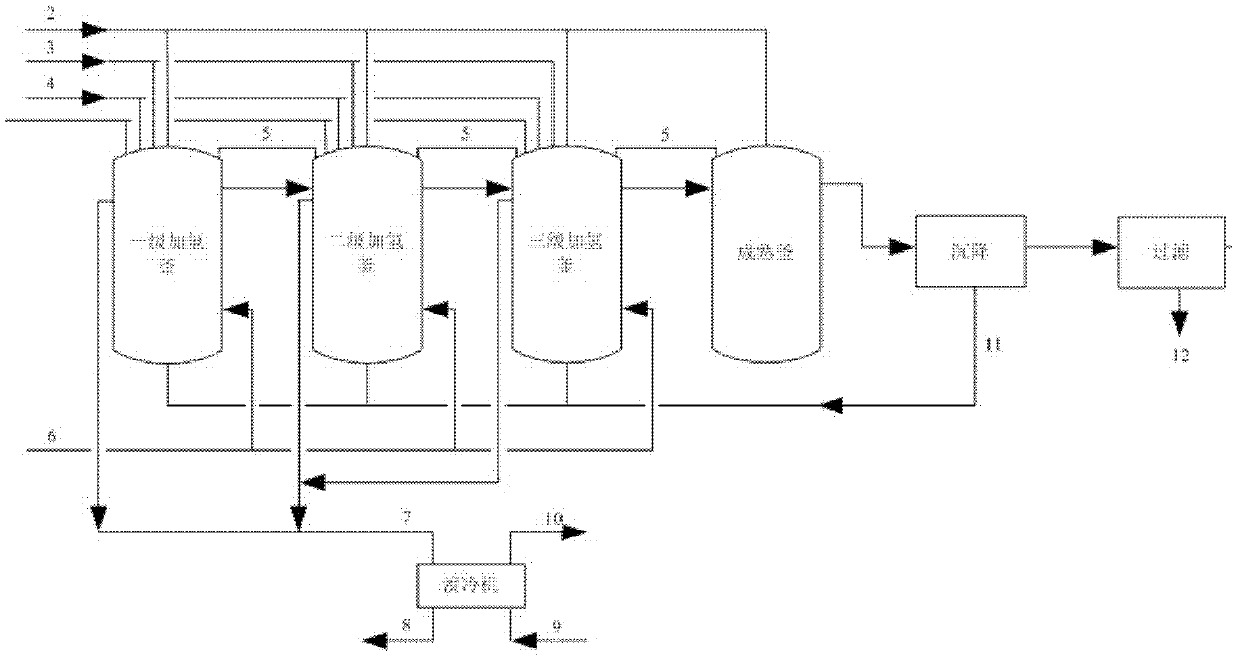
[0024] After the hydrogenation kettle (built-in plate heat exchanger and self-priming stirring device) is qualified by nitrogen and hydrogen replacement, add methanol equivalent to 50% of the total volume of the reaction kettle as a base material, and add catalyst skeleton nickel (Raney nickel, made of Nickel-aluminum alloy powder with a nickel content of 40-50% is prepared by activating NaOH solution. Adding 5% of the mass of mixed dinitrobenzene.), hydrogen gas is introduced under the condition of stirring. Methanol and mixed dinitrobenzene (o-, m-, p-nitrobenzene weight percentages are 10%: 88%: 2%) are continuously fed into hydrogenation tanks at various levels to carry out liquid-phase catalytic hydrogenation reaction, wherein methanol The dosage of mixed dinitrobenzene in the primary hydrogenation tank is controlled at 2.67m 3 / h and 1.33m 3 / h, controlled to 1.8m in the secondary hydrogenation tank 3 / h and 1.2m 3 / h, in the th...
Embodiment 2
[0028] After the hydrogenation kettle is qualified by nitrogen and hydrogen replacement, respectively add methanol equivalent to 50% of the total volume of the reaction kettle as a base material, add skeleton nickel (Raney nickel, add according to 5% of the mass of mixed dinitrobenzene), and start stirring In case, hydrogen gas is introduced. Methanol and mixed dinitrobenzene (o-, m-, p-nitrobenzene weight percentages are 11%: 87.5%: 1.5%) are continuously fed into hydrogenation tanks at various levels to carry out liquid-phase catalytic hydrogenation reaction, wherein methanol The dosage of mixed dinitrobenzene in the primary hydrogenation tank is controlled to 3.33m 3 / h, 1.67m 3 / h, respectively controlled to 1.2m in the secondary hydrogenation tank 3 / h, 1.2m 3 / h, respectively controlled to 1.0m in the three-stage hydrogenation tank 3 / h, 1.0m 3 / h, the reaction temperature of the hydrogenation tank is maintained between 115 ~ 122 °C, and the pressure of the reaction...
Embodiment 3
[0032] With reference to the method described in Example 1, the difference is that the mixed dinitrobenzene in Example 1 is replaced with m-dinitrobenzene, and the carrier nickel (SiO 2 The carrier (with a nickel content of 50-65%) replaces the skeleton nickel as a catalyst to carry out continuous catalytic hydrogenation reaction. The conversion rate of dinitrobenzene in the hydrogenation process is 100%, and the product yield based on m-dinitrobenzene reaches 99.3%. After the catalyst is continuously separated, the hydrogenated material is further dealcoholized, dehydrated, and rectified to obtain a qualified m-phenylenediamine product.
[0033] Demineralized soft water is used as circulating cooling water, and the heat of hydrogenation reaction is removed by circulating flow. After heat exchange in hydrogenation tank, the outlet water temperature reaches about 105°C. The hot water from the three hydrogenation tanks is collected and converted by the hot water type lithium bro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com